Create the needed Pools (one for each service port) with the same VMware Aria Operations for Logs nodes.
-
Select Applications → Pools → CREATE POOL.
Enter a name for this pool. For example: vRLI_UI.
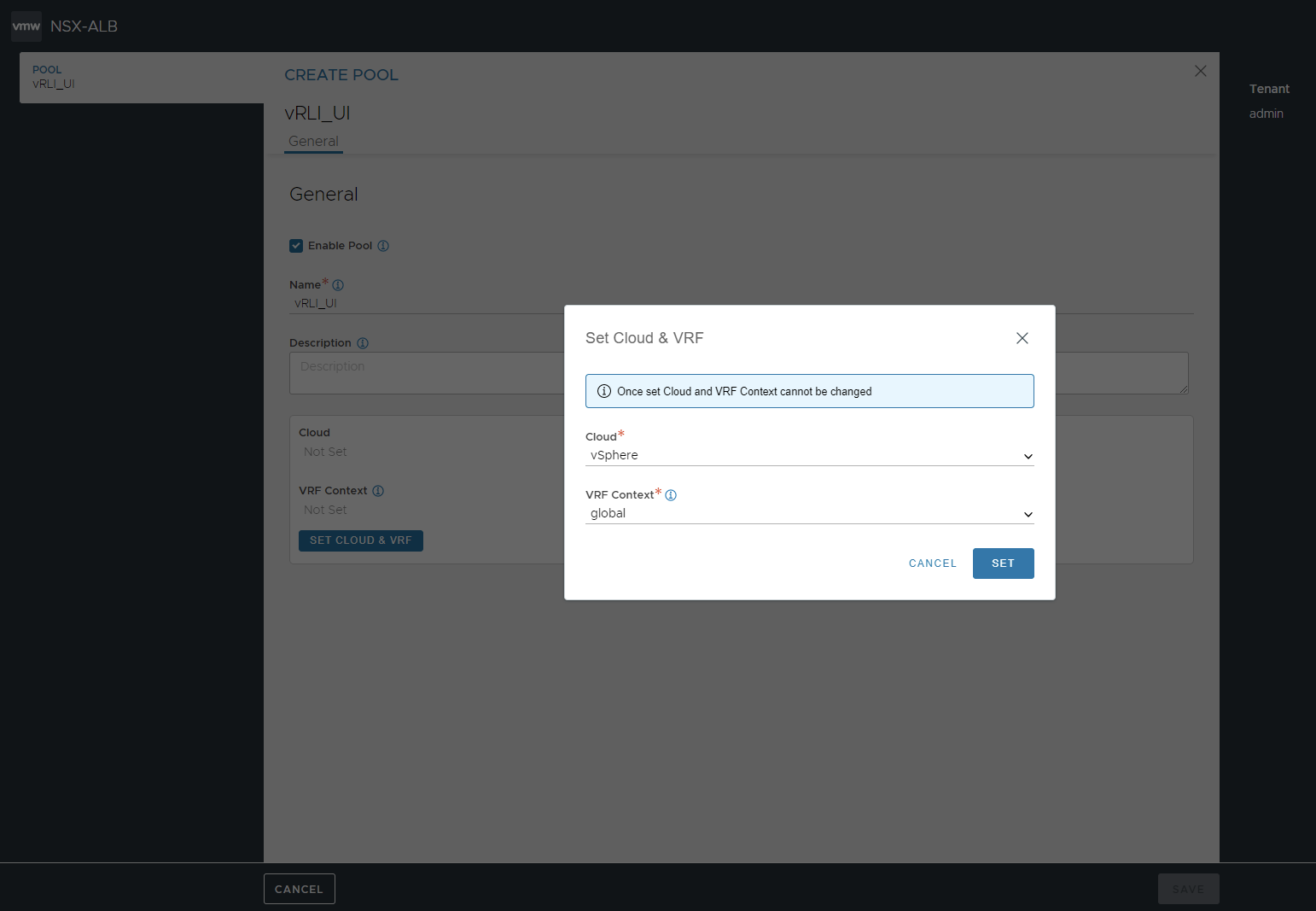
Click to Set Cloud & VRF and choose the appropriate "Cloud" and "VRF Context", then click SET.
