This topic tells you how to install and configure Tanzu Cloud Service Broker for AWS (Cloud Service Broker for AWS).
Prerequisites for Installing Cloud Service Broker for AWS
Before you install Cloud Service Broker for AWS, you must have:
-
A small MySQL database: This database is used as the state database. The broker requires this database to store its state.
-
AWS account credentials:
If the AWS account where the instances are created differs from the one the platform runs in, the user is responsible for setting up the necessary networking. The broker needs the following credentials to manage resources within an account:
- Access Key ID
- Secret Access Key
-
IAM Policies: The AWS account needs the following IAM policies:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Action": [ "dynamodb:CreateTable", "dynamodb:CreateTableReplica", "dynamodb:DeleteTable", "dynamodb:DescribeBackup", "dynamodb:DescribeContinuousBackups", "dynamodb:DescribeTable", "dynamodb:DescribeTimeToLive", "dynamodb:ListTables", "dynamodb:ListTagsOfResource", "dynamodb:TagResource", "dynamodb:UntagResource", "ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupIngress", "ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupEgress", "ec2:CreateSecurityGroup", "ec2:DeleteSecurityGroup", "ec2:DescribeNetworkInterfaces", "ec2:DescribeRouteTables", "ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups", "ec2:DescribeSecurityGroupRules", "ec2:DescribeSubnets", "ec2:DescribeVpcAttribute", "ec2:DescribeVpcs", "ec2:RevokeSecurityGroupEgress", "ec2:RevokeSecurityGroupIngress", "elasticache:AddTagsToResource", "elasticache:RemoveTagsFromResource", "elasticache:ListTagsForResource", "elasticache:CreateCacheSubnetGroup", "elasticache:CreateReplicationGroup", "elasticache:DeleteCacheSubnetGroup", "elasticache:DeleteReplicationGroup", "elasticache:DescribeCacheClusters", "elasticache:DescribeCacheSubnetGroups", "elasticache:DescribeReplicationGroups", "elasticache:IncreaseReplicaCount", "elasticache:DecreaseReplicaCount", "elasticache:ModifyReplicationGroup", "elasticache:ModifyReplicationGroupShardConfiguration", "iam:CreateAccessKey", "iam:CreateUser", "iam:DeleteAccessKey", "iam:DeleteUser", "iam:DeleteUserPolicy", "iam:GetAccountAuthorizationDetails", "iam:GetPolicy", "iam:GetUser", "iam:GetUserPolicy", "iam:ListAccessKeys", "iam:ListAttachedUserPolicies", "iam:ListGroupsForUser", "iam:ListPolicies", "iam:ListUserPolicies", "iam:PutUserPolicy", "logs:CreateLogDelivery", "logs:CreateLogGroup", "logs:DescribeResourcePolicies", "logs:DescribeLogGroups", "logs:GetLogDelivery", "logs:DeleteLogDelivery", "logs:DeleteLogGroup", "logs:ListLogDeliveries", "logs:ListTagsLogGroup", "logs:ListTagsForResource", "logs:UntagLogGroup", "logs:UntagResource", "logs:TagResource", "logs:TagLogGroup", "logs:ListTagsForResource", "logs:PutResourcePolicy", "logs:PutRetentionPolicy", "logs:UpdateLogDelivery", "rds:AddTagsToResource", "rds:RemoveTagsFromResource", "rds:ListTagsForResource", "rds:CreateDBCluster", "rds:CreateDBClusterParameterGroup", "rds:CreateDBInstance", "rds:CreateDBParameterGroup", "rds:CreateDBSubnetGroup", "rds:DeleteDBCluster", "rds:DeleteDBClusterParameterGroup", "rds:DeleteDBInstance", "rds:DeleteDBParameterGroup", "rds:DeleteDBSnapshot", "rds:DeleteDBSubnetGroup", "rds:DescribeDBClusterParameters", "rds:DescribeDBClusters", "rds:DescribeDBClusterParameterGroups", "rds:DescribeDBEngineVersions", "rds:DescribeDBInstances", "rds:DescribeDBParameters", "rds:DescribeDBParameterGroups", "rds:DescribeDBSnapshots", "rds:DescribeDBSubnetGroups", "rds:DescribeGlobalClusters", "rds:ModifyDBClusterParameterGroup", "rds:ModifyDBCluster", "rds:ModifyDBInstance", "rds:ModifyDBParameterGroup", "s3:BypassGovernanceRetention", "s3:BypassGovernanceRetention", "s3:CreateAccessPoint", "s3:CreateAccessPoint", "s3:CreateBucket", "s3:DeleteAccessPointPolicy", "s3:DeleteBucket", "s3:DeleteBucketPolicy", "s3:DeleteObject", "s3:GetAccelerateConfiguration", "s3:GetAccountPublicAccessBlock", "s3:GetBucketAcl", "s3:GetBucketCORS", "s3:GetBucketLogging", "s3:GetBucketObjectLockConfiguration", "s3:GetBucketOwnershipControls", "s3:GetBucketPolicy", "s3:GetBucketPolicyStatus", "s3:GetBucketPublicAccessBlock", "s3:GetBucketRequestPayment", "s3:GetBucketTagging", "s3:GetBucketVersioning", "s3:GetBucketWebsite", "s3:GetEncryptionConfiguration", "s3:GetLifecycleConfiguration", "s3:GetObject", "s3:GetObjectLegalHold", "s3:GetObjectRetention", "s3:GetReplicationConfiguration", "s3:ListBucket", "s3:PutAccessPointPolicy", "s3:PutAccountPublicAccessBlock", "s3:PutBucketAcl", "s3:PutBucketLogging", "s3:PutBucketObjectLockConfiguration", "s3:PutBucketOwnershipControls", "s3:PutBucketOwnershipControls", "s3:PutBucketPolicy", "s3:PutBucketPublicAccessBlock", "s3:PutBucketRequestPayment", "s3:PutBucketTagging", "s3:PutBucketVersioning", "s3:PutEncryptionConfiguration", "s3:PutObject", "s3:PutObjectAcl", "s3:PutObjectLegalHold", "s3:PutObjectRetention", "sqs:CreateQueue", "sqs:DeleteQueue", "sqs:ListQueueTags", "sqs:TagQueue", "sqs:UntagQueue", "sqs:GetQueueAttributes", "sqs:SetQueueAttributes", "sqs:GetQueueUrl", "sqs:ListQueues", "dms:CreateReplicationSubnetGroup" ], "Effect": "Allow", "Resource": "*" } ] } -
IAM policies in Enhanced Monitoring:
To enable the Enhanced Monitoring feature for Amazon RDS, you need to grant additional permissions. This feature requires permission to act on your behalf to send OS metric information to CloudWatch logs. You grant Enhanced Monitoring permissions by using an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role.
To configure the ARN for the IAM role that permits RDS to send enhanced monitoring metrics to CloudWatch logs, the user that you want to access Enhanced Monitoring needs a policy that includes a statement that allows the user to pass the role, like the following. Use your account number and replace the role name with the name of your role.
{ "Sid": "PolicyStatementToAllowUserToPassOneSpecificRole", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "iam:PassRole" ], "Resource": "arn:aws:iam::account-id:role/RDS-Monitoring-Role-Name" }For more information about setting up and enabling Enhanced Monitoring, see the AWS Documentation.
For more information about granting a user permission to pass a role to an AWS service, see the AWS Documentation.
Install Cloud Service Broker for AWS
To use Ops Manager Installation Dashboard to install Cloud Service Broker for AWS:
-
Download the product file from Broadcom Support.
-
Navigate to the Ops Manager Installation Dashboard and click Import a Product to upload the product file.
-
Under Import a Product, click + next to the version number of Cloud Service Broker for AWS in the left sidebar. This adds the tile to your staging area.
-
Click the newly added Cloud Service Broker for AWS tile.
Configure the Cloud Service Broker for AWS
The following procedures describe configuring the panes on the Cloud Service Broker for AWS tile.
Configure AZs and Networks
This section describes how to choose an AZ to run the service broker for Cloud Service Broker for AWS. It also describes how to select networks for Cloud Service Broker for AWS.
