Following the principles of this design and of each product, you deploy, configure, and connect the NSX Edge nodes to support networks in the NSX instances in your VMware Cloud Foundation deployment.
Deployment Model for the NSX Edge Nodes for VMware Cloud Foundation
For NSX Edge nodes, you determine the form factor, number of nodes and placement according to the requirements for network services in a VMware Cloud Foundation workload domain.
An NSX Edge node is an appliance that provides centralized networking services which cannot be distributed to hypervisors, such as load balancing, NAT, VPN, and physical network uplinks. Some services, such as Tier-0 gateways, are limited to a single instance per NSX Edge node. However, most services can coexist in these nodes.
NSX Edge nodes are grouped in one or more edge clusters, representing a pool of capacity for NSX services.
An NSX Edge node can be deployed as a virtual appliance, or installed on bare-metal hardware. The edge node on bare-metal hardware can have better performance capabilities at the expense of more difficult deployment and limited deployment topology use cases. For details on the trade-offs of using virtual or bare-metal NSX Edges, see the NSX documentation.
Deployment Model |
Benefits |
Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
NSX Edge virtual appliance deployed by using SDDC Manager |
|
|
NSX Edge virtual appliance deployed by using NSX Manager |
|
|
Bare-metal NSX Edge appliance |
|
|
Sizing Considerations for NSX Edges for VMware Cloud Foundation
When you deploy NSX Edge appliances, you select a size according to the scale of your environment. The option that you select determines the number of CPUs and the amount of memory of the appliance.
For detailed sizing according to the overall profile of the VMware Cloud Foundation instance you plan to deploy, see VMware Cloud Foundation Planning and Preparation Workbook.
| NSX Edge Appliance Size |
Scale |
|---|---|
| Small |
Proof of concept |
| Medium |
Suitable when only Layer 2 through Layer 4 features such as NAT, routing, Layer 4 firewall, Layer 4 load balancer are required and the total throughput requirement is less than 2 Gbps. |
| Large |
Suitable when only Layer 2 through Layer 4 features such as NAT, routing, Layer 4 firewall, Layer 4 load balancer are required and the total throughput is 2 ~ 10 Gbps. It is also suitable when Layer 7 load balancer, for example, SSL offload is required. |
| Extra Large |
Suitable when the total throughput required is multiple Gbps for Layer 7 load balancer and VPN. |
Network Design for the NSX Edge Nodes for VMware Cloud Foundation
In each VMware Cloud Foundation instance, you implement an NSX Edge configuration with a single N-VDS. You connect the uplink network interfaces of the edge appliance to VLAN trunk port groups that are connected to particular physical NICs on the host.
NSX Edge Network Configuration
The NSX Edge node contains a virtual switch, called an N-VDS, that is managed by NSX. This internal N-VDS is used to define traffic flow through the interfaces of the edge node. An N-VDS can be connected to one or more interfaces. Interfaces cannot be shared between N-VDS instances.
If you plan to deploy multiple VMware Cloud Foundation instances, apply the same network design to the NSX Edge cluster in the second and other additional VMware Cloud Foundation instances.
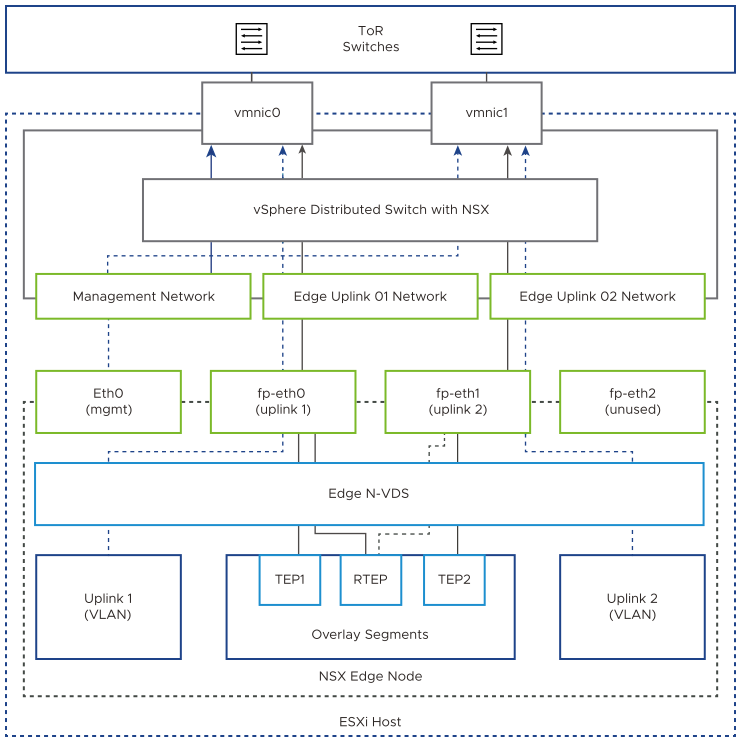
Uplink Policy Design for the NSX Edge Nodes for VMware Cloud Foundation
A transport node can participate in an overlay and VLAN network. Uplink profiles define policies for the links from the NSX Edge transport nodes to top of rack switches. Uplink profiles are containers for the properties or capabilities for the network adapters. Uplink profiles are applied to the N-VDS of the edge node.