Change the Default Server Port to 443.
Choose Round Robin as a Load Balance Algorithm.
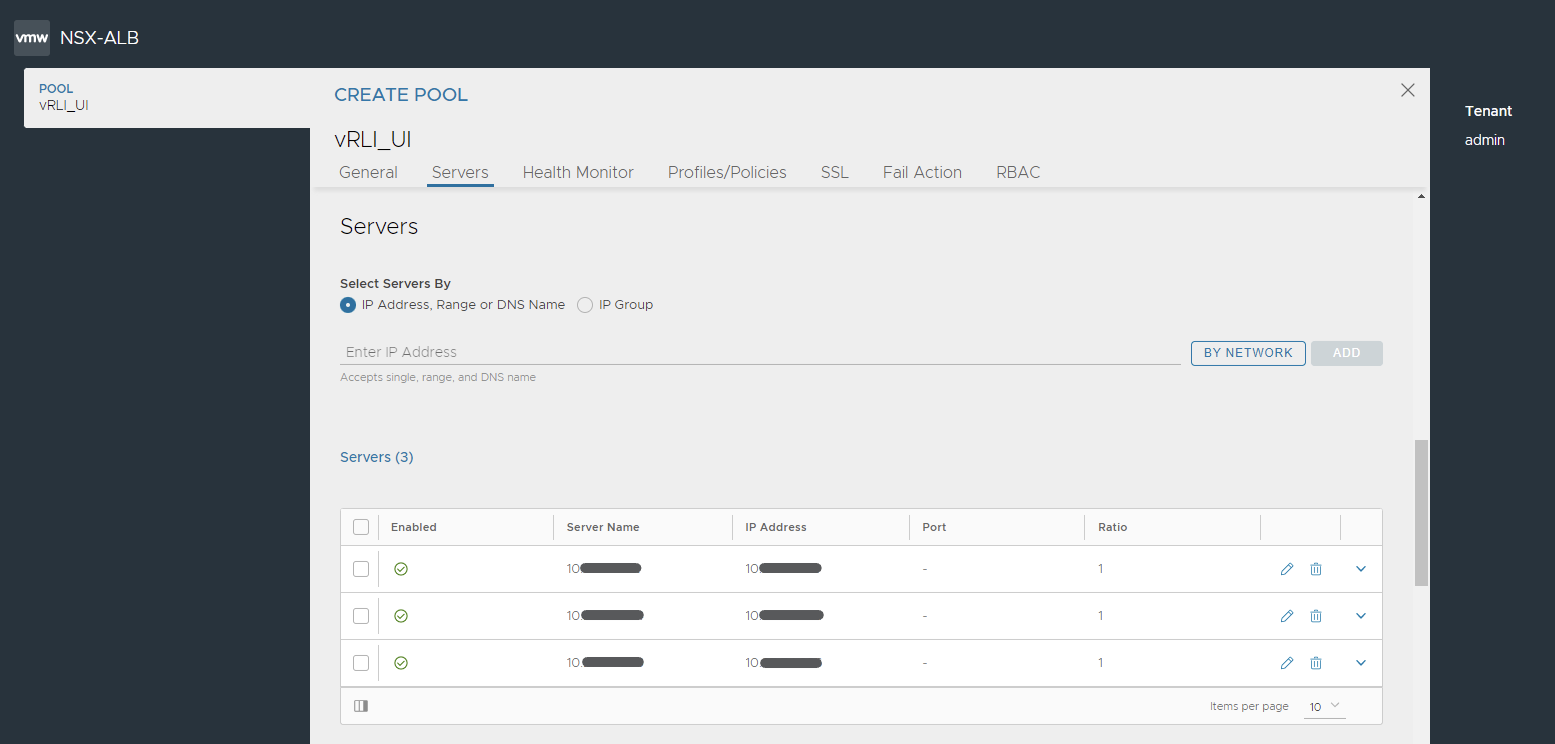
Enter VMware Aria Operations for Logs nodes' IPs.