To configure AZs and networks:
-
Click Assign AZs and Networks.
-
Configure the text boxes as follows:
Text box Instructions Place singleton jobs in Select the AZ in which the broker VM for Cloud Service Broker for AWS runs. The broker runs as a singleton job. Balance other jobs in Select the AZs in which other jobs can run. Network Select a subnet for the Cloud Service Broker for AWS broker. This is typically the same subnet that includes the component VMs for VMware Tanzu Application Service for VMs (TAS for VMs). -
Click Save.
Configure AWS credentials
This section describes how to configure the AWS credentials that Cloud Service Broker for AWS requires to manage service instances.
To configure AWS credentials:
-
Click AWS Config.
-
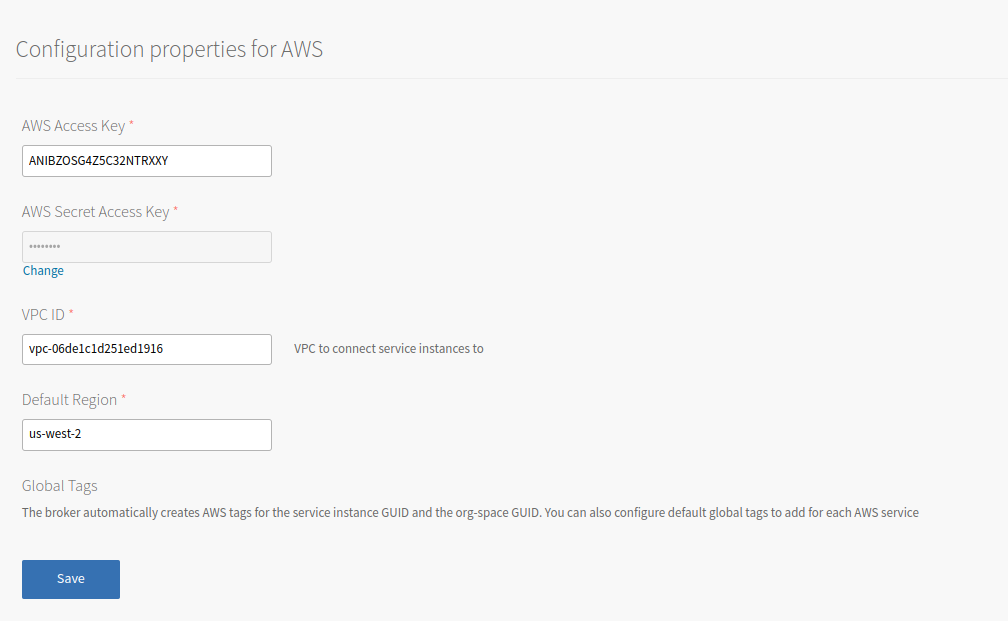
Configure the text boxes as follows:
Text box Instructions AWS Access Key Enter the AWS access key. AWS Secret Access Key Enter the AWS secret access key. VPC ID Default VPC to connect service instances to. You can override this value in plans or at provisioning time. Default Region Enter the region where your VPC is located. -
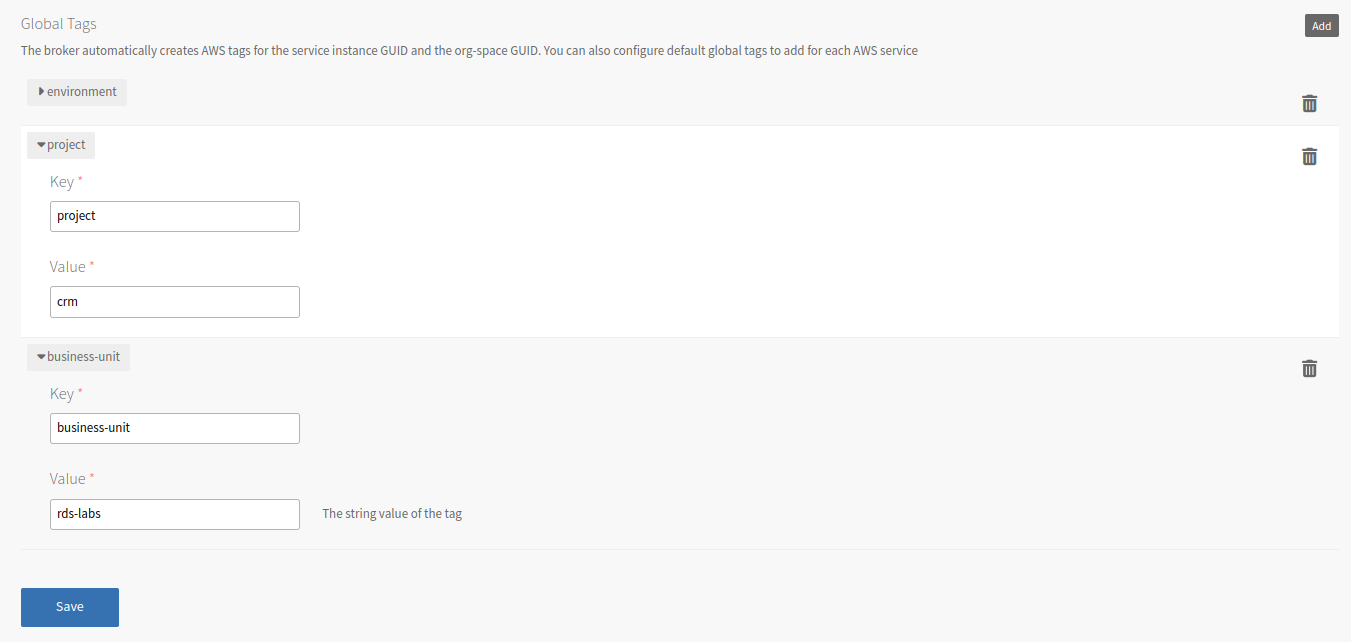
Configure the Global Tags section.
The broker automatically creates AWS tags for the service instance GUID and the org-space GUID. You can also configure default global tags to add for each AWS service. See next example:
-
Click Save.
Configure a State Database
This section describes how to associate Cloud Service Broker for AWS with the MySQL state database.
About Encrypting the State Database
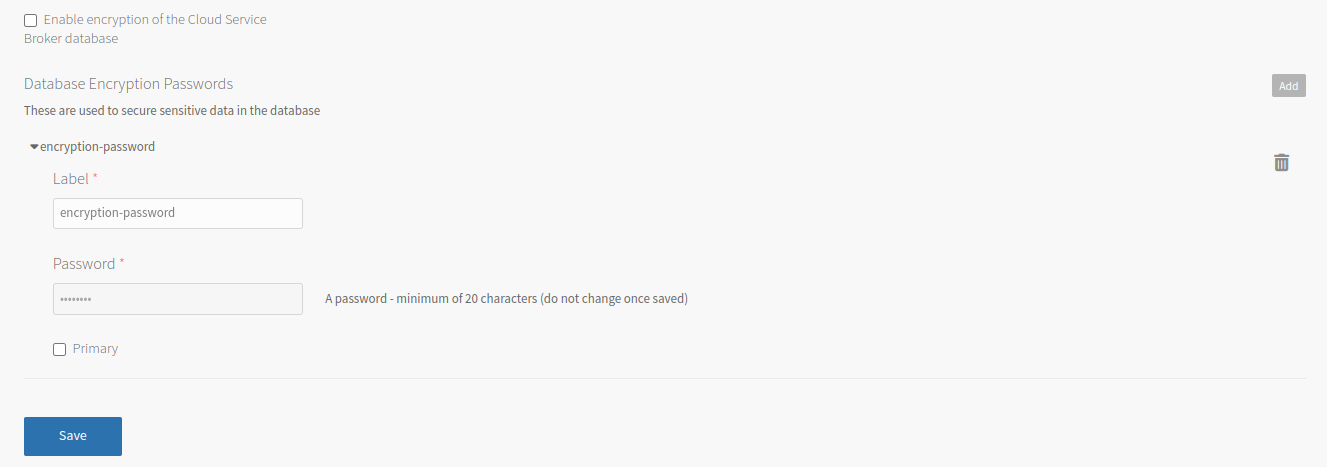
In production environments, VMware recommends that you enable encryption. This encrypts certain sensitive information in the state database, such as IaaS credentials. The encryption password that you enter on the Service Broker Config pane is used to generate an encryption key.