Uplink profiles can use either load balance source or failover order teaming. If using load balance source, multiple uplinks can be active. If using failover order, only a single uplink can be active.
Teaming can be configured by using the default teaming policy or a user-defined named teaming policy. You can use named teaming policies to pin traffic segments to designated edge uplinks.
NSX Edge Node Requirements and Recommendations for VMware Cloud Foundation
Consider the network, N-VDS configuration and uplink policy requirements for using NSX Edge nodes in VMware Cloud Foundation, and the best practices for having NSX Edge nodes operate in an optimal way, such as number and size of the nodes, high availability, and N-VDS architecture, on a standard or stretched cluster.
NSX Edge Design Requirements
You must meet the following design requirements for standard and stretched clusters in your NSX Edge design for VMware Cloud Foundation.
Requirement ID |
Design Requirement |
Justification |
Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
VCF-NSX-EDGE-REQD-CFG-001 |
Connect the management interface of each NSX Edge node to the management VLAN. |
Provides connection from the NSX Manager cluster to the NSX Edge. |
None. |
VCF-NSX-EDGE-REQD-CFG-002 |
|
|
None. |
VCF-NSX-EDGE-REQD-CFG-003 |
Use a dedicated VLAN for edge overlay that is different from the host overlay VLAN. |
A dedicated edge overlay network provides support for edge mobility in support of advanced deployments such as multiple availability zones or multi-rack clusters. |
|
VCF-NSX-EDGE-REQD-CFG-004 |
Create one uplink profile for the edge nodes with three teaming policies.
|
|
None. |
Requirement ID |
Design Requirement |
Justification |
Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
VCF-NSX-EDGE-REQD-CFG-005 |
Allocate a separate VLAN for edge RTEP overlay that is different from the edge overlay VLAN. |
The RTEP network must be on a VLAN that is different from the edge overlay VLAN. This is an NSX requirement that provides support for configuring different MTU size per network. |
You must allocate another VLAN in the data center infrastructure. |
NSX Edge Design Recommendations
In your NSX Edge design for VMware Cloud Foundation, you can apply certain best practices for standard and stretched clusters.
Recommendation ID |
Design Recommendation |
Justification |
Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
VCF-NSX-EDGE-RCMD-CFG-001 |
Use appropriately sized NSX Edge virtual appliances. |
Ensures resource availability and usage efficiency per workload domain. |
You must provide sufficient compute resources to support the chosen appliance size. |
VCF-NSX-EDGE-RCMD-CFG-002 |
Deploy the NSX Edge virtual appliances to the default vSphere cluster of the workload domain, sharing the cluster between the workloads and the edge appliances. |
|
Workloads and NSX Edges share the same compute resources. |
VCF-NSX-EDGE-RCMD-CFG-003 |
Deploy two NSX Edge appliances in an edge cluster in the default vSphere cluster of the workload domain. |
Creates the NSX Edge cluster for satisfying the requirements for availability and scale. |
None. |
VCF-NSX-EDGE-RCMD-CFG-004 |
Apply VM-VM anti-affinity rules for vSphere DRS to the virtual machines of the NSX Edge cluster. |
Keeps the NSX Edge nodes running on different ESXi hosts for high availability. |
None. |
VCF-NSX-EDGE-RCMD-CFG-005 |
In vSphere HA, set the restart priority policy for each NSX Edge appliance to high. |
|
If the restart priority for another management appliance is set to highest, the connectivity delays for management appliances will be longer . |
VCF-NSX-EDGE-RCMD-CFG-006 |
Configure all edge nodes as transport nodes. |
Enables the participation of edge nodes in the overlay network for delivery of services to the SDDC management components such as routing and load balancing. |
None. |
|
VCF-NSX-EDGE-RCMD-CFG-007
|
Create an NSX Edge cluster with the default Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) configuration between the NSX Edge nodes in the cluster. |
|
None. |
VCF-NSX-EDGE-RCMD-CFG-008 |
Use a single N-VDS in the NSX Edge nodes. |
|
None. |
Recommendation ID |
Design Recommendation |
Justification |
Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
VCF-NSX-EDGE-RCMD-CFG-009 |
Add the NSX Edge appliances to the virtual machine group for the first availability zone. |
Ensures that, by default, the NSX Edge appliances are powered on upon a host in the primary availability zone. |
None. |