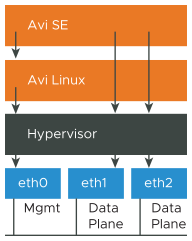
This section focuses on the custom TCP stack for data plane services running on the Avi Load Balancer SEs. Though SEs run on Ubuntu Linux, the data NICs utilize a modified BSD TCP stack to provide a leaner profile and faster performance. The different modes that the Avi Load Balancer supports for handling TCP traffic and various parameters that can be tuned for optimization of the TCP traffic are also detailed here.
This section focuses on the data-plane NICs of the Avi Load Balancer SEs. The TCP stack outlined, excludes the SE management NIC and the Avi Load Balancer Controller, which rely on a different TCP stack.
TCP Settings - TCP Profile
Every virtual service configured on the Avi Load Balancer requires a TCP/UDP profile. The profile is a reusable template containing defined settings for establishing network connections. Two different modes are supported to handle TCP traffic for a virtual service:
TCP Proxy
TCP Fast Path
By default, most new virtual services use the System-TCP-Proxy profile, which is configured for TCP proxy. This is the recommended setting for protocols such as HTTP. Some protocols such as DNS, can automatically select a different TCP/UDP profile, such as UDP.