After you download the macOS Agent installer, verify the package integrity. As an additional security measure, you can verify the digital signature of the internal binaries.
- To verify package integrity: use steps 1 and 2.
- To verify the digital signatures of the internal binaries, do one or both of the following:
- using the
codesigncommand: use steps 3 and 4. - using the
spctlcommand: use steps 3 and 5.
- using the
Procedure
- Execute the following command to verify the integrity of the macOS Agent Installer package:
%pkgutil –check-signature ./${Mac_Package}The result of the command should be similar to the following text:
Package "./${Mac_Package}": Status: signed by a developer certificate issued by Apple for distribution Signed with a trusted timestamp on: 2021-10-04 10:35:48 +0000 Certificate Chain: 1. Developer ID Installer: Carbon Black, Inc. (7AGZNQ2S2T) Expires: 2023-01-09 18:06:36 +0000 SHA256 Fingerprint: 17 A6 E5 4F 0B 7F CE E1 14 7C E8 36 81 DA 31 5D 86 12 4D 93 46 3B 2B 33 33 58 C3 C3 A9 A3 A8 12 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 2. Developer ID Certification Authority Expires: 2027-02-01 22:12:15 +0000 SHA256 Fingerprint: 7A FC 9D 01 A6 2F 03 A2 DE 96 37 93 6D 4A FE 68 09 0D 2D E1 8D 03 F2 9C 88 CF B0 B1 BA 63 58 7F ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 3. Apple Root CA Expires: 2035-02-09 21:40:36 +0000 SHA256 Fingerprint: B0 B1 73 0E CB C7 FF 45 05 14 2C 49 F1 29 5E 6E DA 6B CA ED 7E 2C 68 C5 BE 91 B5 A1 10 01 F0 24 - Verify that the Certificate Chain Developer ID Installer is: Carbon Black, Inc.(7AGZNQ2S2T).
 Warning: If the Certificate Chain Developer ID Installer value is not a match, do not proceed and contact Carbon Black Support.
Warning: If the Certificate Chain Developer ID Installer value is not a match, do not proceed and contact Carbon Black Support. - To verify the digital signatures of the internal binaries, you must first extract the main packages and internal packages.
Binaries in the macOS Agent Installer package:
- appc-es-loader.app
- b9cli
- b9daemon
- b9kernel.kext
- b9notifier.app
- libcrypto.dylib
- libssl.dylib
Use the following set of commands to extract each of the main and internal packages:
pkgutil --expand Bit9Agent.pkg pkg_tmp cd pkg_tmp cd b9kernel.pkg tar xvf Payload cd .. cd bit9.pkg tar xvf Payload - To use the
codesigncommand to verify the digital signature of the binaries:%codesign -vvvv -R="notarized" --check-notarization ./${Mac_Binary}The result of the command should be:
host-a01:$ codesign -vvvv -R="notarized" --check-notarization ./${Mac_Binary} ./${Mac_Binary} : valid on disk ./${Mac_Binary} : satisfies its Designated Requirement ./${Mac_Binary} : explicit requirement satisfiedA file without signing and notarization does not run on macOS. In this case, the following output displays:
% codesign -vvvv -R="notarized" --check-notarization ./${Mac_Binary} ./${Mac_Binary} code object is not signed at all In architecture: x86_64The following image shows verification of all binaries in the Bit9Agent package using the
codesigncommand:
- To use the
spctlcommand to verify the digital signatures of the binaries, use the following command:% spctl -a -t exec -vvv ./${Mac_Binary}The result of the command should be:
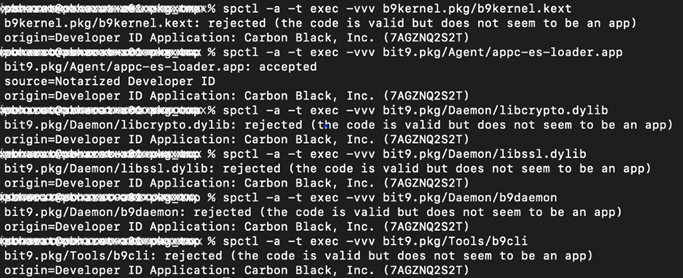
./${Mac_Binary}: accepted source=Notarized Developer ID origin=Developer ID Application: Carbon Black, Inc. (7AGZNQ2S2T)If the binary does not belong to any .app package, the output shows:rejected (the code is valid but does not seem to be an app)% spctl -a -t exec -vvv ./${Mac_Binary} ./${Mac_Binary} : rejected (the code is valid but does not seem to be an app) origin=Developer ID Application: Carbon Black, Inc. (7AGZNQ2S2T)As shown in the following image, rejected output is shown for all binaries except .app files. In this case, the file is valid — rejection is because file is not an app. Instead of looking at rejected, you can verify that the Developer ID Application equals: Carbon Black, Inc. (7AGZNQ2S2T).
The following image shows verification of all the binaries in the Bit9Agent package using the
spctlcommand.