Applying changes takes longer than normal when you first enable encryption and when you change the encryption password.
CautionEnable backup and restore capabilities in the MySQL database before attempting encryption. This is because if something goes wrong, and your database is only partially encrypted, it is safest to revert to the most recent database backup.
Prerequisite
You must have a small MySQL database to use as the state database. The state database stores text information about each state change of each service instance, so it does not have to be large. For most use cases, 10 GB is more than enough to cover the needs of Cloud Service Broker for AWS.
Procedure: Configure a State Database
To configure Cloud Service Broker for AWS with a database:
-
Click Service Broker Config.
-
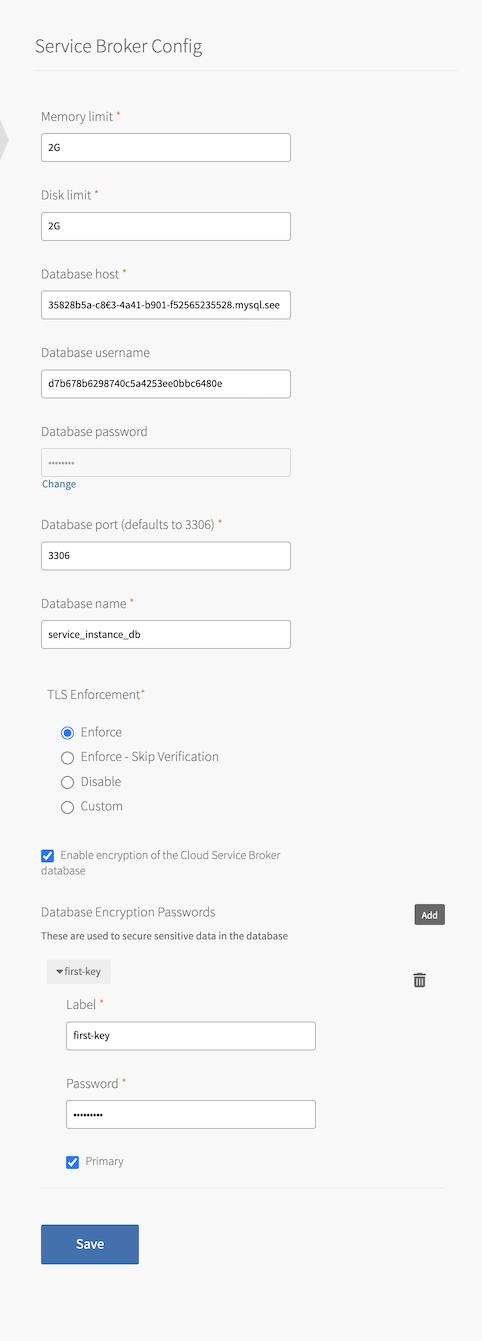
Configure the text boxes as follows:
Text box Instructions Memory limit Memory limit (for example, 1024M, 2G) for the Service Broker app defaults to 2G.Disk limit Disk limit (for example, 1024M, 2G) for the Service Broker defaults to 2G.Database host Enter the host name of the prerequisite state database. Database username and Database password Enter the credentials for the state database. The example shown in the screenshot in the earlier step refers to setting the user name for a MySQL tile provisioned database. If you are configuring a database provisioned by another service, see the documentation for that service for the correct user name format. For RDS MySQL, see the AWS documentation. Database port Enter the port number for connection to the state database. Defaults to 3306.Database name Enter the name of an existing database to use as the state database. TLS Enforcement Select the type of TLS enforcement you want. If you select Custom, enter your CA certificate, client certificate, and key. Enable encryption of the Cloud Service Broker database If you want the sensitive data to be encrypted, select this check box and the Add button. If you do not want to encrypt the data, leave the check box unselected and do not fill in the Database Encryption Passwords text boxes. Label Enter a unique password label. You cannot change this label after you save. Password Enter a secure password that is at least 20 characters long. You cannot change this password after you save. Primary Select this check box if this is the password that you want to use to encrypt the data. You must mark one and only one password as primary. -
Click Save.
