The VM-VM path provides the path visibility between the NSX Advanced Load Balancer Virtual Services in your environment.
Before viewing the path topology, learn about the core components of the NSX Advanced Load Balancer platform. For more information, see the Overview of NSX Advanced Load Balancer topic.
VMware Aria Operations for Networks does not support vNIC - vNIC path in NSX Advanced Load Balancer.
VMware NSX-T or VMware vCenter manages the network of NSX Advanced Load Balancer pool members. Therefore, you can view the following VM-VM paths only:
- VMware NSX-T and NSX Advanced Load Balancer and VMware vCenter
- VMware Cloud and NSX Advanced Load Balancer
- VMware Cloud on AWS NSX-T and VMware vCenter and NSX Advanced Load Balancer
VM-VM Path Through a Virtual Service
To see the VM-VM path through a virtual service, perform the following steps on the Path Topology page:
- Select the Source and Destination VMs.
- Select the NSX Advanced Load Balancer virtual service from the Path via Load Balancer drop-down menu.
An example of VM-VM path through an NSX Advanced Load Balancer virtual service is as follows:

VM-VM Path Through a Virtual Service That Uses Multiple Service Engines
When a virtual service is scaled across multiple service engines, by default, VMware Aria Operations for Networks displays the VM-VM path through the primary service engine.
To see the VM-VM path through a secondary service engine, perform the following steps:
- Select the Source and Destination VMs.
- Select the NSX Advanced Load Balancer virtual service from the Path via Load Balancer drop-down menu.
- Select the secondary service engine from the Service Engine drop-down menu.
An example of the VM-VM path through a secondary service engine is as follows:
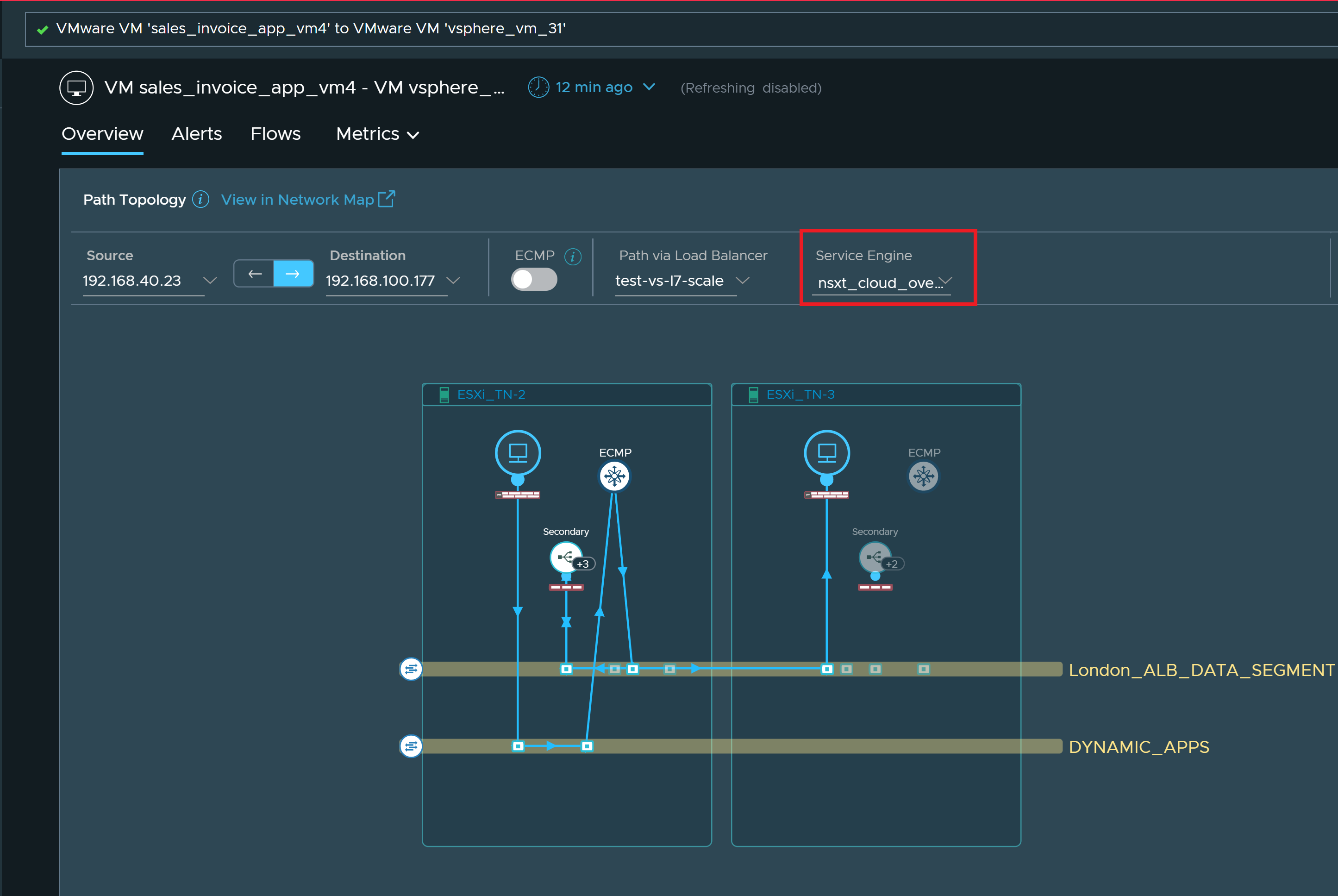
In this example, +3 indicates that the traffic of the virtual service in ESXi_TN-2 is distributed to three service engines, and +2 indicates that the traffic of the virtual service in ESXi_TN-3 is distributed to two service engines.
