Avi Load Balancer can be deployed in front of Unified Access Gateways (UAG), connection servers, app volume managers and, so on, as required. This section explains the recommended way to configure Avi Load Balancer for load balancing traffic to UAG servers in VMware Horizon deployments.It also covers the steps to load balance connection servers and app Volume managers.
Sample Topology
Consider the request flow with the sample topology:
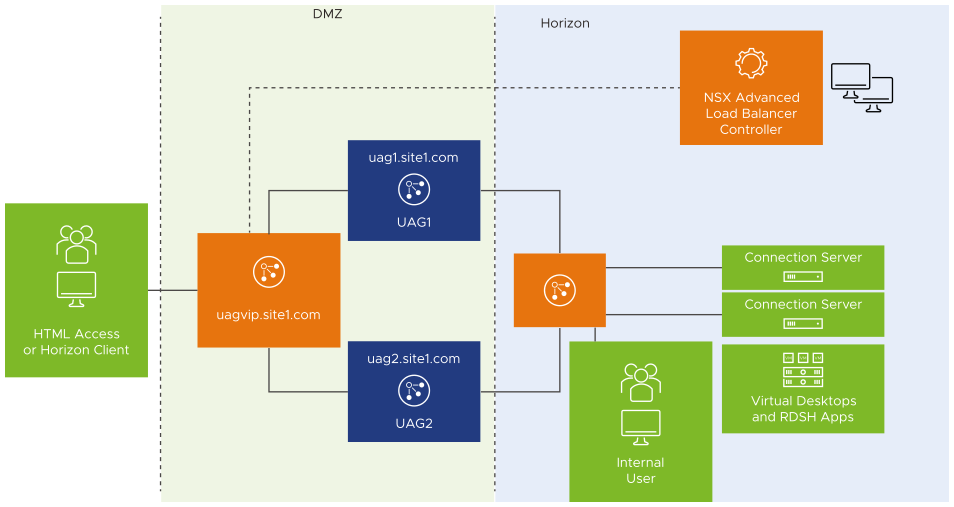
The sample topology illustrates UAG deployment in a DMZ network. However, the Avi Load Balancer supports deployment in both DMZ and non-DMZ networks.
FQDN |
Entity Description |
Entity Description |
Real IP |
|---|---|---|---|
uagvip.site1.com |
FQDN of Avi Load Balancer LB VIP |
VIP 1 |
10.10.5.200 |
uag1.site1.com |
FQDN of UAG server 1 on site 1 |
VIP 1 |
10.58.17.163 |
uag2.site1.com |
FQDN of uag server 2 on site 1 |
VIP 1 |
10.58.17.164 |
The IP and FQDN used in the example are for illustration purposes only. Replace this with your real environment details.
Request Flow
The request flow for this deployment is as shown below:
User sends a request to access uagvip.site1.com over the internet.
The request comes to the Avi Load Balancer.
The Avi Load Balancer does the load balancing and sends the request to one of the backend UAG servers. In this case, let’s assume that Avi Load Balancer sent the request to UAG server 1 that is, uag1.site1.com
UAG sends 307 redirect to client with uag1.site1.com FQDN. UAG servers must be configured with the 307 feature as explained in Unified Access Gateway Support for HTTP Host Redirect. A sample UAG configuration is explained in Important Configurations to Check on UAG for this Solution.
Client looks for location header and queries the host in the location header (uag1.site1.com).
Using the DNS entries that were created (shown in the table above), the FQDN (uag1.site1.com) will be resolved to Avi Load Balancer VIP IP.
From the 307 redirect, all further flows will have the host header set.
Client starts authentication with new UAG FQDN (uag1.site1.com).
When the request comes to the Avi Load Balancer, the Avi Load Balancer virtual service parses the host header and forwards to UAG based on the host header (uag1.site1.com) using the HTTP policies.
UAG1.site1.com performs authentication, verifies entitlements and returns the secondary protocol information which includes the external URL’s for the protocols, along with their configured custom ports.
When the client launches the application, the L4 virtual service uses a DataScript to send the request to correct UAG server based on the incoming destination port that is, custom ports.
Configurations for Load Balancing
The steps to configure the load balance UAG are as below:
To add HTTP Request Policies, Click the Policies tab in the above created virtual service.
Click HTTP Request tab
Click the + plus icon to add the HTTP Request rules.
Save the configuration.
Note:As mentioned in the request flow, the Avi Load Balancer L7 virtual service looks for host header in the incoming requests from client. Based on the host header, request is sent to one of the UAG servers.
In the http policies shown above, the rules are created to look for the Host header and then route the request to one of the backend UAG servers based on the Host header.