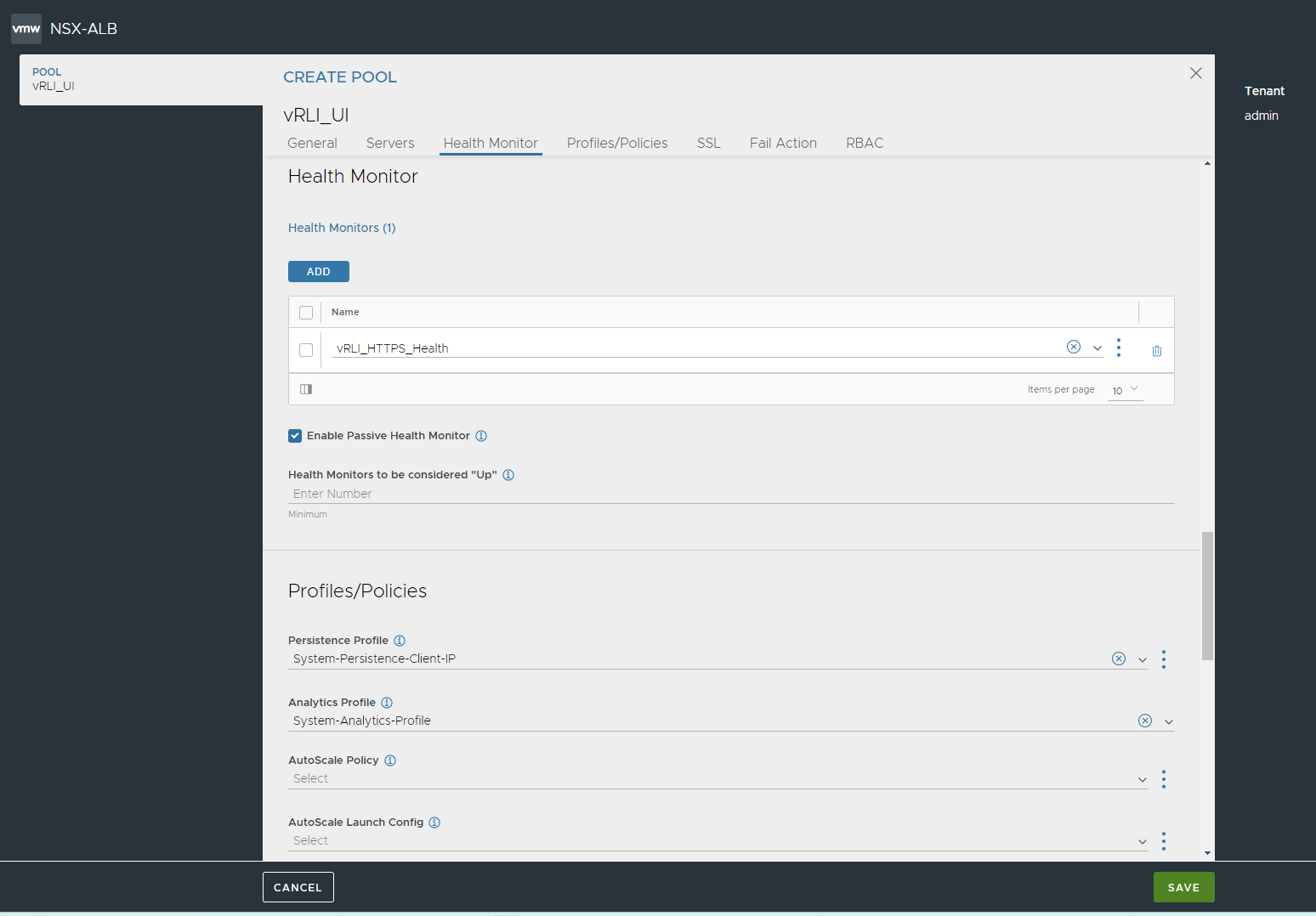
Under Health Monitors click to ADD and choose the one we just created at step 3.1 vRLI_HTTPS_Health.
