In its most generic form, alerts are a construct intended to inform administrators of significant events within the Avi Load Balancer system. Once an alert is triggered, it can be used to notify an administrator through one or more notification actions. Alerts can trigger ControlScripts to alter the system configuration or communicate to remote systems.
Alert Scope
Alerts can be viewed in multiple places within the UI, including under Virtual Services, Pools, Service Engine, and All Alerts pages. Navigate to to view all current alerts, logged across the system. Alert lists under SEs, Virtual Services, and Pools include alerts specific to the context.
Alerts are transient and can exist or be true only for a defined period. After the configured alert expiry time lapses, the alert is removed. The underlying event or metric that triggered the alert still exists as a permanent log of what occurred.
Alert Workflow
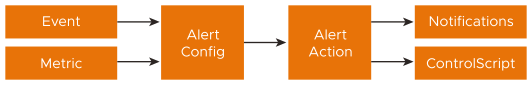
Configuring custom alerts requires walking through the workflow to build the alert config (the alert’s trigger) based on one or more metrics from a list of more than 500 events and metrics. When the alert configuration’s conditions are met, the actions configured in the alert action are executed. The alert action can list the notifications to be generated and potentially call for further action, such as application autoscaling or execution of a ControlScript.
Alert Config
The Alert Config page is used to define the triggers that will generate an alert. The Avi Load Balancer has a number of canned alert configs, which are used to generate alerts in a default deployment.
