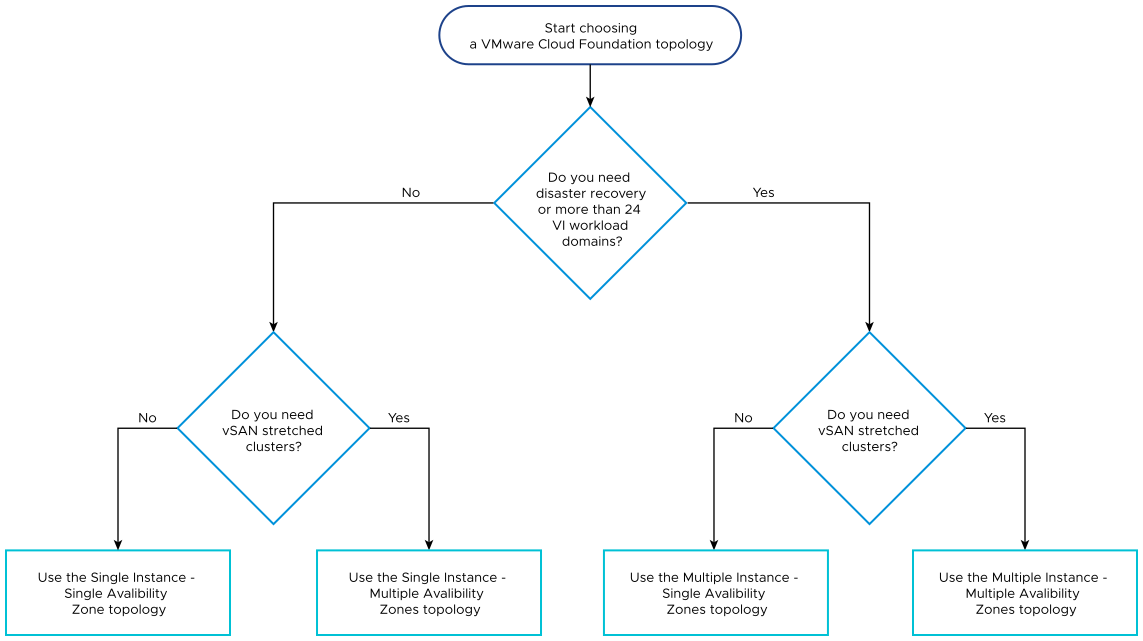
VMware Cloud Foundation supports multiple topologies that provide different levels of availability and scale.
Availability Zones and VMware Cloud Foundation Instances
- Availability zone
-
An availability zone is a fault domain at the SDDC level.
You create multiple availability zones for the purpose of creating vSAN stretched clusters. Using multiple availability zones can improve availability of management components and workloads running within the SDDC, minimize downtime of services, and improve SLAs.
Availability zones are typically located either within the same data center, but in different racks, chassis, rooms, or in different data centers with low-latency high-speed links connecting them. One availability zone can contain several fault domains.
Note:Only stretched clusters created by using the Stretch Cluster API, and are therefore vSAN storage based, are considered by and treated as stretched clusters by VMware Cloud Foundation.
- VMware Cloud Foundation Instance
-
Each VMware Cloud Foundation instance is a separate VMware Cloud Foundation deployment and might contain one or two availability zones. VMware Cloud Foundation instances may be geographically separate.
VMware Cloud Foundation Topologies
Several topologies of VMware Cloud Foundation exist according to the number of availability zones and VMware Cloud Foundation instances.
| Topology |
Description |
|---|---|
| Single Instance - Single Availability Zone |
Workload domains are deployed in a single availability zone. |
| Single Instance - Multiple Availability Zones |
Workload domains might be stretched between two availability zones. |
| Multiple Instances - Single Availability Zone per VMware Cloud Foundation instance |
Workload domains in each instance are deployed in a single availability zone. |
| Multiple Instances - Multiple Availability Zones per VMware Cloud Foundation instance |
Workload domains in each instance might be stretched between two availability zones. |
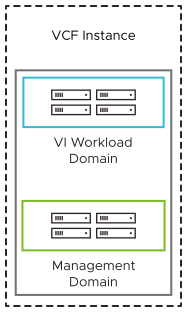
Single Instance - Single Availability Zone
Single Instance - Single Availability Zone is the simplest VMware Cloud Foundation topology where workload domains are deployed in a single availability zone.
The Single Instance - Single Availability Zone topology relies on vSphere HA to protect against host failures.
| Attributes |
Detail |
|---|---|
| Data centers |
Single data center |
| Workload domain rack mappings |
|
| Scale |
|
| Resilience |
vSphere HA provides protection against host failures |
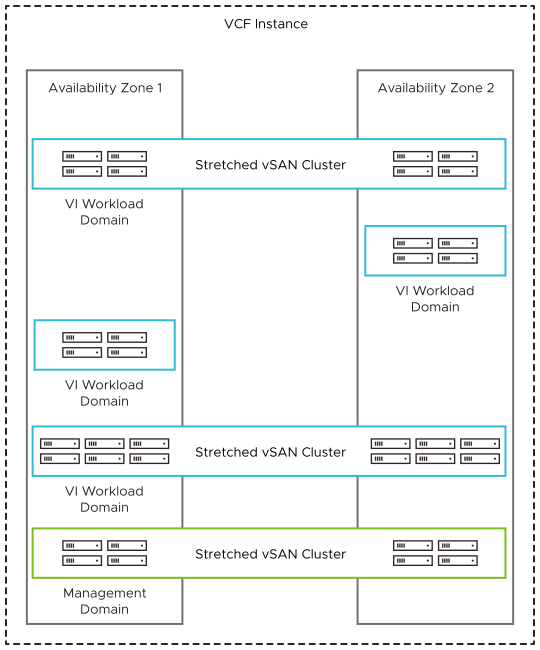
Single Instance - Multiple Availability Zones
You protect your VMware Cloud Foundation environment against a failure of a single hardware fault domain by implementing multiple availability zones.
