VMware Data Services Manager requires access to a vCenter Server system, ESXi hosts, and one or more clusters. Requirement of resource pools is optional. Each host running VMware Data Services Manager must meet certain hardware and software requirements.
Supported Platforms
Refer to the Release Notes for information about the server platforms, browsers, and data services supported by this release of VMware Data Services Manager.
Supported Versions of vSphere Components
VMware Data Services Manager is supported on VMware vSphere 6.7 and later. The following table lists information about the components of vSphere required and the versions supported.
| Component | Supported Versions |
|---|---|
| vCenter | 6.7, 7.0, and 8.0 |
| ESXi | 6.7 and 7.0 |
| VMFS | 5 and 6 |
| PostgreSQL | 11.19.0, 12.14.0, 13.10.0, 14.7.0, and 15.2.0 |
| MySQL | 8.0.32 |
| MinIO/AWS S3 | Not Applicable |
| VMC | SDDC Version 1.14v6 |
Disk Space, Memory, and CPU Requirements
The type of environment in which it will run, and the volume of services that it will manage, will determine the amount of resources that are configured for a Provider VM or an Agent VM. The default configuration for the VMs follows:
| VM | Environment | Memory | CPU | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provider VM | Default configuration | 16 GB | 8 vCPU | 736 GB (thin provisioning) |
| Agent VM | Default configuration | 16 GB | 8 vCPU | 668 GB (thin provisioning) |
The provisioning user specifies the amount of memory and CPU resources for any database that they deploy. These amounts may be bounded by the VM Configuration Mode in place for the organization to which the user belongs.
vSphere Storage Requirements
VMware Data Services Manager has no specific storage requirement for its deployments. The environment admininstrator can choose to configure the number and types of datastores. A VMware Data Services Manager deployment uses the datastores available.
Object Storage Requirements
VMware Data Services Manager requires an S3-compatible local and a cloud object storage solution (for example, AWS or MinIO).
If all of the six repositories - Provider repo, Provider log repo, Provider backup repo, and Agent local storage, Agent cloud storage, and Template storage - are on the same server, a minimum of 100GB capacity of S3-compatible local and cloud object storage is required. The recommended size of the S3-compatible local and a cloud object storage depends on the size of data backups and retention policy.
Before you deploy VMware Data Services Manager, configure and deploy S3-compatible local and a cloud object storage and create the following buckets:
- A bucket for Provider Repo
- A bucket for Provider Logs
- A bucket for Provider Backups
- A bucket for Database Backup Local Storage
- A bucket for Database Backup Cloud Storage
- A bucket for Database Template Storage
These endpoints must be resolvable by the DNS server specified at the time of Provider VM deployment.
Naming Convention of Object Storage Buckets
Ensure that you use the following naming conventions for the object storage buckets:
- Bucket names should be between 3 and 63 characters long.
- Bucket names should not contain upper-case letters.
- Bucket names should not contain underscores (_).
- Bucket names should not end with a dash (-).
- Bucket names should not contain dashes next to periods (for example, my-.bucket.com and my.-bucket are invalid).
- Bucket names should not contain periods.
Network Configuration Requirements
You can deploy a basic configuration of one Provider and one VMware Data Services Manager Agent in a single vCenter cluster. One VMware Data Services Manager Agent can manage one vSphere entity, such as a vCenter cluster or Resource pool. Neither can multiple VMware Data Services Manager Agents manage the same vSphere entity nor can a single VMware Data Services Manager Agent manage multiple vSphere entities.
Secure, reliable operation of VMware Data Services Manager depends on a secure, reliable network that supports DHCP, a network time service, and other services.
VMware Data Services Manager requires a minimum of one dedicated subnet that has access to DHCP, DNS, and NTP services. DNS resolution is required for Database network of database VMs. DNS resolution is mandatory only for database clusters. Ensure that DHCP server provides IP addresses for the databases that you create. Configure the subnet so that IP addresses are assigned by DHCP for each provisioned database.
If you are deploying in an environment with internet connectivity, ensure that your network is able to access VMware Tanzu Network and cloudfront.net. Tanzu net uses Cloudfront.net for storage purposes. Your environment must meet the following network requirements before you begin installing VMware Data Services Manager.
