Moving an application physically from one VMware Cloud Foundation instance to another represents a networking challenge, especially if applications have static IP addresses. With overlay-backed network segments, applications can move between VMware Cloud Foundation instances without changing IP addresses.
Network Segment
This design uses NSX overlay network segments. Overlay network segments have the following benefits:
- Single IP network address space providing IP mobility between data centers
- Simplified disaster recovery procedures
After a failover, the recovered application is available under the same IP address.
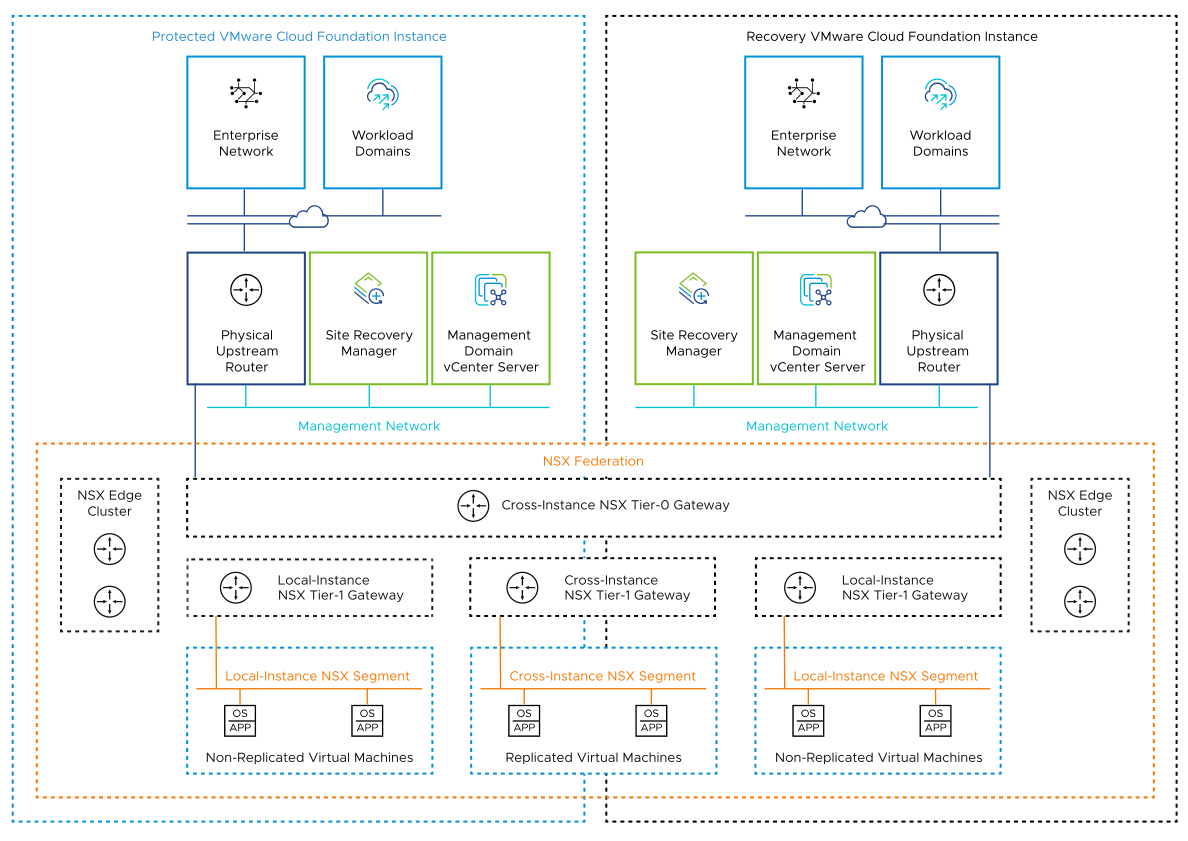
NSX provides load balancing functionality through a standalone Tier-1 load balancer. In each VMware Cloud Foundation instance, you use the same configuration for the management applications and the relevant placeholder virtual machines.
Decision ID |
Design Decision |
Design Justification |
Design Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
SPR-SRM-NET-001 |
Place the Site Recovery Manager instances on the management network. |
Places the Site Recovery Manager on the same network as the VMware Cloud Foundation components that the appliance must communicate with. |
None. |
SPR-VR-NET-001 |
Place the vSphere Replication instances on the management network. |
Places the vSphere Replication on the same network as the VMware Cloud Foundation components that the appliance must communicate with. |
None. |
IP Addressing Scheme
You can assign IP addresses to Site Recovery Manager and vSphere Replication using static or dynamic allocation based on the network configuration of your environment. It is recommended to reserve an IP address from the selected local network segment and statically assign it to the corresponding Site Recovery Manager and vSphere Replication instances.
Decision ID |
Design Decision |
Design Justification |
Design Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
SPR-SRM-NET-002 |
Allocate and assign a static IP address to the Site Recovery Manager instances. |
Using assigned IP addresses removes the constraints and risks associated with providing and managing DHCP on your management networks. |
The use of static IP addresses requires precise IP address management. |
SPR-VR-NET-002 |
Allocate and assign a static IP address to the vSphere Replication instances. |
Using assigned IP addresses removes the constraints and risks associated with providing and managing DHCP on your management networks. |
The use of static IP addresses requires precise IP address management. |
Name Resolution
Name resolution provides the translation between an IP address and a fully qualified domain name (FQDN). This portion of the design consists of characteristics and decisions that support name resolution for Site Recovery Manager and vSphere Replication.
Decision ID |
Design Decision |
Design Justification |
Design Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
SPR-SRM-NET-003 |
Configure both forward (A) and reverse (PTR) DNS records for each Site Recovery Manager instance. |
Site Recovery Manager is accessible using a fully qualified domain name. |
|
SPR-VR-NET-003 |
Configure both forward (A) and reverse (PTR) DNS records for each vSphere Replication instance. |
vSphere Replication is accessible using a fully qualified domain name. |
|
Time Synchronization
Decision ID |
Design Decision |
Design Justification |
Design Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
SPR-SRM-NET-004 |
Configure the Site Recovery Manager instances to use NTP servers rather than using VMTools to synchronize with the ESXi hosts on which it is running. |
|
|
SPR-VR-NET-004 |
Configure the vSphere Replication instances to use NTP servers rather than using VMTools to synchronize with the ESXi hosts on which it is running. |
|
|