vCenter Server design considers the location, size, high availability, and identity domain isolation of the vCenter Server instances for the workload domains in a VMware Cloud Foundation environment.
Logical Design for vCenter Server for VMware Cloud Foundation
Each workload domain has a dedicated vCenter Server that manages the ESXi hosts running NSX Edge nodes and customer workloads. All vCenter Server instances run in the management domain.
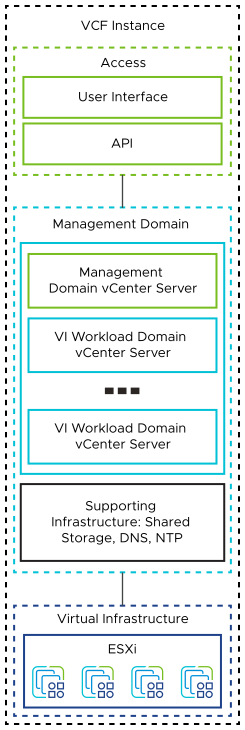
VMware Cloud Foundation Instances with a Single Availability Zone |
VMware Cloud Foundation Instances with Multiple Availability Zones |
|---|---|
|
|
Sizing Considerations for vCenter Server for VMware Cloud Foundation
You select an appropriate vCenter Server appliance size according to the scale of your environment.
When you deploy a workload domain, you select a vCenter Server appliance size that is suitable for the scale of your environment. The option that you select determines the number of CPUs and the amount of memory of the appliance. For detailed sizing according to a collective profile of the VMware Cloud Foundation instance you plan to deploy, refer to the VMware Cloud Foundation Planning and Preparation Workbook .
vCenter Server Appliance Size |
Management Capacity |
|---|---|
Tiny |
Up to 10 hosts or 100 virtual machines |
Small * |
Up to 100 hosts or 1,000 virtual machines |
Medium ** |
Up to 400 hosts or 4,000 virtual machines |
Large |
Up to 800 hosts or 10,000 virtual machines |
X-Large |
Up to 800 hosts or 45,000 virtual machines |
* Default for the management domain vCenter Server
** Default for VI workload domain vCenter Server instances
High Availability Design for vCenter Server for VMware Cloud Foundation
Protecting vCenter Server is important because it is the central point of management and monitoring for each workload domain.
VMware Cloud Foundation supports only vSphere HA as a high availability method for vCenter Server.
High Availability Method |
Supported in VMware Cloud Foundation |
Considerations |
|---|---|---|
vSphere High Availability |
Yes |
- |
vCenter High Availability (vCenter HA) |
No |
|
vSphere Fault Tolerance (vSphere FT) |
No |
|
vCenter Server Design Requirements and Recommendations for VMware Cloud Foundation
Each workload domain in VMware Cloud Foundation is managed by a single vCenter Server instance. You determine the size of this vCenter Server instance and its storage requirements according to the number of ESXi hosts per cluster and the number of virtual machines you plan to run on these clusters.
vCenter Server Design Requirements for VMware Cloud Foundation
| Requirement ID |
Design Requirement |
Justification |
Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| VCF-VCS-REQD-CFG-001 |
Deploy a dedicated vCenter Server appliance for the management domain of the VMware Cloud Foundation instance. |
|
Requires a separate license for the vCenter Server instance in the management domain |
| VCF-VCS-REQD-NET-001 |
Place all workload domain vCenters Server appliances on the VM management network in the management domain. |
|
None. |
vCenter Server Design Recommendations
In your vCenter Server design for VMware Cloud Foundation, you can apply certain best practices for sizing and high availability.
| Recommendation ID |
Design Recommendation |
Justification |
Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| VCF-VCS-RCMD-CFG-001 |
Deploy an appropriately sized vCenter Server appliance for each workload domain. |
Ensures resource availability and usage efficiency per workload domain. |
The default size for a management domain is Small and for VI workload domains is Medium. To override these values, you must use the Cloud Builder API and the SDDC Manager API. |
| VCF-VCS-RCMD-CFG-002 |
Deploy a vCenter Server appliance with the appropriate storage size. |
Ensures resource availability and usage efficiency per workload domain. |
The default size for a management domain is Small and for VI Workload Domains is Medium. To override these values, you must use the API. |
| VCF-VCS-RCMD-CFG-003 |
Protect workload domain vCenter Server appliances by using vSphere HA. |
vSphere HA is the only supported method to protect vCenter Server availability in VMware Cloud Foundation. |
vCenter Server becomes unavailable during a vSphere HA failover. |
| VCF-VCS-RCMD-CFG-004 |
In vSphere HA, set the restart priority policy for the vCenter Server appliance to high. |
vCenter Server is the management and control plane for physical and virtual infrastructure. In a vSphere HA event, to ensure the rest of the SDDC management stack comes up faultlessly, the workload domain vCenter Server must be available first, before the other management components come online. |
If the restart priority for another virtual machine is set to highest, the connectivity delay for the management components will be longer. |
vCenter Server Design Recommendations for Stretched Clusters with VMware Cloud Foundation
The following additional design recommendations apply when using stretched clusters.
| Recommendation ID |
Design Recommendation |
Justification |
Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| VCF-VCS-RCMD-CFG-005 |
Add the vCenter Server appliance to the virtual machine group for the first availability zone. |
Ensures that, by default, the vCenter Server appliance is powered on a host in the first availability zone. |
None. |
vCenter Single Sign-On Design Requirements for VMware Cloud Foundation
vCenter Server instances for the VI workload domains in a VMware Cloud Foundation instance can be either joined to the vCenter Single Sign-On domain of the vCenter Server instance for the management domain or deployed in isolated vCenter Single Sign-On domains.