Events trigger alerts to actively highlight important information. Default alerts are created through the Alert Config page. These alerts configs can be modified or disabled, but not deleted. Alert configs are triggers that determine whether or not an alert should be generated.
To create a new alert config:
Navigate to .
Click Create and Enter the Name.
By default, Enable Alert Trigger is selected. Click the option to disable the alert.
Select the system events or the type of client log used as Source for this alert configuration.
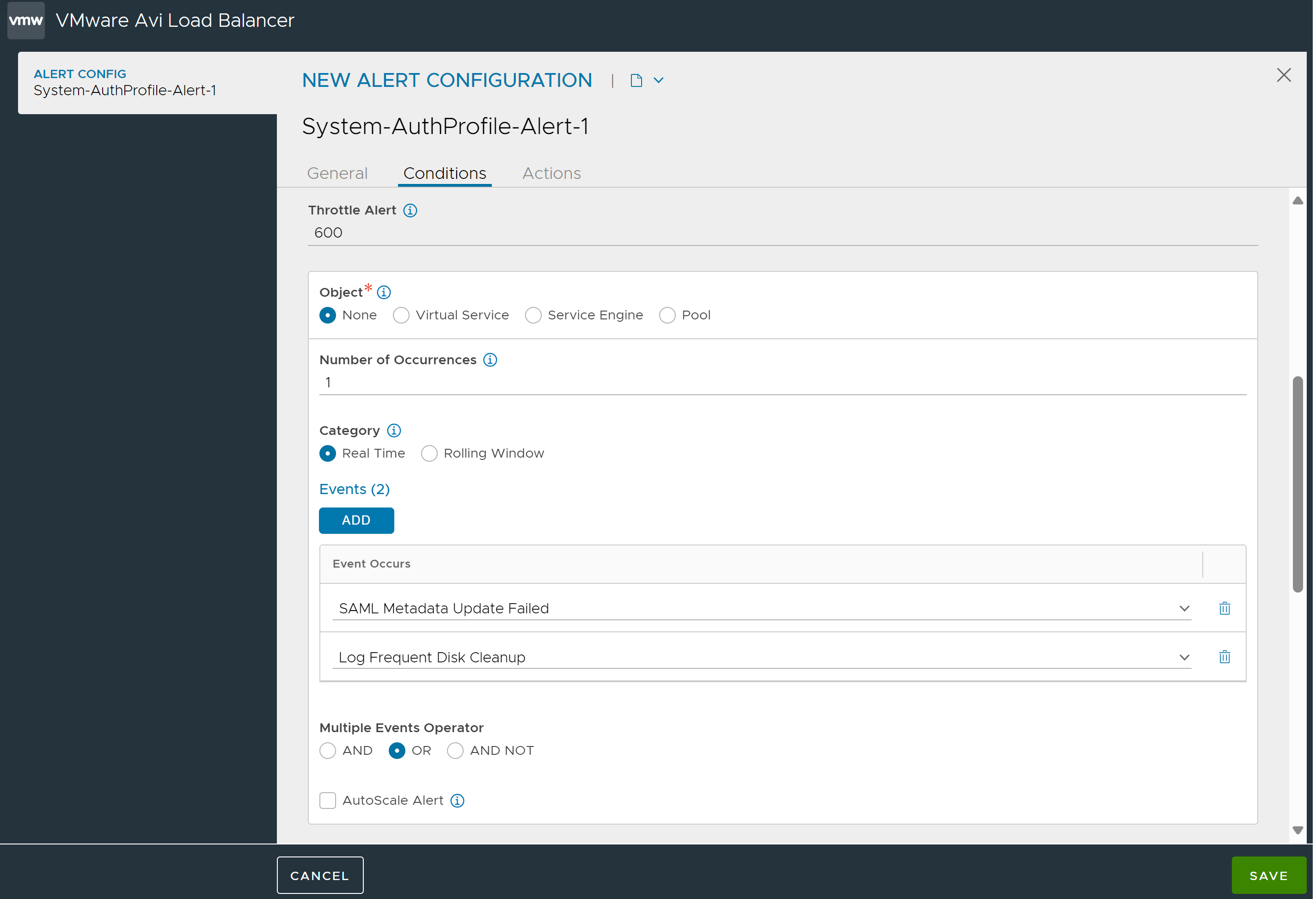
Choose the Conditions that must be true to trigger an alert. The source can be an event or a metric. If multiple conditions exist, then all conditions must be true.
Enter the Throttle Alert, the threshold after which the alert must be triggered. The timer begins once the alert is triggered.
Select the Object to which the alert config is associated with. It can be a Virtual Service, Service Engine, or Pool.
Enter the minimum number of times the event muct occur before the alert is created.
Under Category, select either one:
- Real Time
-
The alert is raised immediately when the event occurs.
- Rolling Window
-
The alert is raised if the number of events specified in the Number of Occurences field is met within the Time Window configured.
Click Add and select the event that triggers this alert.
If there are multiple events, click Add and select the next event. Choose the appropriate Multiple Events Operator. See the Events List for a list and brief description of all events.
Note:Ensure that at least one event is added to save an event-based alert.
Select Autoscale Alert to enable this alert for autoscaling.