VDS and N-VDS port groups that should be available to host components of VMware Data Services Manager are:
Management network connected to:
- S3-compatible object storage (optional)
- Provider VM (through NIC 1 or eth0) for management and data access purposes
- Agent VM (through NIC 1 and eth0) for management and data access purposes
- Databases (through NIC 1 and eth0) for data access purposes
Database network connected to databases (through NIC 2 or eth1) for database access purposes
The choice of port group type depends on the appliance to which it is connected:
- A Provider VM's Management network can connect to a Standard, DVS, or N-VDS port group.
- An Agent VM's Management network can be connected to a Standard,DVS,or N-VDS port group.
- A Database VM's Management network and Database network can be connected to DVS or N-VDS port group.
Though the Management network and the Database network for databases get their IP addresses from the DHCP server, the IP addresses for Management network for Provider and Agent VMs are static and configured manually or provided through DHCP.
Network Time Service
You must use the NTP network time service to synchronize the clocks of all VMware Data Services Manager deployed VMs.
Provider
The Provider VM requires one network for UI or management traffic:
VMware Data Services Manager refers to the network that NIC 1 (eth 0) connects to as the Management Network. This network is used for the VMware Data Services Manager user interface and API calls. The network must have access to the internet so that it can access the S3-compatible object store. The VMware Data Services Manager console runs on this network, and it requires a static IP address or an IP address through DHCP.
The Management Network is configured when you deploy the Provider VM, and cannot be changed after deployment.
Agent
An Agent VM requires:
- A single NIC (eth0) and network for management traffic. VMware Data Services Manager refers to this network as the Management Network. The Management Network must have connectivity to the Management Network of the Provider VM. The Management Network of the Agent VM requires a static IP address or an IP address through DHCP for Agent recovery to work.
- Access to vCenter.
- Access to an external network for cloud object storage.
The Management Network is configured when you deploy an Agent VM, and cannot be changed after deployment.
Database
A database requires:
Either a single network for both management traffic and database traffic or two networks, one for management traffic and one for access by client applications:
- NIC 1 (eth0): This NIC is used for communication between the Agent and the database. VMware Data Services Manager refers to the network that this NIC connects to as the Management Network. If the database VM is in a different subnet than the Agent VM; to access NTP servers, agents, DNS servers, and local storage; the Management network must be routable.
- NIC 2 (eth1): This NIC is used for client application access to the database. VMware Data Services Manager refers to the network that this NIC connects to as the Database Network. To access databases using database client applications from different subnets, the Database network must be routable.
Access to an external network for cloud object storage.
Each NIC in a database must be configured to obtain its IP address from DHCP.
The Management Network and the Database Network for a specific onboarded Cluster are configured when you onboard the Agent with VMware Data Services Manager. When a user provisions a database that specifies the associated cluster Environment, the deployed database utilizes those networks.
Database Network Addressing
VMware Data Services Manager expects that databases that it deploys reside in their own subdomain under a corporate domain. For example: dms.myco.com.
VMware Data Services Manager hosts a DNS server on every Provider VM. The Provider VM acts as a DNS for all databases provisioned in the associated Onboarded Cluster.
You can use your existing corporate DNS server to resolve database addresses by configuring the server to forward all DNS requests in the subdomain to the Provider VM DNS server.
If there is another DNS configured in your vCenter for VMware Data Services Manager, this DNS must have Forward Lookup Zone and Conditional forwarding set for each DB FQDN Suffix so that an Provider VM handles all DNS resolution for its databases.
VMware Data Services Manager assigns the IP address of a database that is provisioned by an Organization using DHCP. Agent VM generates and creates a DNS entry for a database FQDN based on the DB FQDN Suffix specified when a Provider creates the Organization.
