VMware Cloud Foundation consists of workload domains which represent application-ready infrastructure units including ESXi hosts, vCenter Server, storage (vSAN, NFS, VMFS on FC, or vVols), and NSX. According to the business requirements and resource availability, you can run the management components and customer workloads in separate workload domains following the standard architecture or in a shared workload domain following the consolidated architecture.
For information on designing a VMware Cloud Foundation environment including VMware Cloud Foundation requirements and industry recommendations, see the VMware Cloud Foundation Design documentation.
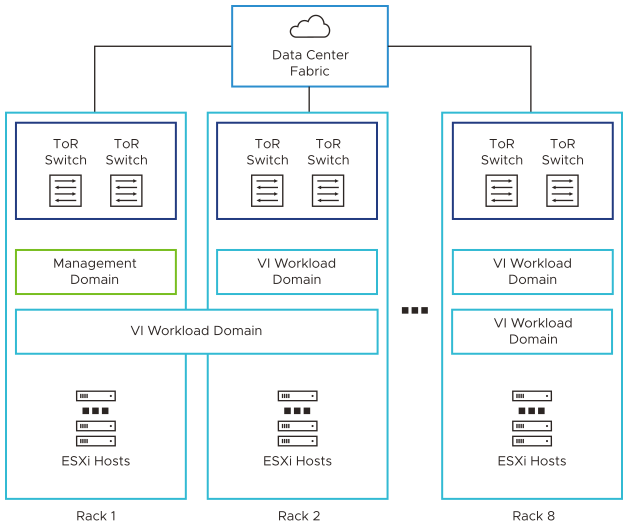
Workload Domains in VMware Cloud Foundation
VMware Cloud Foundation consists of workload domains which represent an application-ready infrastructure. A workload domain represents a logical unit that groups ESXi hosts managed by a vCenter Server instance with specific characteristics according to VMware best practices.
A workload domain can consist of one or more vSphere clusters, provisioned automatically by SDDC Manager. Each workload domain contains the following components:
ESXi hosts
One VMware vCenter Server™ instance
At least one vSphere cluster with vSphere HA and vSphere DRS enabled.
One vSphere Distributed Switch per cluster for system traffic and NSX segments for workloads.
One NSX Manager cluster for configuring and implementing software-defined networking.
One NSX Edge cluster, added after you create the workload domain, that connects the workloads in the workload domain for logical switching, logical dynamic routing, and load balancing.
One or more shared storage allocations.
VMware Cloud Foundation supports two types of workload domains - the management domain and virtual infrastructure (VI) workload domains.
Management Domain
The management domain is created during the bring-up process by VMware Cloud Builder and contains the VMware Cloud Foundation management components as follows:
Minimum four ESXi hosts
An instance of vCenter Server
A three-node NSX Manager cluster
SDDC Manager
-
vSAN datastore
One or more vSphere clusters each of which can scale up to the vSphere maximum of 64
VI Workload Domains
You create VI workload domains to run customer workloads. For each VI workload domain, you can choose the storage option - vSAN, NFS, vVols, or VMFS on FC.
A VI workload domain consists of one or more vSphere clusters. Each cluster starts with a minimum of three hosts and can scale up to the vSphere maximum of 64 hosts. SDDC Manager automates the creation of the VI workload domain and the underlying vSphere clusters.
For the first VI workload domain in your environment, SDDC Manager deploys a vCenter Server instance and a three-node NSX Manager cluster in the management domain. For each subsequent VI workload domain, SDDC Manager deploys an additional vCenter Server instance. New VI workload domains can share the same NSX Manager cluster with an existing VI workload domain or you can deploy a new NSX Manager cluster. VI workload domains cannot use the NSX Manager cluster for the management domain.
VMware Cloud Foundation Architecture Models
VMware Cloud Foundation supports two architecture models - standard and consolidated, according to the requirements of your organization and the resource capabilities of your environment. Implement a standard architecture for workload provisioning and mobility across VMware Cloud Foundation instances according to production best practices. If you plan to deploy a small-scale environment and extend it according to customer adoption, or if you are working on an SDDC proof-of-concept, implement a consolidated architecture.
Standard Architecture Model
With the standard architecture model, management workloads run on a dedicated management domain and customer workloads are deployed in separate virtual infrastructure (VI) workload domains. Each workload domain is managed by a separate vCenter Server instance which provides for scalability and allows for autonomous licensing and life cycle management.
Standard architecture is the recommended model because it aligns with the VMware best practice of separating management workloads from customer workloads. It provides better long term flexibility and expansion options. Workload domains can be on the same rack or can span across racks.
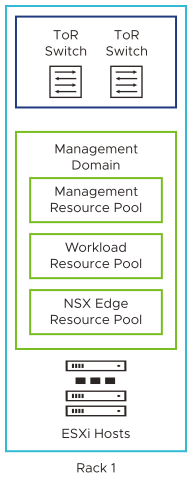
Consolidated Architecture Model
In this model, the management and customer workloads run together on a shared management domain. The environment is managed from a single vCenter Server and vSphere resource pools provide isolation between management and customer workloads. Resource pools must be properly configured as the domain is shared by the management and compute workloads.
As you add additional hosts to a VMware Cloud Foundation system deployed on a consolidated architecture, you can migrate to the standard architecture by creating a VI workload domain and moving the customer workload VMs from the compute resource pool to the newly-created VI workload domain. After moving these VMs, you might need to update shares and reservations on the compute resource pool in the management domain.