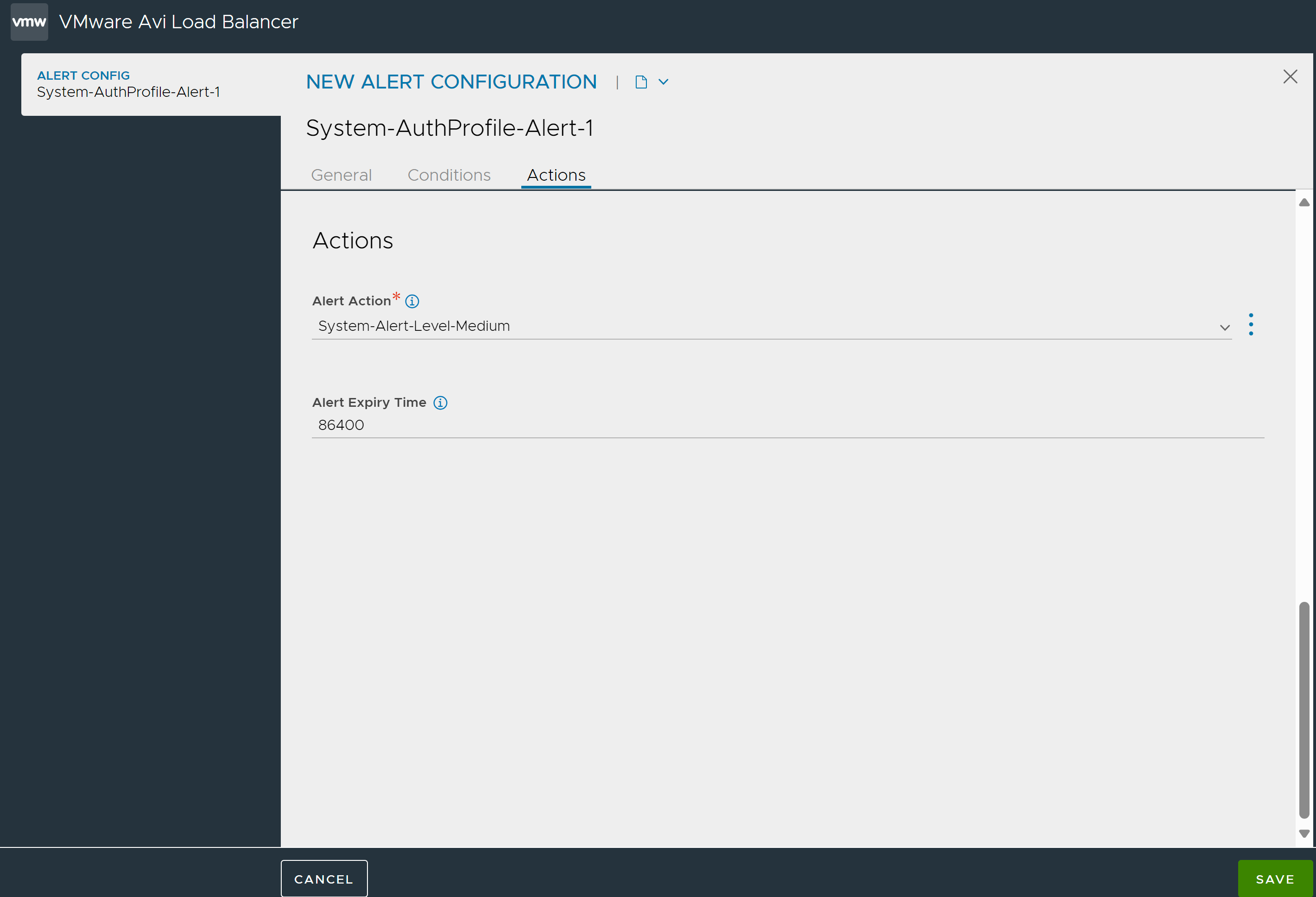
6. Under Actions, configure the following options:
- Alert Action
-
Select the alert action to define the type of notifications to be generated or any other tasks as a result of the triggered alert.
- Alert Expiry Time
-
The triggered alert will be visible in the web interface for this duration of time, after which it is deemed expired and deleted.
7. Click Save.
Notifications
Alerts can be sent to four notification destinations. The first is the local UI. These notifications show up as colored bell icons in the Controller UI to indicate that an alert has occurred. The other three notifications namely, email, syslog, and SNMP v2c traps can be configured in the page.
Notifications can be classified into Local notifications, SNMP TRAP, Syslog and Email.
For more information on notification types, see Types of Notifications.
ControlScript
ControlScripts are Python-based scripts, executed from the Controller. They can be used to alter the Avi Load Balancer configuration or communicate to remote systems (such as Email, Syslog, and/or SNMP servers).
For example, if it is detected that an IP address is sending a SYN flood attack, the alert action can notify administrators by email and also invoke a ControlScript that adds the offending client to a blocklist IP group, attached to a network security policy, for rate shaping or blocking attackers.