The following diagram provides a representation of a network topology of VMware Data Services Manager using a single network or the Management network only:
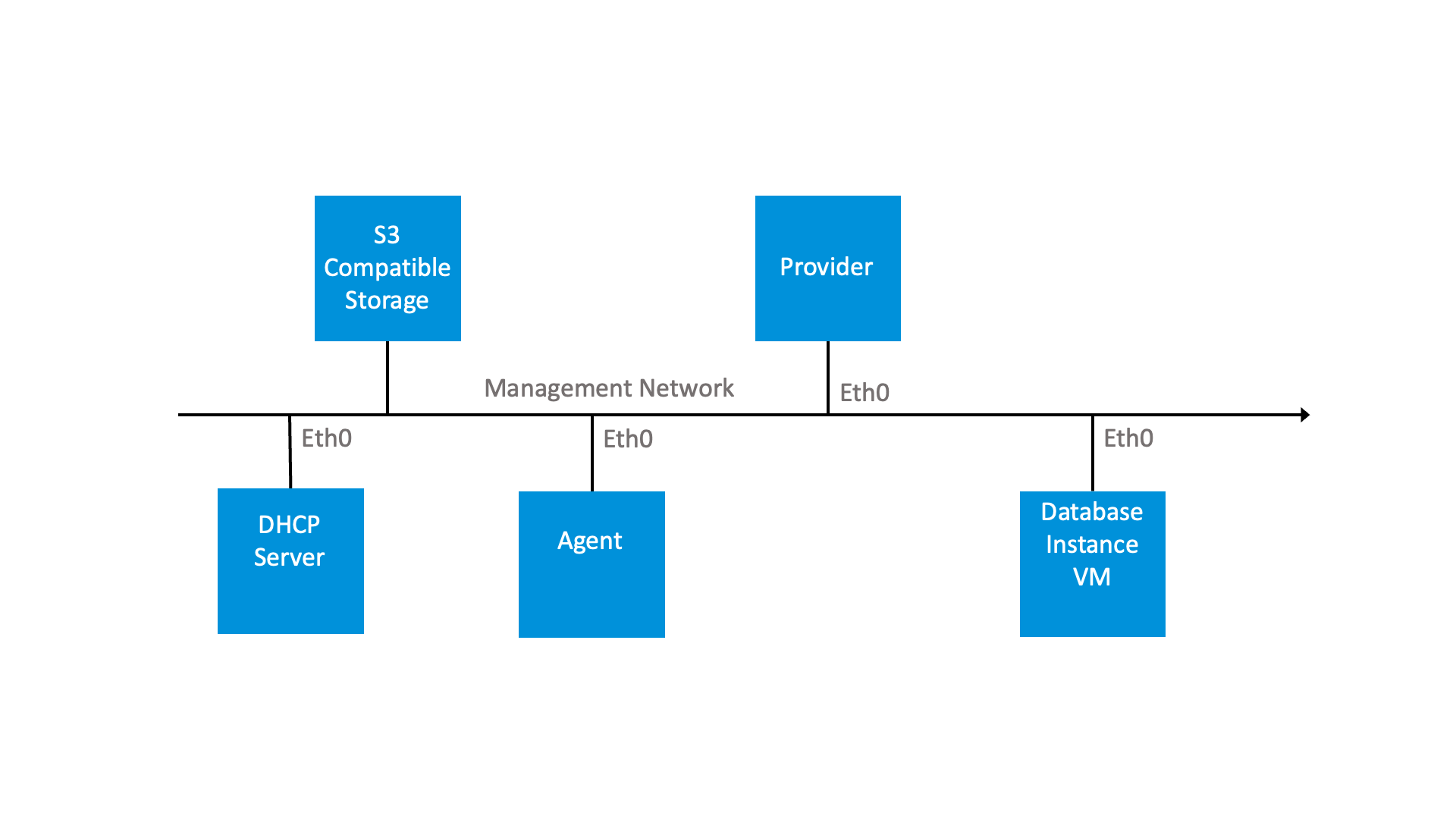
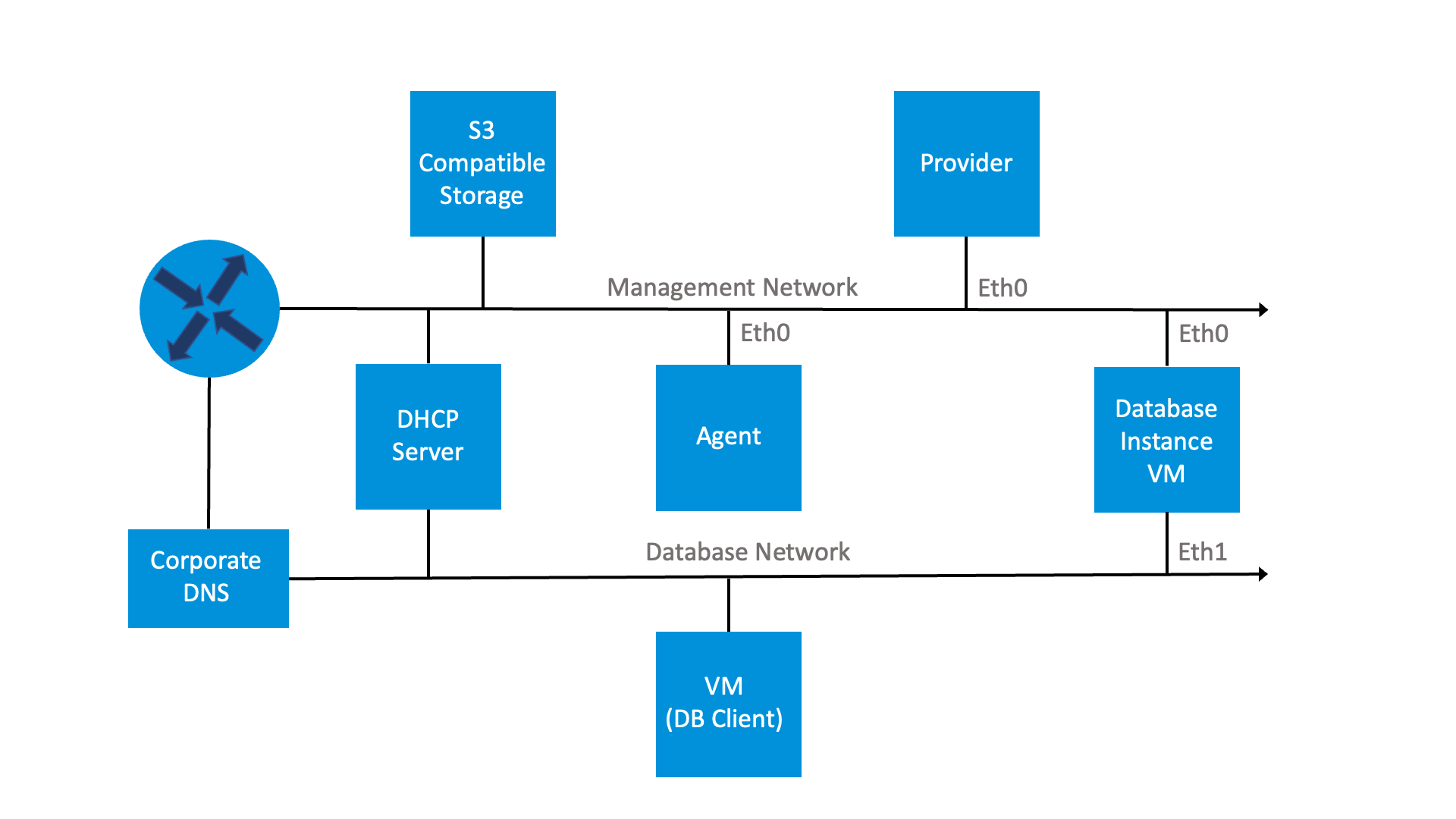
The following diagram provides a representation of a network topology of VMware Data Services Manager using two networks, that is the Management network and the Database network:
Network Security Requirements
The following ports are opened for incoming/outgoing traffic during Provider VM deployment:
| Protocol | Port Number | NIC |
|---|---|---|
| ICMP | ||
| TCP (SSH) | 22 | eth0 |
| UDP (DNS) | 53 | eth0 |
| TCP (DNS) | 53 | eth0 |
| TCP (https) | 443 | eth0 |
| TCP (RabbitMQ) | 5671 | eth0 |
The following ports are opened for incoming and outgoing traffic during Agent VM deployment:
| Protocol | Port Number | NIC |
|---|---|---|
| ICMP | ||
| TCP (SSH) | 22 | eth0 |
| TCP (https) | 443 | eth0 |
The following ports are opened for incoming and outgoing traffic during database deployment:
| Protocol | Port Number | NIC |
|---|---|---|
| ICMP | ||
| TCP (SSH) | 22 | eth1 |
| TCP (https) | 443 | eth0 |
| TCP (MySQL) | 3306 | eth0 or eth1 |
Network Requirements Summary
External Network Requirements:
| Connection From | Connection To | Type | Protocol | Port Number | NIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provider VM | S3-compatible Provider storage | http/https | TCP | eth0 | |
| Provider VM | VMware Tanzu Network | https | TCP | 443 | eth0 |
| Provider VM | cloudfront.net | https | TCP | 443 | eth0 |
| Corporate DNS | Provider VM | DNS | TCP/UDP | 53 | eth0 |
| Agent VM | S3-compatible Agent storage (local) | http/https | TCP | eth0 | |