Incorporating multiple availability zones in your design can help reduce the blast radius of a failure and can increase application availability. You usually deploy multiple availability zones across two independent data centers.
| Attributes |
Detail |
|---|---|
| Workload domain rack mappings |
|
| Stretched cluster |
|
| Scale |
|
| Resilience |
|
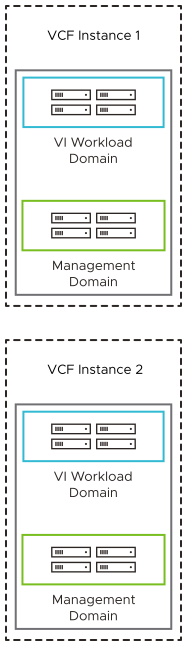
Multiple Instances - Single Availability Zone per Instance
You protect against a failure of a single VMware Cloud Foundation instance by implementing multiple VMware Cloud Foundation instances.
Incorporating multiple VMware Cloud Foundation instances in your design can help reduce the blast radius of a failure and can increase application availability across larger geographical distances than cannot be achieved by using multiple availability zones. You usually deploy this topology in the same data center for scale or across independent data centers for resilience.
| Attributes |
Detail |
|---|---|
| Workload domain rack mapping |
|
| Multiple instances |
Using multiple VMware Cloud Foundation instances can facilitate the following use cases:
If you plan to use NSX Federation between instances, VMware Cloud Foundation supports a maximum of two connected instances with a maximum round-trip latency between them of 150 ms. |
| Scale |
|
| Resilience |
|
Multiple Instances - Multiple Availability Zones per Instance
You protect against a failure of a single VMware Cloud Foundation instance by implementing multiple VMware Cloud Foundation instances. Implementing multiple availability zones in an instance protects against a failure of a single hardware fault domain.
Incorporating multiple VMware Cloud Foundation instances into your design can help reduce the blast radius of a failure and can increase application availability across larger geographical distances that cannot be achieved using multiple availability zones.
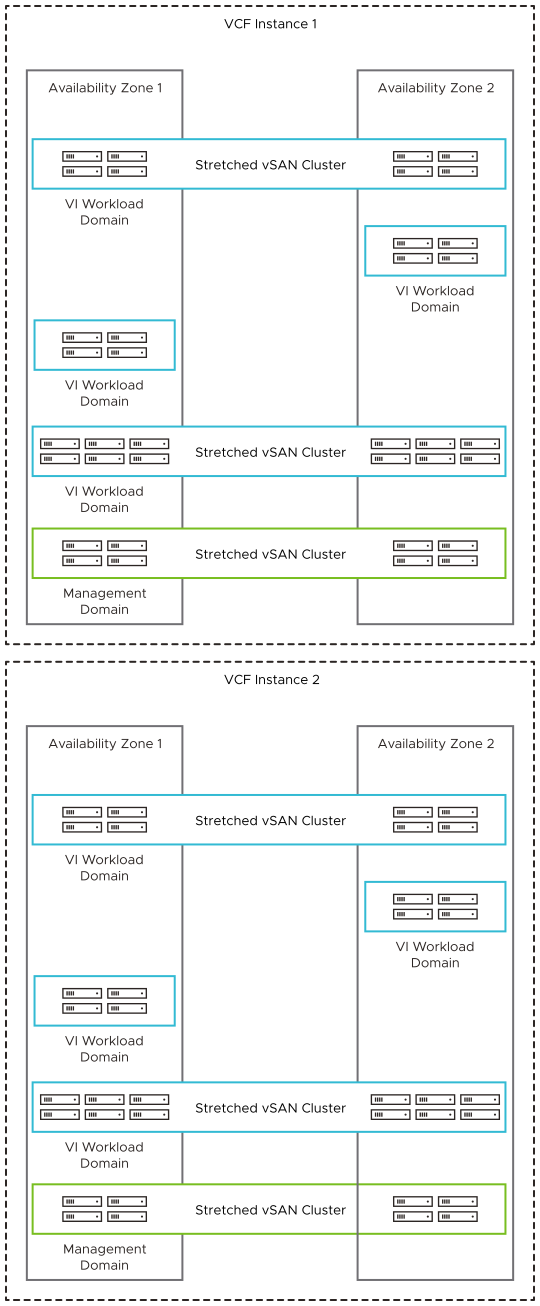
| Attributes |
Detail |
|---|---|
| Workload domain rack mapping |
|
| Multiple instances |
Using multiple VMware Cloud Foundation instances can facilitate the following:
If you plan to use NSX Federation between instances, VMware Cloud Foundation supports a maximum of two connected instances with a maximum round-trip latency between them of 150 ms. |
| Stretched cluster |
|
| Scale |
|
| Resilience |
|