-
If upgrading from a previous tile version, service instances might need upgrading. By default, the tile upgrades all instances during installation. To configure the upgrade task, see Upgrade All Service Instances Configuration. For version-specific upgrade instructions, see Upgrading Cloud Service Broker for AWS.
-
Return to the Ops Manager Installation Dashboard.
-
Click Review Pending Changes.
-
Click Apply changes to install the Cloud Service Broker for AWS tile.
If you later want to change the password on the state database, see Rotate the encryption password on the state database later in the topic.
If you later want to deactivate encryption, see Remove encryption from the state database later in the topic.
Configure Services with Cloud Service Broker for AWS
This section describes how to configure services and service plans offered by the Cloud Service Broker for AWS within the Cloud Foundry Marketplace on your instance of Cloud Foundry.
Cloud Service Broker for AWS specifies new service plans through JSON. An example is provided, using the smallest possible size, within each service.
To configure services and service plans:
-
Click the already-installed Cloud Service Broker for AWS tile in your Ops Manager tile dashboard.
-
Find the service you want to make available in the left navigation under the Settings tab.
-
Enter additional plans as additional JSON objects within the provided text box. For details about properties for each service configuration, see Service plan reference.
Note
When developers create or update a service instance, they cannot override any plan-level properties that you set in this text box.
-
(Optional) To use different credentials to the ones specified in the AWS Config tab, supply the credentials as properties to a plan instance in the additional plans box:
[ { "name" : "PLAN-NAME", "id" : "UUID", "description" : "PLAN-DESCRIPTION", "aws_access_key_id" : "AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID", "aws_secret_access_key" : "AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY", ... } ] -
Click Save.
-
Return to the Ops Manager Installation Dashboard and click Review Pending Changes.
-
Click Apply changes.
-
Review your Cloud Foundry Marketplace to see the new plans.
Configure Feature Flags
This section describes how to enable feature flags for Cloud Service Broker for AWS.
To configure feature flags:
-
Click Feature Flags.
-
By default, the
Enable Beta service offeringsflag isfalse. To enable all service offerings tagged as beta, select the check box. -
Click Save.
-
Return to the Ops Manager Installation Dashboard and click Review Pending Changes.
-
Click Apply changes.
-
Review your Cloud Foundry Marketplace to see the new services.
Rotate the Encryption Password on the State Database
If you have already set an encryption password and want to change it, see the following instructions steps:
To rotate the password on the state database:
-
Click Service Broker Config.