You can click the number on respective hosts to see the list of service engines associated with that host. You can also select a different service engine from the list to see the VM-VM path through the selected service engine.
VM-VM Path Through a Virtual Service That Uses Server Name Indication
Server Name Indication (SNI) is a method of virtual hosting multiple domain names for a single virtual IP.
In NSX Advanced Load Balancer, SNI hosting is implemented as parent and child virtual services. For more information, see the NSX Advanced Load Balancer documentation.
If you have configured your virtual service to use SNI, select the child virtual service (through which you want to view the VM-VM path) from the Path via Load Balancer drop-down menu.
An example of a VM-VM path through a child virtual service is as follows:
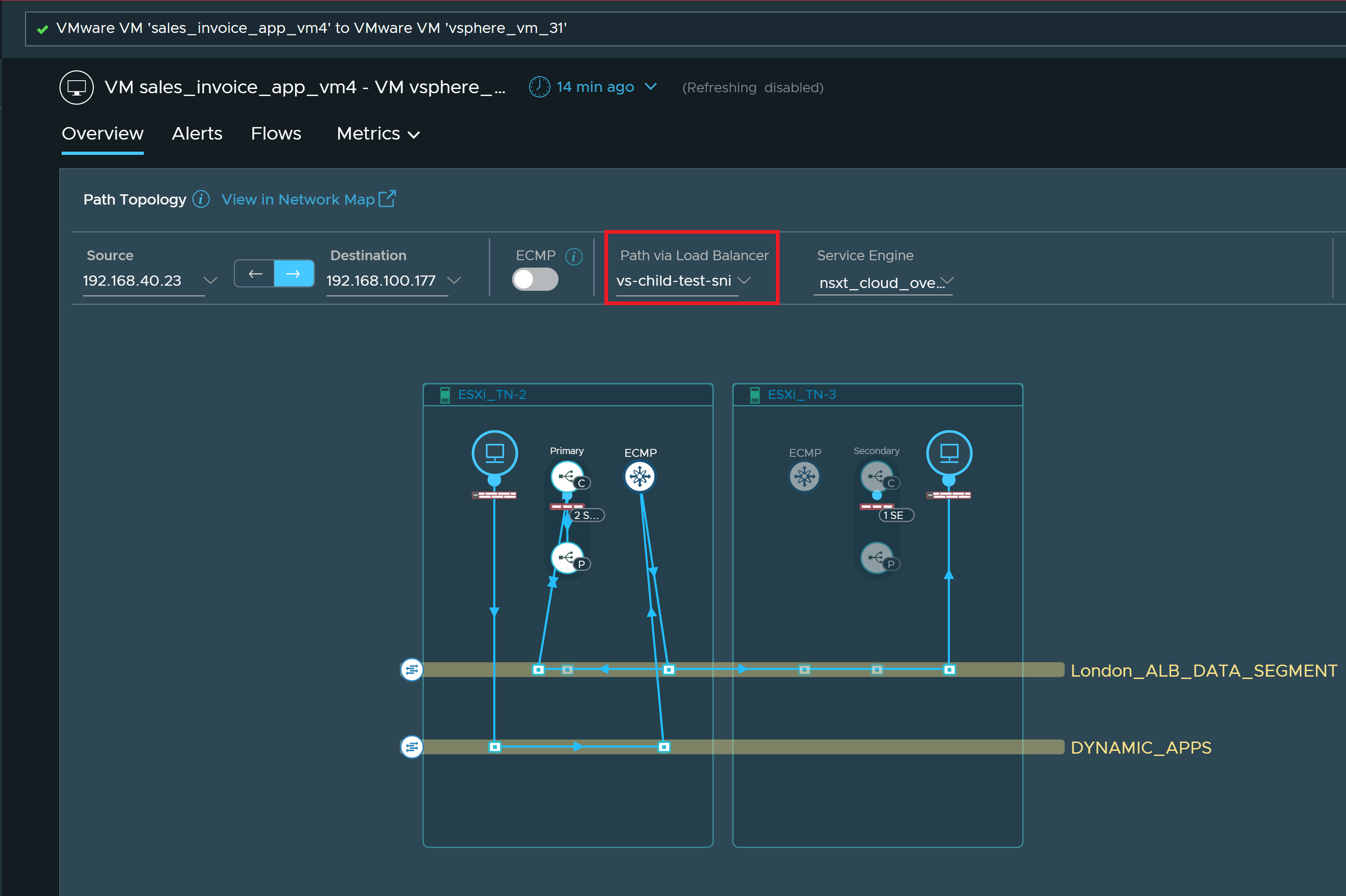
In this example, 2SE indicates that the traffic of the virtual service in ESXi_TN-2 is distributed to two service engines, and 1SE indicates that the traffic of the virtual service in ESXi_TN-3 is handled by a single service engine. You can click SE on respective hosts to see the list of service engines associated with the host. You can also select a different service engine from the list to view the VM-VM path through the selected service engine.