For example, if the host header is uag1.site1.com, send the request to UAG1 server. If host header is uag2.site1.com, send the request to UAG2 server
-
Note:
The custom ports here, that is, 4001 and 4002 are used for Blast and 5001 and 5002 are used for PCoIP. These are configured on UAG. Note that there is no restriction to use only these port numbers. You can use any non standard port numbers here, but you need to ensure that configuration of these port numbers are same on UAG and on Avi Load Balancer.
A sample configuration is explained in Important Configurations to Check on UAG for this Solution.
-
Note:
This DataScript is to ensure that requests coming on specific ports are routed to the appropriate UAG server. The ports (4001/4002/5001/5002) are used to establish persistence logic using this DataScript. It is ensured that Avi Load Balancer translate the port to the standard blast/PCoIP ports that is, 8443/4172 while sending the requests to one of the UAG servers. This is important because UAG servers listen on ports 8443 and 4172 for Blast and PCoIP respectively. UAG servers do not understand the custom ports -4001/4002/5001/5002.
If there more UAG servers, ensure all the server IP:port pairs are added to the L4 pool before creating the DataScript.
Important Configurations to Check on UAG for this Solution
Blast URL must point to the UAG hostname/FQDN with the correct port numbers as shown below, for example:
Site 1 – UAG1 - https://<UAG1 FQDN>:4001/?UDPPort=4001
Site 1 – UAG2 - https://<UAG2 FQDN>:4002/?UDPPort=4002
Similarly, PCoIP must point to Avi Load Balancer VIP with correct port numbers.
Site 1 – UAG1 - https://<Avi Load Balancer VIP IP on site 1>:5001/
Site 1 – UAG2 - https://<Avi Load Balancer VIP IP on site 1>:5002/
Host Redirect mapping must be configured on all UAGs.
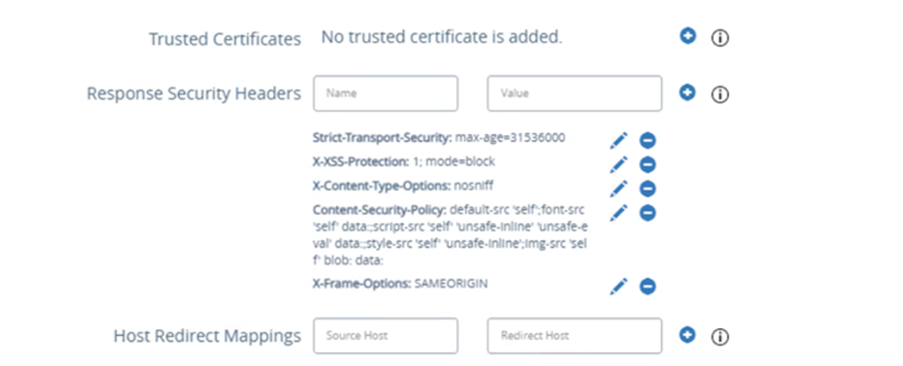
The source host is the LB FQDN. For example, uagvip.site1.com
The redirect host is the UAG’s FQDN. For example, uag1.site1.com
Upload the Avi Load Balancer VS certificate on all the UAG servers
Other Considerations
All the host names or FQDNs have to be added in SAML IDP.
Install the same certificate and key pair on Avi Load Balancer and bind it to the UAG L7 VS.
In some cases, when accessing the VMware Horizon Client, multiple icons for the same site can be displayed as shown below:
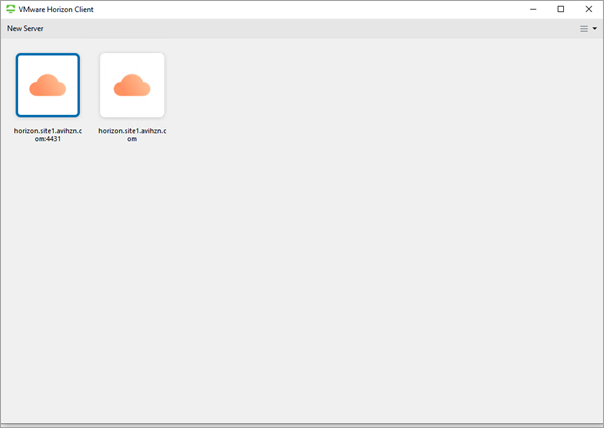
This issue will be resolved in the upcoming releases for Horizon Client.
Enabling WAF for UAG Traffic
For more information, see Enabling WAF For UAG Traffic.
Load Balancing Connection Server
Both L4 and L7 virtual services are supported to load balance traffic to connection servers. However, it is recommended to use L7 virtual services.
To know how to use L7 virtual service to load balance traffic to connection servers, see Load Balancing Traffic to Connection Servers.