Runtime Defined Entities
A Runtime Defined Entity (RDE) is a package that contains a JSON payload. Each RDE is an instance of an RDE Type that specifies the format of the JSON payload using a JSON Schema.
Examples of how an RDE can be created, retrieved, and modified can be found in the Defined Entity Operations section.
Defined Entity Lifecycle
Defined Entities pass through three phases during their lifecycle:
CreationUtilizationDeletion
In simple cases, both the Creation and the Deletion phases can be immediate. In other cases, they can be long-running processes.
Defined Entity States
Each Defined Entity has a state that indicates what phase it is in.
The state of a Defined Entity is contained in the entityState property. The possible values are the following:
PRE_CREATEDRESOLVEDRESOLUTION_ERRORIN_DELETION
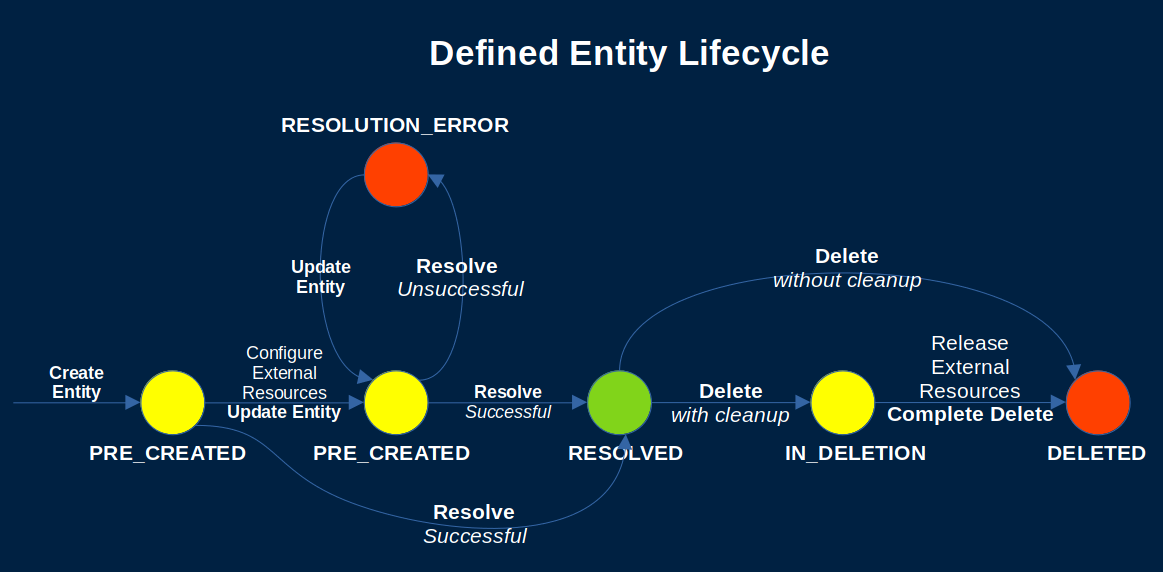
Creation Phase
The Creation Phase starts when the Defined Entity is created. During that phase the external resources that would be represented by the Defined Entity are typically allocated and initialized.
The state of the entity in that phase is PRE_CREATED.
During the Creation Phase the entity contents do not have to be valid with respect to the JSON schema of the entity type. That allows the information about the represented resource to be collected and gradually added to the entity contents as external resources are allocated, for example.
The initialization process and the content update can be done either explicity via the API or automatically via a PostCreate behavior hook.
Note: An entity cannot be deleted while it is in the Creation Phase. It has to be resolved first, either successfully or unsuccessfully.
Utilization Phase
Once the needed Defined Entity information has been fully collected and the entity contents have been updated to satisfy the requirements of the type’s JSON Schema, the entity can then be resolved.
Note: If the initally provided entity contents already contain all of the necessary information, it is possible to skip the Creation Phase and immediately attempt to resolve the entity upon creation.
Once the resolution process validates the entity contents against the JSON schema of the entity type, the entity state is changed to RESOLVED. If the validation fails, then the entity will be placed in a RESOLUTION_ERROR state.
A resolved entity is considered complete and ready for use. It becomes possible to perform operations on it such as behavior invocations.
If a resolved entity is updated, its new contents are re-validated immediately and the entity state is changed to RESOLVED or RESOLUTION_ERROR depending on validation result.
Deletion Phase
A resolved entity can be deleted immediately if no cleanup is needed.
If there are related resources that need to be released, however, then a multi-stage deletion process is initiated and the entity is placed in the IN_DELETION state. The entity can be fully deleted once the cleanup process completes.