For file transfer protocol (FTP) communication, clients open a TCP-based control channel on port 21. For active FTP, a second data channel is initiated from the server to the client through port 21. Avi Load Balancer only supports passive FTP, in which the client initiates the data channel through a high port negotiated with the server.
Passive FTP
A Note on High Availability
Exactly one SE in an SE group may deliver the FTP service at any given time. Virtual service scale-out to two or more SEs is not supported with Avi Load Balancer FTP. Therefore, legacy active/standby and 1+M elastic HA are supported. Active/active elastic HA is not.
The virtual settings configuration is as follows:
Application Profile |
L4 |
TCP/UDP Profile |
TCP Proxy |
Service Ports |
Set to Advanced through the Avi Load Balancer UI |
Port |
21 |
Virtual Service Settings:
Application Profile: L4
TCP/UDP Profile: TCP-proxy
Service Ports: Set to Advanced through the Avi Load Balancer UI
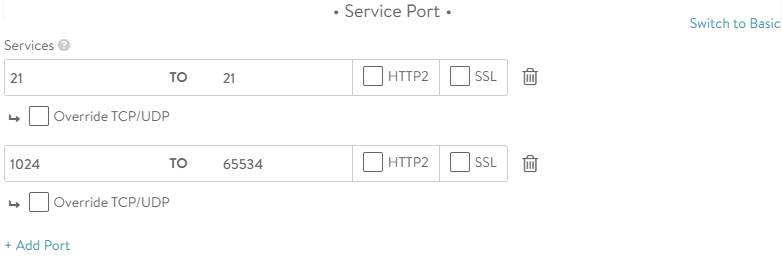
Port: 21
Port: 1024-65534
Pool Settings:
Load Balance Algorithm: Least Connections
Persistence: Client IP
Health Monitor: TCP
Health Monitor Port: 21
Port Translation: Deactivated
Active FTP
Active FTP is not supported. Avi Load Balancer recommends the use of passive FTP as a workaround.
> ftp ftp.test.com Connected to ftp.test.com. ftp.test.com FTP server ready. Name (test:user): anonymous Password required for anonymous. Password: ****** User anonymous logged in. Remote system type is UNIX. Using binary mode to transfer files. ftp> passive Passive mode on.