Determine the number, networking, and high-availability configuration of the Tier-0 and Tier-1 gateways in NSX-T Data Center for a VI workload domain of VMware Cloud Foundation. Identify the BGP configuration for a single availability zone and two availability zones in the environment.
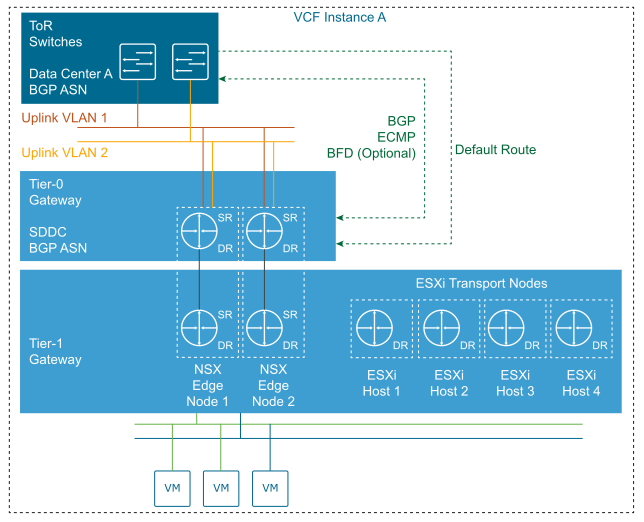
North-South Routing
Routing can be defined in the following directions:
North-south traffic is traffic leaving or entering the NSX domain, for example, a virtual machine on an overlay network communicating with an end-user device on the corporate network.
East-west traffic is traffic that remains in the NSX domain, for example, two virtual machines on the same or different segments communicating with each other.
As traffic flows north-south, edge nodes can be configured to pass traffic in an active-standby or an active-active model, where active-active can scale up to 8 active nodes. Service routers (SRs) for north-south routing in NSX-T Data Center are configured an active-active equal-cost multi-path (ECMP) mode that supports route failover of Tier-0 gateways in seconds.
Design Component |
Active-Active |
Active-Standby |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
Bandwidth per node |
0 |
0 |
Bandwidth per node is the same because it is independent of the Tier- 0 gateway failover model. |
Total aggregate bandwidth |
↑↑↑↑ |
0 |
|
Availability |
↑ |
0 |
With up to 8 active-active NSX Edge nodes, availability can be as high as N+7, while for the active-standby mode it is N+1. |
Failover Time |
0 |
0 |
Both are capable of sub-second failover with use of BFD, only when using the bare-metal edge form factor. |
Routing Protocol Support |
↓ |
0 |
The active-active mode requires BGP for ECMP failover. |
Decision ID |
Design Decision |
Design Justification |
Design Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-001 |
Deploy an active-active Tier-0 gateway. |
Supports ECMP north-south routing on all Edge nodes in the NSX Edge cluster. |
Active-active Tier-0 gateways cannot provide stateful services such as NAT. |
Decision ID |
Design Decision |
Design Justification |
Design Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-002 |
To enable ECMP between the Tier-0 gateway and the Layer 3 devices (ToR switches or upstream devices), create two VLANs. The ToR switches or upstream Layer 3 devices have an SVI on one of the two VLANs and each NSX Edge node in the cluster has an interface on each VLAN. |
Supports multiple equal-cost routes on the Tier-0 gateway and provides more resiliency and better bandwidth use in the network. |
Additional VLANs are required. |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-003 |
Assign a named teaming policy to the VLAN segments to the Layer 3 device pair. |
Pins the VLAN traffic on each segment to its target Edge node interface. From there the traffic is directed to the host physical NIC that is connected to the target top of rack switch. |
None. |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-004 |
Create a VLAN transport zone for edge uplink traffic. |
Enables the configuration of VLAN segments on the N-VDS in the edge nodes. |
Additional VLAN transport zones are required if the edge nodes are not connected to the same top of rack switch pair. |
Decision ID |
Design Decision |
Design Justification |
Design Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-005 |
Use BGP as the dynamic routing protocol. |
|
In environments where BGP cannot be used, you must configure and manage static routes. |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-006 |
Configure the BGP Keep Alive Timer to 4 and Hold Down Timer to 12 between the top of rack switches and the Tier-0 gateway. These timers must be aligned with the data center fabric design of your organization. |
Provides a balance between failure detection between the top of rack switches and the Tier-0 gateway and overburdening the top of rack switches with keep-alive traffic. |
By using longer timers to detect if a router is not responding, the data about such a router remains in the routing table longer. As a result, the active router continues to send traffic to a router that is down. |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-007 |
Do not enable Graceful Restart between BGP neighbors. |
Avoids loss of traffic. On the Tier-0 gateway, BGP peers from all the gateways are always active. On a failover, the Graceful Restart capability increases the time a remote neighbor takes to select an alternate Tier-0 gateway. As a result, BFD-based convergence is delayed. |
None. |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-008 |
Enable helper mode for Graceful Restart mode between BGP neighbors. |
Avoids loss of traffic. During a router restart, helper mode works with the graceful restart capability of upstream routers to maintain the forwarding table which in turn will forward packets to a down neighbor even after the BGP timers have expired causing loss of traffic. |
None. |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-009 |
Enable Inter-SR iBGP routing. |
In the event that an edge node has all of its northbound eBGP sessions down, north-south traffic will continue to flow by routing traffic to a different edge node. |
None. |
This design assumes that physical network does not support Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD). To provide faster convergence, enable BFD if the network supports and is configured for BFD.
Intra-SDN Routing
Gateways are needed to provide routing between logical segments created in the SDN of NSX-T Data Center. Logical segments can be connected directly to a Tier-0 or Tier-1 gateway.
