When Credential Harvesting/Dumping is observed, analysts must determine which users were logged in at the time and might have had their credentials compromised.
The Splunk SIEM app includes a Run Live Query Alert Action.
The first search runs as an Alert in Splunk SIEM on a regular basis, perhaps every 5 – 10 minutes, and identifies any possible instances of credential theft. It also defines the Live Query SQL to run.
eventtype="vmware_cbc_cb_analytics" threat_indicators{}.ttps{} = "MITRE_T1003_OS_CREDENTIAL_DUMP"
| eval query_logged_in_users = "SELECT * FROM logged_in_users;"
| dedup device_id
Each result triggers the VMware CBC Run Livequery Alert Action using the following parameters:
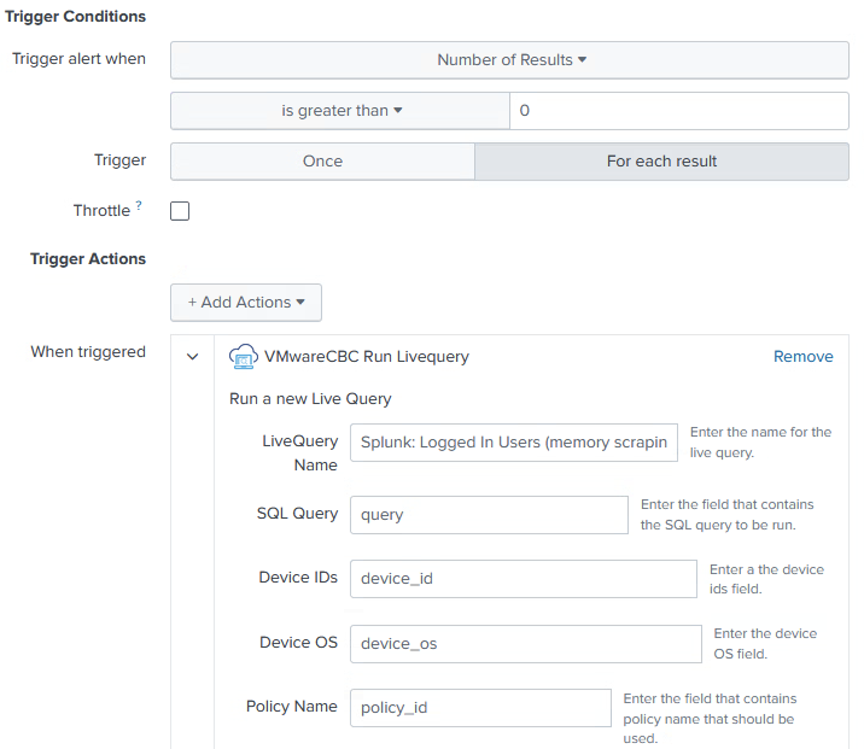
When Carbon Black Cloud detects credential scraping, Splunk SIEM will automatically figure out who was logged in to the impacted endpoints, and bring in those results through the App's built-in Live Query input. You can then run a Splunk query to combine the original alerts with the logged in user information.
eventtype="vmware_cbc_cb_analytics" threat_indicators{}.ttps{} = "MITRE_T1003_OS_CREDENTIAL_DUMP"
| dedup id
| reltime
| join device_id type=outer [
search eventtype="vmware_cbc_base_index" sourcetype="vmware:cbc:livequery:result" query_name="Splunk: Logged In Users (memory scraping)" status=matched
| rename device.* as device_*, fields.* as *
| eval _time = time
| reltime
| strcat "User=" user ", type=" tty ", SID=" sid ", " reltime login_string
| stats values(login_string) as logins by device_id
]
| table device_id, device_name, reltime, sensor_action, threat_cause_actor_name, reason, logins
