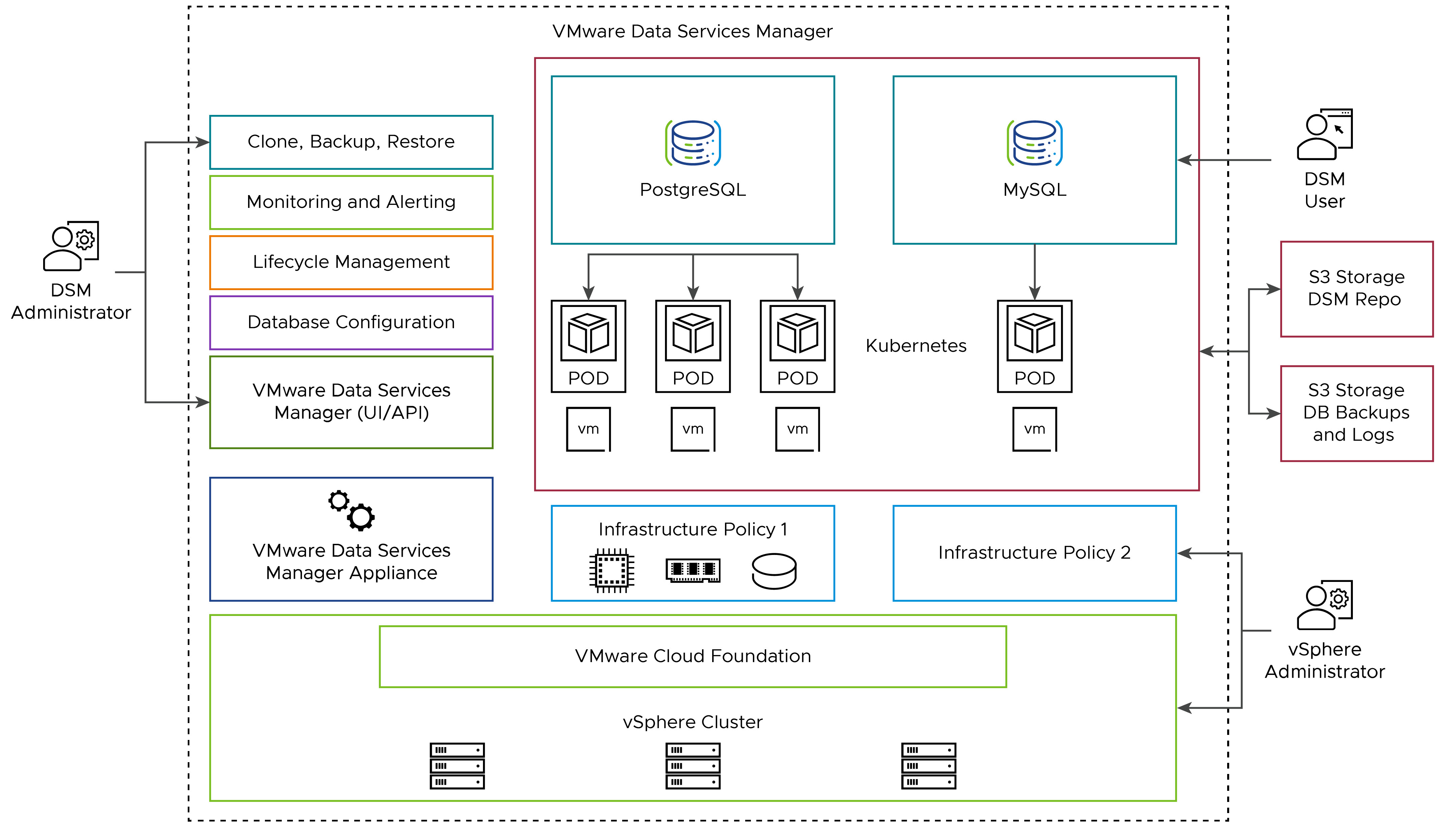
Architecture of VMware Data Services Manager has a number of components which are interconnected through a management network.
The following main components of the architecture are:
VMware Data Services Manager Appliance - An appliance deployed in the vSphere data center. It might also be called DSM provider VM or DSM plugin VM. The VMware Data Services Manager installation includes a single instance of the appliance. The appliance provides the API gateway and user interface that serves as a central control plane for all VMware Data Services Manager users in a hosted instance.
The appliance comes as an OVA file that a vSphere administrator installs in vCenter Server. The installation creates a DSM UI extension, or plugin, in the vSphere Client with additional UI entries for the DSM. vSphere administrators use the DSM UI plugin to configure infrastructure policies for DSM. In addition, the DSM appliance provides a portal, or a DSM console, that DSM users can access.
Resiliency of the VMware Data Services Manager plugin VM is provided through vSphere High Availability. To know more about vSphere High Availability, refer to vSphere documentation.
Infrastructure Policy - Defines the compute, storage, and networking resources for the database to be deployed. It also references the list of allowed VM classes. The VM class controls the size of the virtual machines that is provisioned to back the data services.
Infrastructure policies are configured by a vSphere administrator, who selects clusters, resource pools, storage policies that map to any of the underlying storage available on that cluster, and other components of the infrastructure policies.
DSM Console - A UI that DSM administrator and users can access to create databases or data services and perform the life cycle management operations for the data services.
Database VM - An Ubuntu VM that hosts a data service created by a VMware Data Services Manager user. VMware Data Services Manager supports provisioning MySQL and PostgreSQL databases.
After a DSM user defines a data service configuration, DSM provisions VMs and deploys a Kubernetes cluster across VMs. Kubernetes operators deploy data services depending on the requested type of the data service.
Database Topology - When defining a data service configuration, the DSM user can specify database topology. Depending on the topology, the database can be replicated or standalone.
VMware Data Services Manager supports one Kubernetes node for standalone and three or five nodes for replicated databases. The Kubernetes nodes are of dual purpose. They act as the control plane and as the worker nodes, and run Kubernetes and the data service modules.
In the architecture diagram below, the VMware Data Services Manager appliance and database VMs are all running in the same vSphere cluster.