The 3-node cluster's infrastructure design is similar to the 2-node cluster and aims to provide high availability in compute, storage, and networking at the edge. A vSAN cluster will provide shared storage, and hosts will use physical uplinks and TOR switches for vSAN connectivity. Hosts should have a minimum of 2 NICs and it's recommended to use 10Gbps and higher throughput links. Use VDS for networking, and if the TOR switches support EtherChannel, configure a LAG for network connectivity.
Infrastructure and Networking
The infrastructure design for the 3-node cluster is similar to the 2-node cluster with a goal to provide high availability in compute, storage, and networking at the edge. An external or integrated router or firewall will provide networking services and routing for the VMs and workloads deployed in the cluster. The vSphere hosts in the cluster should use a minimum of 2 NICs – preferably configured in a link aggregation group (LAG) using LACP, to connect to the TOR switches.
A vSAN cluster will be formed to provide shared storage for the three nodes. The stored VM data as well as witness components will be distributed between the nodes in the cluster. Unlike a 2-node cluster, hosts in the 3-node cluster will not use Direct Connect for vSAN connectivity to each other. Instead, the VMkernel adapters enabled for vSAN will leverage the hosts’ physical uplinks and the TOR switches to connect to other hosts inside the vSAN cluster. It’s recommended to use 10Gbps and higher throughput links for the uplinks given this requirement.
Same as the other edge types, the 3-node cluster should leverage vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS) for networking and create the four VLANs and the uplink (trunk port) in VDS. If the switches are stacked and support EtherChannel/port-channel and LACP, configure a link aggregation group (LAG) for connectivity to the TOR switches and add the physical uplinks to the LAG from each host. The same VDS and LAG configuration can be applied to all three hosts. The switches will need matching EtherChannel and layer 2 configurations on their ports. If the TOR switches do not support EtherChannel, bypass LACP and NIC Teaming configurations and simply configure the vmnics as DVS uplinks.
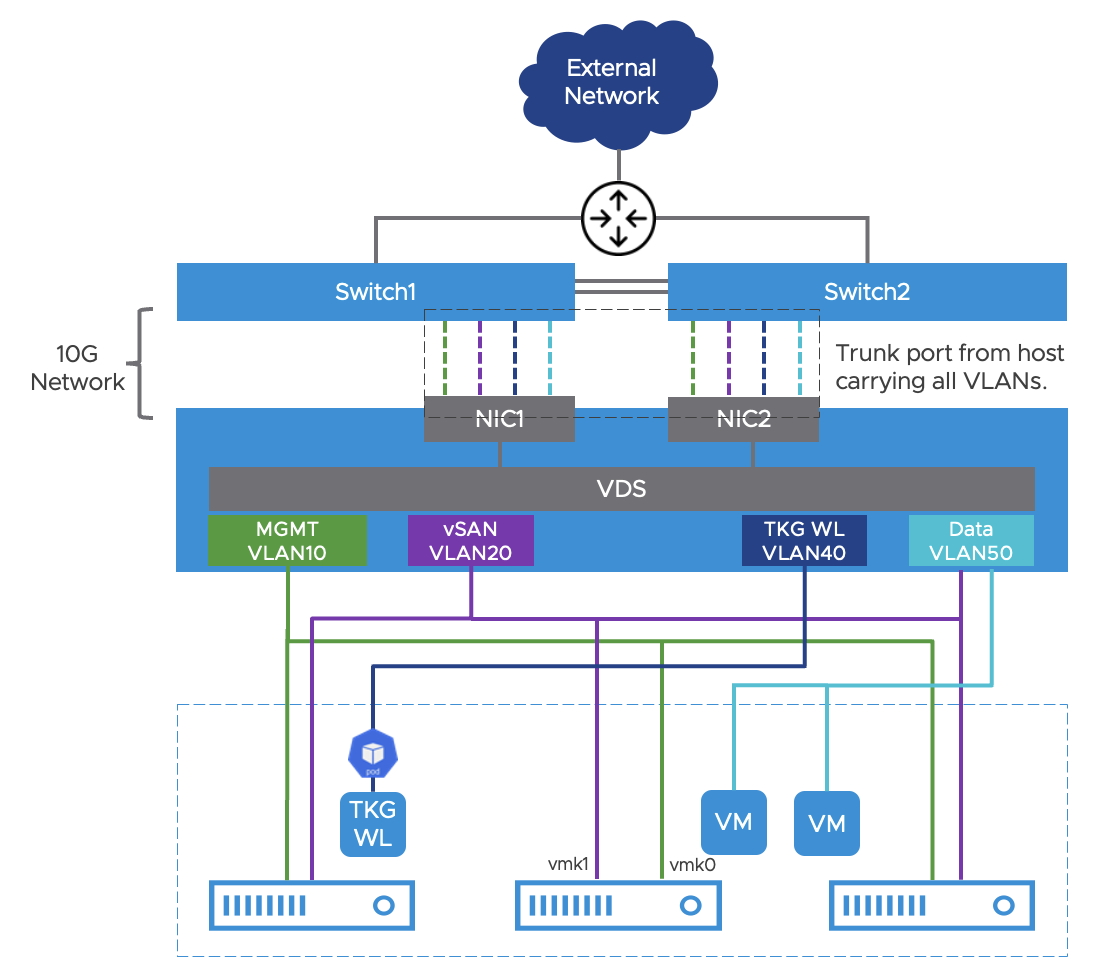
A reference network design is provided with the following requirements:
Use a minimum of two NICs per host to connect to the switches. Each NIC should connect to a different switch for redundancy.
If the TOR switches are stacked and/or support EtherChannel, configure LACP for the uplinks in VDS and enable NIC Teaming and Failover for workload port groups. use ‘Route based on IP hash’ for the load balancing setting. This is optional.
The upstream network device will serve as the DHCP server and default gateway for the four VLAN subnets and advertise the network prefixes to the data center.
For vSAN networking, create a separate VMkernel interface – i.e., vmk1 and map it to the configured vSAN port group.
TKG Management Cluster in the data center must have connectivity to ‘TKG WL’ VLAN to configure the workload clusters.
Internet access for the pods in the TKG workload clusters.
vSphere HA and DRS
vSphere HA and DRS will provide compute high-availability and load balance virtual machine distribution in the vSphere cluster. Upon deployment of TKG workload clusters containing multiple master and worker nodes, DRS will evaluate the cluster resources and spread the nodes among the hosts accordingly. vSphere HA will also handle the failover of the TKG control plane and worker nodes in case of host failures. As of vSphere version 7.0U3, vSphere HA does not work for Virtual machines configured with real-time attributes.
Workload Clusters
The TKG workload clusters will be deployed by the TKG management cluster in the data center. For a 3-node vSphere cluster, although it satisfies quorum and can support 3 master nodes and their subsequent etcd databases, it is recommended to run a single master node in the workload cluster. This is due to anti-affinity and spreading of workload cluster nodes across multiple hosts being an experimental feature. With one workload cluster master node, vSphere HA and vSAN (or shared storage) will failover the node to another host in the event of a host or virtual machine failure. The decision of the number of worker nodes to deploy in the TKG cluster does not change.
Integrated SD-WAN
Integrated SD-WAN is not recommended for a 3-node cluster. This is due to the requirements for consistent binding between the physical WAN connection, the host, and the SD-WAN appliance. Given the only two SD-WAN virtual appliances in a HA setup with two WAN circuits – one from each of the two service providers and the three nodes in the cluster, they cannot achieve predictable and consistent high-availability results in a 3-node cluster.