Configure the basic setting for a virtual service like the VS VIP Address, pool, profiles and policies and more.
Procedure
- Enter a unique Name for the virtual service
- The Enabled toggle icon is green by default. This implies that the virtual service will accept and process traffic normally. To deactivate the virtual service click the toggle button. The existing concurrent connections will be terminated, and the virtual service will be unassociated from all Service Engines. No health monitoring is performed for deactivated virtual services.
- The Traffic Enabled? option is enabled by default. Click the option to stop virtual service traffic on its assigned service engines. This option is effective only when the virtual service is enabled.
- Select Virtual Hosting VS if this virtual service participates in virtual hosting via SSL’s Server Name Indication (SNI). This allows a single SSL decrypting virtual service IP:port to forward traffic to different internal virtual services based on the name of the site requested by the client. The virtual hosting VS must be either a parent or a child.
Option Description Parent
The parent virtual service is external facing, and owns the listener IP address, service port, network profile, and SSL profile. Specifying a pool for the parent is optional, and will only be used if no child virtual service matches a client request.
The SSL certificate may be a wildcard certificate or a specific domain name. The parent’s SSL certificate will only be used if the client’s request does not match a child virtual service domain.
The parent virtual service will receive all new client TCP connections, which will be reflected in the statistics. The connection is internally handed off to a child virtual service, so subsequent metrics such as concurrent connections, throughput, requests, logs and other stats will only be shown on the child virtual service.
Child
The child virtual service does not have an IP address or service port. Instead, it points to a parent virtual service, which must be created first.
The domain name is a fully qualified name requested by the SNI-enabled client within the SSL handshake. The parent matches the client request with the child’s domain name. It does not match against the configured SSL certificate. If no child matches the client request, the parent’s SSL certificate and pool are used.
- Select the Virtual Hosting Type as Enhanced Virtual Hosting or SNI.
- Enter the VS VIP address.
- Under Profiles, select the following.
- The TCP/ UDP Profile to determine thenetwork settings such as protocol, TCP or UDP,and related options for the protocol.
- The Application Profile to enable application layer specific features for the virtual service
- Bot Detection Policy
- ICAP Profile to configure the ICAP server when checking the HTTP request.
- The Error Page Profile to be used for this virtual service. This profile is used to send the custom error page to the client generated by the proxy.
- Under the Service Port section, enter the Services, which are the service ports that the virtual service will listen for incoming traffic. Click Add Port to add multiple ports.
- Click Switch to Advanced to enter a range of service ports.
- SelectUse as Horizon Primary/Tunnel Protocol Ports in case of a Horizon deployment. This option is used for L7 redirect.
- Select an Application Profile under Override Application Profile to enable application layer specific features for the this specific service.
- Enable Override TCP/UDP and select the profile required to override the virtual service's default TCP/UDP profile on a per-service port basis.
- Click Add Port to add another range of service ports and configure the same.
- Under the Pool section, either select a Pool or a Pool Group. Using the Pool drop-down list, select the required pool that contains destination servers and related attributes such as load-balancing and persistence. The Minimum Pools Up option is the minimum numer of pools in UP state required to make a virtual service status UP.
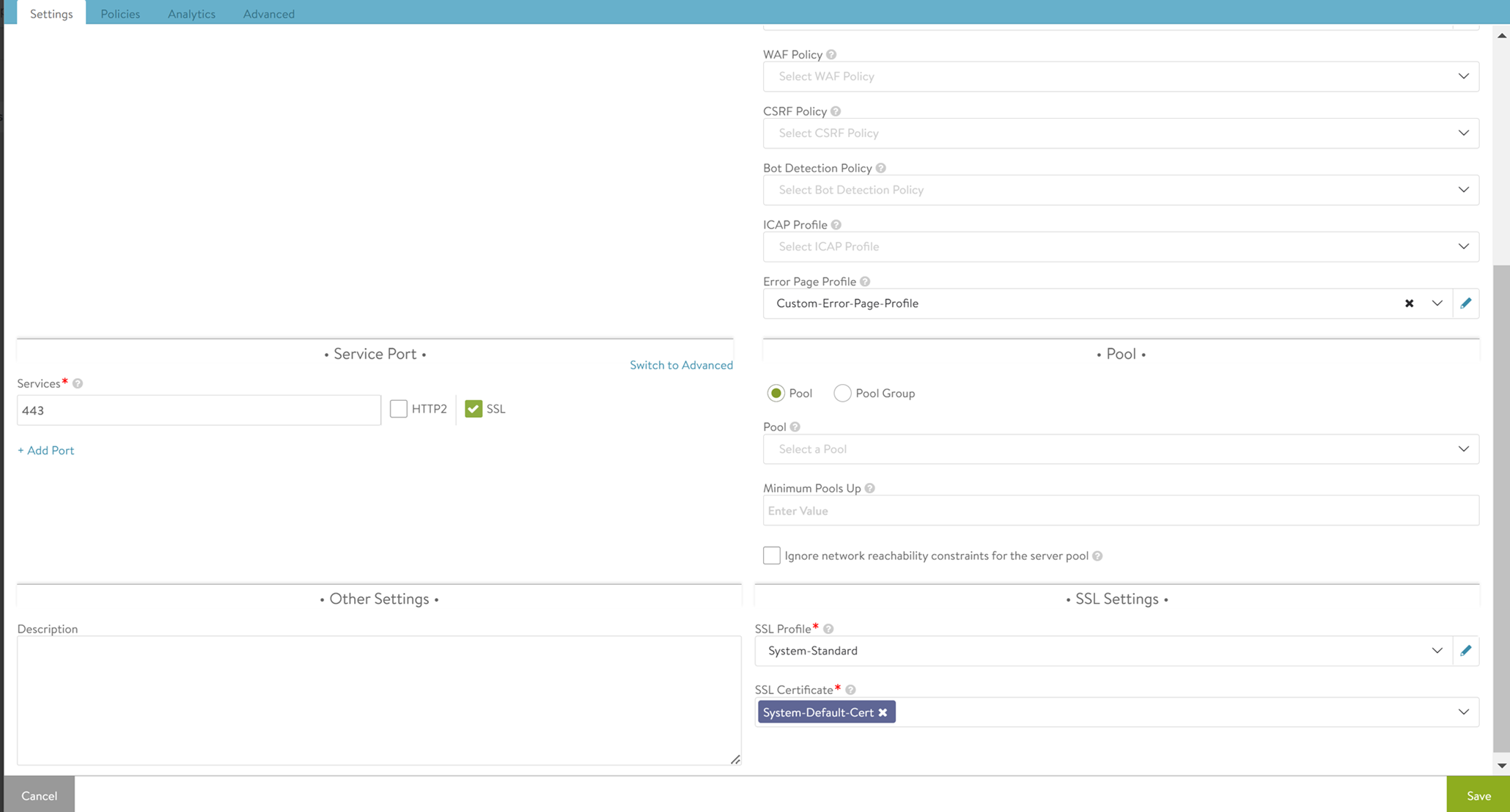
- Select Ignore network reachability constraints for the server pool, if required. If the pool contains servers in networks unknown or inaccessible to Avi Load Balancer, the Controller is unable to place the new virtual service on a SE, as it does not know which SE has the best reachability. This requires you to manually choose the virtual service placement. Selecting this option will allow the Controller to place the virtual service, even though some or all servers in the pool may be inaccessible. For instance, you can select this option while creating the virtual service, and later configure a static route to access the servers.