You select the vCenter Single Sign-On topology according to the needs and design objectives of your deployment.
VMware Cloud Foundation Topology |
vCenter Single Sign-On Domain Topology |
Benefits |
Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
Single vCenter Server Instance - Single vCenter Single Sign-On Domain |
One vCenter Single Sign-On domain with the management domain vCenter Server instance only. |
Enables a small environment where customer workloads run in the same cluster as the management domain components.
|
- |
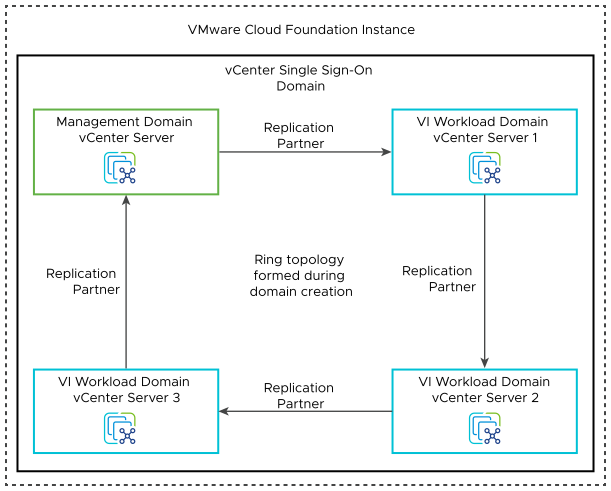
Multiple vCenter Server Instances - Single vCenter Single Sign-On Domain |
One vCenter Single Sign-On domain with the management domain and all VI workload domain vCenter Server instances in enhanced linked mode (ELM) using a ring topology. |
Enables sharing of vCenter Server roles, tags and licenses between all workload domain instances. |
Limited to 15 workload domains per VMware Cloud Foundation instance including the management domain. |
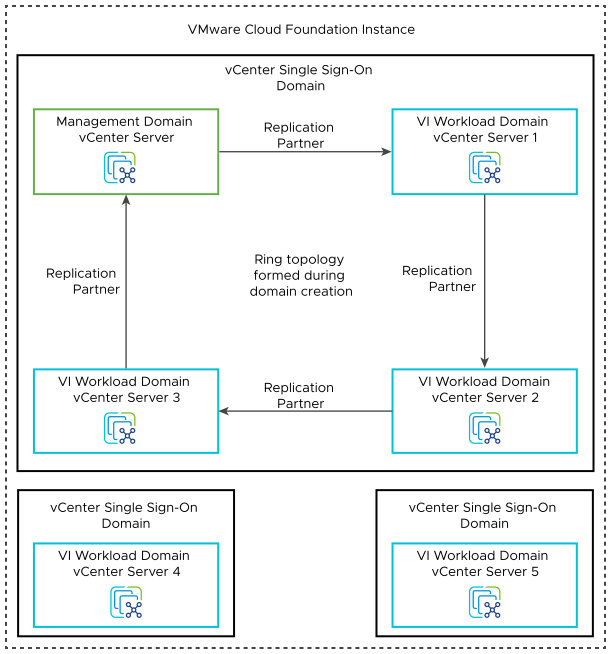
Multiple vCenter Server Instances - Multiple vCenter Single Sign-On Domains |
|
|
Additional password management overhead per vCenter Single Sign-On domain. |
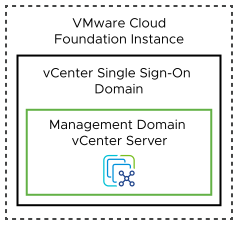
Because the Single vCenter Server Instance - Single vCenter Single Sign-On Domain topology contains a single vCenter Server instance by definition, no relevant design requirements or recommendations for vCenter Single Sign-On are needed.
| Requirement ID |
Design Requirement |
Justification |
Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| VCF-VCS-REQD-SSO-STD-001 |
Join all vCenter Server instances within aVMware Cloud Foundation instance to a single vCenter Single Sign-On domain. |
When all vCenter Server instances are in the same vCenter Single Sign-On domain, they can share authentication and license data across all components.
|
|
| VCF-VCS-REQD-SSO-STD-002 |
Create a ring topology between the vCenter Server instances within the VMware Cloud Foundation instance. |
By default, one vCenter Server instance replicates only with another vCenter Server instance. This setup creates a single point of failure for replication. A ring topology ensures that each vCenter Server instance has two replication partners and removes any single point of failure. |
None. |
| Requirement ID |
Design Requirement |
Justification |
Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| VCF-VCS-REQD-SSO-ISO-001 |
Create all vCenter Server instances within a VMware Cloud Foundation instance in their own unique vCenter Single Sign-On domains. |
|
|