Select the Persistence Profile type as Client IP Address (System-Persistence-Client-IP).
Click SAVE.
-
Select Applications → Pools → CREATE POOL.
Enter a name for this pool. For example: vRLI_UDP.
Click to Set Cloud & VRF and choose the appropriate "Cloud" and "VRF Context", then click SET.
Change the Default Server Port to 514.
Choose Round Robin as a Load Balance Algorithm.
Enter VMware Aria Operations for Logs nodes' IPs.
Under Health Monitors click to ADD and choose the one we just created at step 3.2 → vRLI_UDP_Health.
The UDP health monitor service sends a generic UDP packet and awaits a response. If there is no response, the port is assumed to be open and a UDP packet specific to the service on that port is sent to detect the service. If an ICMP error packet is returned, the port is considered closed. This will not cover the case when the server is down itself. This is why adding System-Ping as a second health monitor is recommended.
Click SAVE.
-
Select Applications → Pools → CREATE POOL.
Enter a name for this pool. For example: vRLI_TCP_514.
Click to Set Cloud & VRF and choose the appropriate "Cloud" and "VRF Context", then click SET.
Change the Default Server Port to 514.
Choose Round Robin as a Load Balance Algorithm.
Enter VMware Aria Operations for Logs nodes' IPs.
Under Health Monitors click to ADD and choose the one we just created at step 3.3 - vRLI_TCP_Health.
Click SAVE.
-
Select Applications → Pools → CREATE POOL.
Enter a name for this pool. For example: vRLI_TCP_1514.
Click to Set Cloud & VRF and choose the appropriate "Cloud" and "VRF Context", then click SET.
Change the Default Server Port to 1514.
Choose Round Robin as a Load Balance Algorithm.
Enter VMware Aria Operations for Logs nodes' IPs.
Under Health Monitors click to ADD and choose the one we just created at step 3.3 - vRLI_TCP_Health.
Click SAVE.
-
Select Applications → Pools → CREATE POOL.
Enter a name for this pool. For example: vRLI_TCP_6514.
Click to Set Cloud & VRF and choose the appropriate "Cloud" and "VRF Context", then click SET.
Change the Default Server Port to 6514.
Choose Round Robin as a Load Balance Algorithm.
Enter VMware Aria Operations for Logs nodes' IPs.
Under Health Monitors click to ADD and choose the one we just created at step 3.3 - vRLI_TCP_Health.
Click SAVE.
-
Select Applications → Pools → CREATE POOL.
Enter a name for this pool. For example: vRLI_TCP_9000.
Click to Set Cloud & VRF and choose the appropriate "Cloud" and "VRF Context", then click SET.
Change the Default Server Port to 9000.
Choose Round Robin as a Load Balance Algorithm.
Enter VMware Aria Operations for Logs nodes' IPs.
Under Health Monitors click to ADD and choose the one we just created at step 3.3 - vRLI_TCP_Health.
Click SAVE.
-
Select Applications → Pools → CREATE POOL.
Enter a name for this pool. For example: vRLI_TCP_9543.
Click to Set Cloud & VRF and choose the appropriate "Cloud" and "VRF Context", then click SET.
Change the Default Server Port to 9543.
Choose Round Robin as a Load Balance Algorithm.
Enter VMware Aria Operations for Logs nodes' IPs.
Under Health Monitors click to ADD and choose the one we just created at step 3.3 - vRLI_TCP_Health.
Click SAVE.