Decision ID |
Design Decision |
Design Implication |
Design Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-010 |
Deploy a Tier-1 gateway and connect it to the Tier-0 gateway. |
Creates a two-tier routing architecture. Abstracts the NSX logical components which interact with the physical data center from the logical components which provide SDN services. |
A Tier-1 gateway can only be connected to a single Tier-0 gateway. In cases where multiple Tier-0 gateways are required, you must create multiple Tier-1 gateways. |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-011 |
Deploy a Tier-1 gateway to the NSX-T Edge cluster. |
Enables stateful services, such as load balancers and NAT, for SDDC management components. Because a Tier-1 gateway always works in active-standby mode, the gateway supports stateful services. |
None. |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-012 |
Deploy a Tier-1 gateway in non-preemptive failover mode. |
Ensures that after a failed NSX-T Edge transport node is back online, it does not take over the gateway services thus causing a short service outage. |
None. |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-013 |
Enable standby relocation of the Tier-1 gateway. |
Ensures that if an edge failure occurs, a standby Tier-1 gateway is created on another edge node. |
None. |
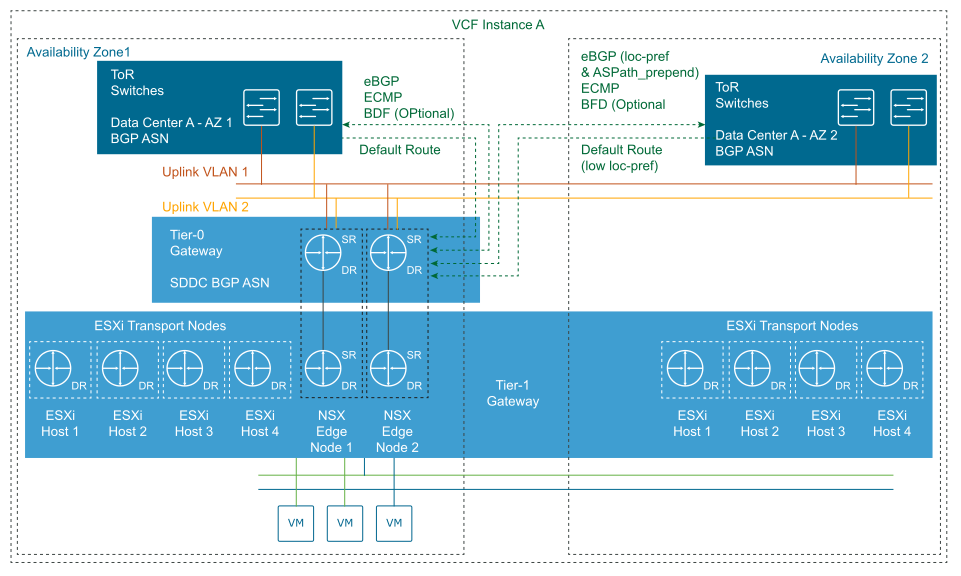
Dynamic Routing for Multiple Availability Zones
Decision ID |
Design Decision |
Design Implication |
Design Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-014 |
Extend the uplink VLANs to the top of rack switches so that the VLANs are stretched between both availability zones. |
Because the NSX Edge nodes will fail over between the availability zones, ensures uplink connectivity to the top of rack switches in both availability zones regardless of the zone the NSX Edge nodes are presently in. |
You must configure a stretched Layer 2 network between the availability zones by using physical network infrastructure. |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-015 |
Provide this SVI configuration on the top of the rack switches or upstream Layer 3 devices.
|
Enables the communication of the NSX Edge nodes to the top of rack switches in both availability zones over the same uplink VLANs. |
You must configure a stretched Layer 2 network between the availability zones by using the physical network infrastructure. |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-016 |
Provide this VLAN configuration.
|
Supports multiple equal-cost routes on the Tier-0 gateway, and provides more resiliency and better bandwidth use in the network. |
Extra VLANs are required. Requires stretching uplink VLANs between Availability zones |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-017 |
Create an IP prefix list that permits access to route advertisement by |
Used in a route map to prepend a path to one or more autonomous system (AS-path prepend) for BGP neighbors in Availability Zone 2. |
You must manually create an IP prefix list that is identical to the default one. |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-018 |
Create a route map-out that contains the custom IP prefix list and an AS-path prepend value set to the Tier-0 local AS added twice. |
|
You must manually create the route map. The two NSX Edge nodes will route north-south traffic through the second availability zone only if the connection to their BGP neighbors in the first availability zone is lost, for example, if a failure of the top of the rack switch pair or in the availability zone occurs. |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-019 |
Create an IP prefix list that permits access to route advertisement by network |
Used in a route map to configure local-reference on learned default-route for BGP neighbors in the second availability zone. |
You must manually create an IP prefix list that is identical to the default one. |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-020 |
Apply a route map-in that contains the IP prefix list for the default route |
|
You must manually create the route map. The two NSX Edge nodes will route north-south traffic through the second availability zone only if the connection to their BGP neighbors in the first availability zone is lost, for example, if a failure of the top of the rack switch pair or in the availability zone occurs. |
VCF-WLD-NSX-SDN-021 |
Configure the neighbors of the second availability zone to use the route maps as In and Out filters respectively. |
Makes the path in and out of the second availability zone less preferred because the AS path is longer. As a result, all traffic passes through the first zone. |
The two NSX Edge nodes will route north-south traffic through the second availability zone only if the connection to their BGP neighbors in the first availability zone is lost, for example, if a failure of the top of the rack switch pair or in the availability zone occurs. |