| Agent VM | S3-compatible Agent storage (cloud) (external) | http/https | TCP | eth0 | |
| Agent VM | vCenter | https | TCP | 443 | eth0 |
| Database | S3-compatible Agent storage | http/https | TCP | eth0 or eth1 | |
| Agent Onboarding UI Client | Agent VM | https | TCP | 443 | eth0 |
| VMware Data Services Manager Console Client | Provider VM | https | TCP | 443 | eth0 |
| End User (Terminal) | Provider VM | SSH | TCP | 22 | eth0 |
| End User (Terminal) | Agent VM | SSH | TCP | 22 | eth0 |
| End User (Terminal) | Database | SSH | TCP | 22 | eth0 |
| End User | Database | https | TCP | 443 | eth0 |
| Database Client | Database | PostgreSQL | TCP | 5432 | eth0 or eth1 |
| Database Client | Database | MySQL | TCP | 3306 | eth0 or eth1 |
Internal Network Requirements:
| Connection From | Connection To | Type | Protocol | Port Number | (From/To) NIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agent VM | Provider VM | RabbitMQ | TCP | 5671 | eth0/eth0 |
| Agent VM | Database | https | TCP | 443 | eth0/eth0 |
| Agent VM | Provider VM | https | TCP | 443 | eth0/eth0 |
Connection Ports from MySQL Client to MySQL Router in a MySQL Cluster
Connection ports from Mysql client to Mysql Router for different use cases are specified in the following table:
| Default Port/Protocol | Connection Description | SSL or Other Encryption? | Connection Required? | Network Flow Direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6446/TCP | Read-write SQL from the MySQL client to the MySQL router (classic MySQL protocol) | Yes. Inherited from the MySQL client and server. If the client --ssl-mode is VERIFY-IDENTITY, the router must have the same IP address as the server. |