-
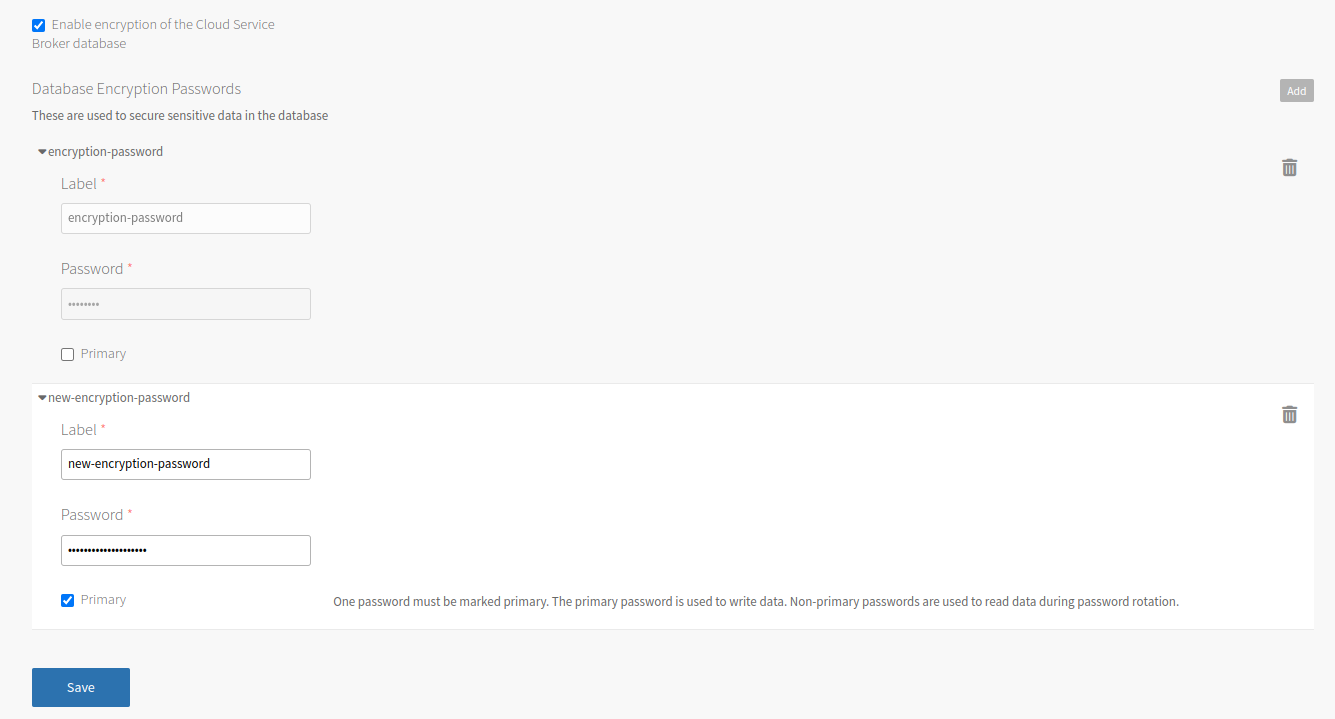
Deselect the Primary check box.
-
Click Add.
-
Enter a new Label and Password for the new password, and select Primary. You cannot change the label or password after you save.
-
Click Save.
-
Return to the Ops Manager Installation Dashboard.
-
Click Review Pending Changes.
-
Click Apply changes to install the Cloud Service Broker for AWS tile.
-
(Recommended) After the apply changes process completes, delete the non-primary label and password pair and apply changes again.
Remove Encryption from the State Database
If the data in the state database was previously encrypted and you want to deactivate encryption, remove encryption from the state database:
-
Click Service Broker Config.
-
Deselect the Enable encryption of the Cloud Service Broker database check box.
-
Deselect the Primary check box, but do not change the Label or Password text boxes.
-
Click Save.
-
Return to the Ops Manager Installation Dashboard.
-
Click Review Pending Changes.
-
Click Apply changes to install the Cloud Service Broker for AWS tile.
-
(Recommended) After the apply changes process completes, delete all label and password pairs and apply changes again.
