Avi Load Balancer Service Engines proxy DNS requests to a backend pool of DNS servers. A virtual service with a System-DNS (or similar) application profile is defined as usual. However, a pool of backend servers loaded with DNS software packages must be assigned.
Hosting Manual or Static DNS Entries
Avi Load Balancer DNS can host manual or static DNS entries. For a given FQDN, you can configure an A, AAAA, SRV, CNAME, or NS record to be returned.
Avi Load Balancer supports text record (TXT) record and mail exchanger (MX) record.
TXT record: This is used to store text-based information for the configured domain.
MX record: This is used in mail delivery based on the configured domain.
Virtual Service IP Address DNS Hosting
Avi Load Balancer DNS can host the names and IP addresses of the virtual services configured in Avi Load Balancer. Avi Load Balancer serves as DNS provider for the hosted virtual services. For complete configuration details, see Service Discovery using NSX Advanced Load Balancer as IPAM and DNS Provider.
Hosting GSLB Service DNS Entries
The Avi Load Balancer DNS virtual service can host GSLB service DNS entries, and automatically update its responses based on the application service health, service load and proximity of clients to sites implementing the application service. Avi Load Balancer GSLB automatically populates these DNS entries. For more information on Avi Load Balancer GSLB, see the following topics in Avi Load BalancerGSLB guides:
Avi Load BalancerGSLB Overview
Avi Load BalancerGSLB Site Configuration and Operations
Avi Load BalancerGSLB Service Health Monitoring
DNS for Avi Load Balancer hosted Virtual Services
Avi Load Balancer-SE-hosted DNS virtual services translate the FQDNs of Avi Load Balancer-hosted virtual services into IP addresses. This configuration does not require pool assignment, as the translation is completely done within the SE VMs.
Navigate to and select DNS Service.
Under the DNS Virtual Services section, click the drop-down menu to either choose a pre-defined DNS virtual service or create a virtual service.
For more information on configuration steps for DNS virtual services, see to Configuring a Local DNS Virtual Service on All Active Sites that host DNS topic in Avi Load BalancerGSLB Guide.
DNS for GSLB
For GSLB configuration, the DNS is not defined by the DNS virtual service but it is configured as a GSLB site object. As part of the GSLB site configuration, a few pre-existing DNS service (s) is (are) designated to serve in the role.
The following are the steps to configure DNS for GSLB:
Navigate to .
Click Add New Site button in the Site Configuration tab.
Specify relevant information for all fields in the editor. Enable the check box for Active Member option and click Save and Set DNS Virtual Services.
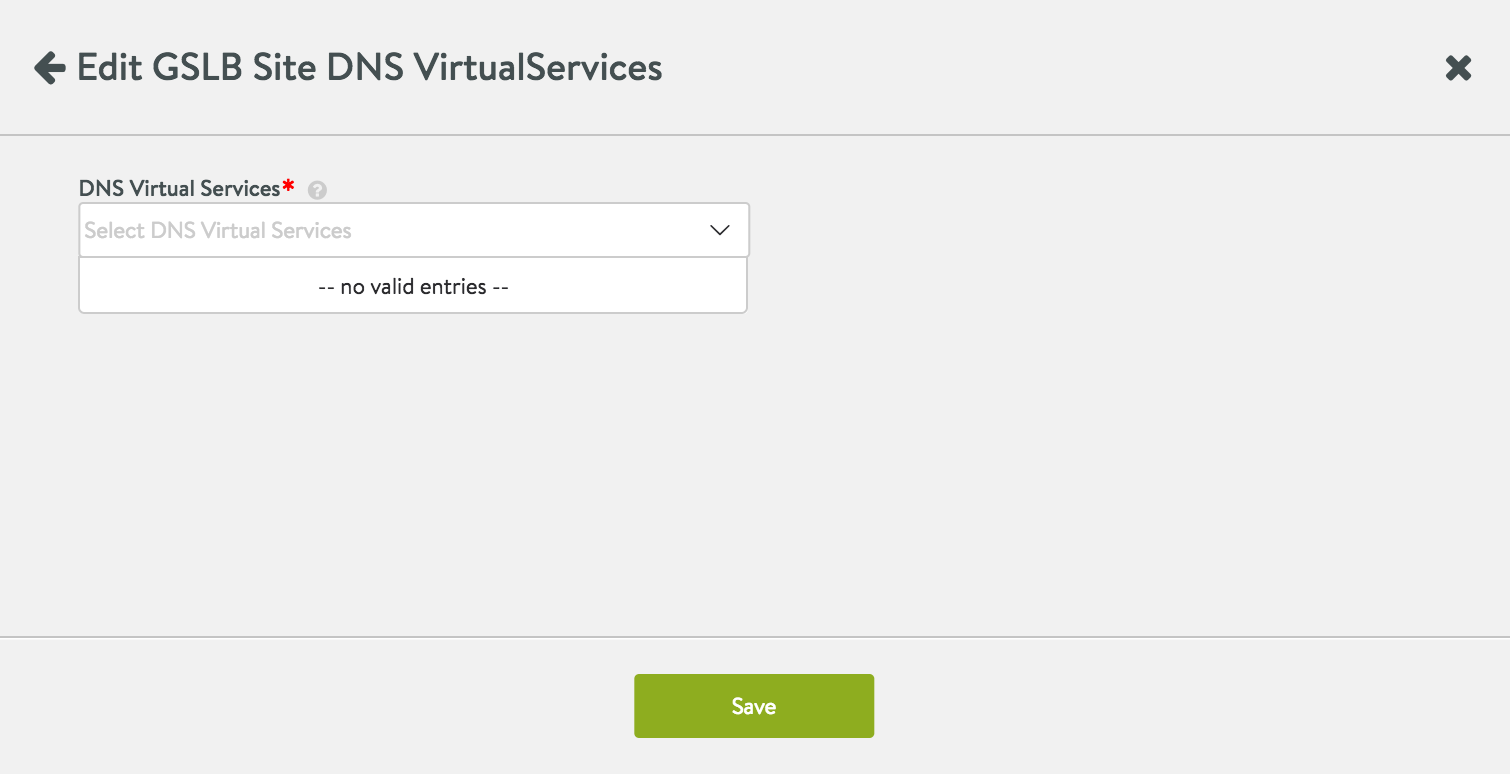
Select from one or more DNS virtual services in the drop-down menu and click Save to enable it for the GSLB configuration.
This below screenshot illustrates, the case where there are no DNS virtual services to choose. An active GSLB site does not require a DNS, though it may be preferred, as described in the next section.
High Availability Recommendations for GSLB
For high availability, it is recommended to configure DNS for GSLB on an SE group that is scalable to two or more Service Engines. It is also recommended to implement DNS for GSLB in more than one location. This can be implemented in the following two ways:
You must have at least two geographically separated active GSLB sites. For each site, configure DNS to a scalable SE group.
If only one active site is defined then, ensure a minimum of at least one geographically remote cloud. On that remote cloud, configure DNS for GSLB on a scalable SE group. Also, define all virtual services to support the mission-critical applications running on the original location.