Required if MySQL router provides read-write access | MYSQL client read-write access to MySQL router |
| 6447/TCP | Read-only SQL from the MySQL Client to the MySQL router (classic MySQL protocol) | Yes. Inherited from the MySQL client and server. If the client --ssl-mode is VERIFY-IDENTITY, the router must have the same IP address as the server. |
Required if MySQL router provides read-only access | MySQL client read-only access to MySQL router |
| 6448/TCP | Read-write API calls from the MySQL Client to the MySQL router (X protocol) | Yes. Inherited from the MySQL client and server. If the client --ssl-mode is VERIFY-IDENTITY, the router must have the same IP address as the server. |
Required if MySQL router provides read-write access | MySQL client to MySQL router |
| 6449/TCP | Read-only calls from the MySQL Client to the MySQL router (X protocol) | Yes. Inherited from the MySQL client and server. If the client --ssl-mode is VERIFY-IDENTITY, the router must have the same IP address as the server. |
Required if MySQL router provides read-only access | MySQL client to MySQL router |
| 3306/TCP | MySQL router to the MySQL server (classic MySQL protocol) | Yes. Inherited from the MySQL client and server. If the client --ssl-mode is VERIFY-IDENTITY, the router must have the same IP address as the server. |
Required | MYSQL router to the MySQL server |
| 33060/TCP | MySQL router to the MySQL server (X protocol) | Yes. Inherited from the MySQL client and server. If the client --ssl-mode is VERIFY-IDENTITY, the router must have the same IP address as the server. |
Required | MYSQL router to the MySQL server |