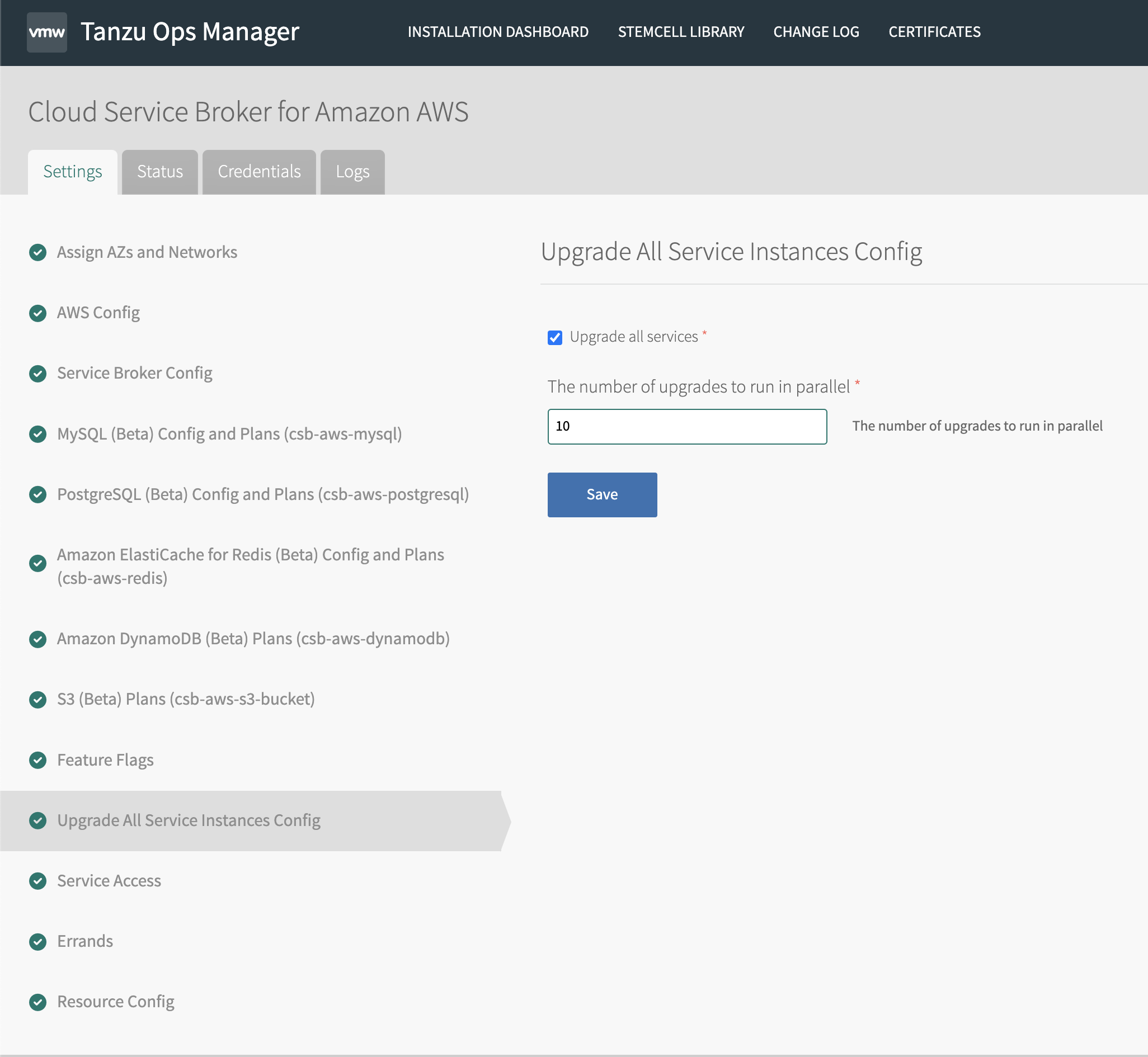
Upgrade All Services Instances Configuration
If upgrading from a previous tile version, service instances might need upgrading. By default, the tile upgrades all instances from active service plans during installation.
This section is about configuring the Upgrade All Service Instances task. For the overall upgrade process and version-specific upgrade instructions, see Upgrading Cloud Service Broker for AWS.
If the Upgrade all services check box is not selected, service instances are not upgraded during installation. The broker might be unable to manage service instances that are not upgraded. Any operations on that instance, such as update, bind, unbind, or delete, are blocked until you run the upgrade task. You can run the upgrade task at any time, and as many times as needed.
ImportantFailure to upgrade one or more instance does not cause the tile installation to fail. Review the
deploy allerrand logs to ensure all instances have been upgraded successfully.
To configure the upgrade task:
-
Go to the Upgrade All Service Instances Config tab.
-
Configure the text boxes.
Text box Description Upgrade all services Checked by default. Indicates if service instances are upgraded during product installation. The number of upgrades to run in parallel Indicates the number of instances that can be in the upgradingstatus at any given time. By default, the number of parallel upgrades is set to 5. This impacts the time required to perform the upgrades, however, the upgrades do not cause downtime. Setting this to a higher number can cause the broker to fail due to insufficient memory. -
Click Save.