Describes the common floor map features supported by VMware Edge Network Intelligence.
All data in the floor maps page is currently set to a full 2-week window.
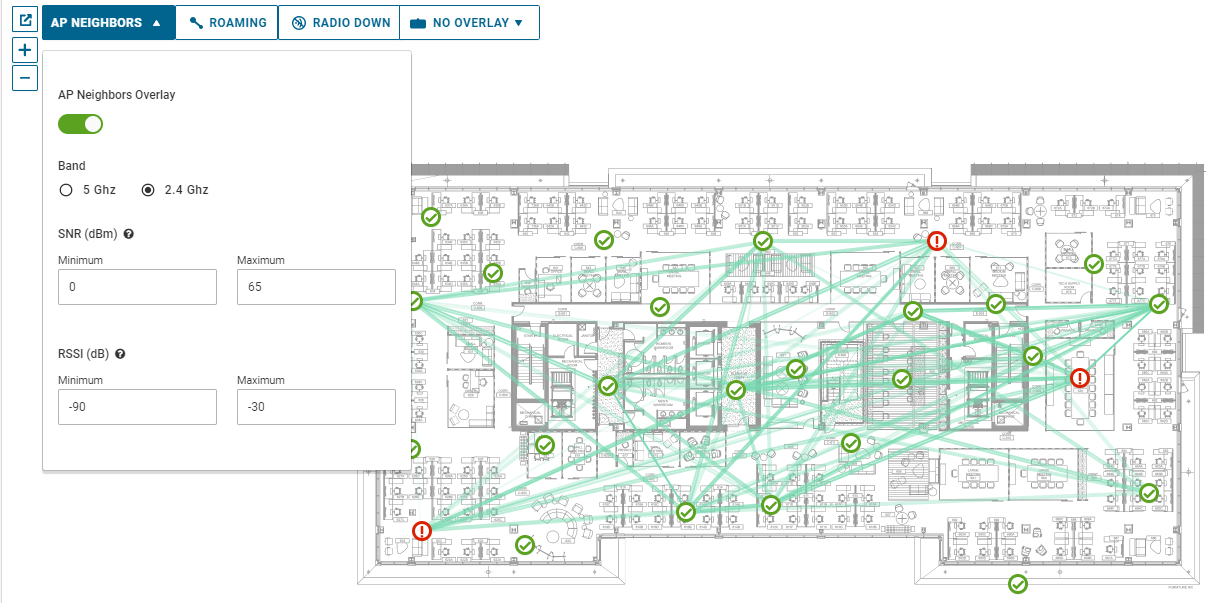
AP Neighbors
Access Point (AP) Neighbors is one of the overlays you can use on the floor maps. You can enable AP Neighbors Overlay feature to view all the neighbors for the selected AP. ENI also allows you to filter the number of neighbors seen on the map by configuring the RF band, Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), and Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) thresholds.
For SNR - The allowable range is 0 dBm (minimum) through 65 dBm (maximum).
For RSSI - The allowable range is -90 dB (minimum) through -30 dB (maximum).
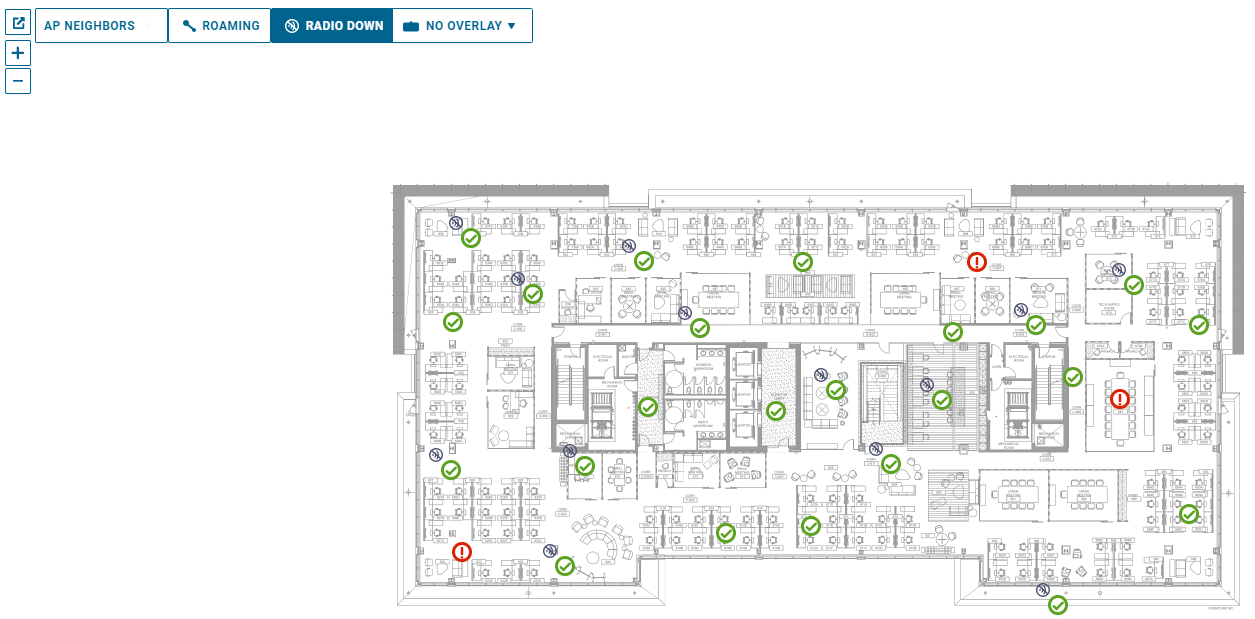
Radios Offline
You can quickly see if APs have offline radios using the RADIO DOWN button on the top left of the Floor Map page. When you enable the RADIO DOWN button, this will place a small icon  next to the APs that have radios disabled. The RADIO DOWN button will have a dark background and light lettering if roaming is OFF, and vice versa if roaming is ON.
next to the APs that have radios disabled. The RADIO DOWN button will have a dark background and light lettering if roaming is OFF, and vice versa if roaming is ON.
Roaming Patterns
You can see roaming patterns across a floor by using the floor map Roaming feature. You can enable the roaming feature by using the ROAMING button on the top left of the Floor Map page. When you enable the Radio Down button, the roaming patterns appear as purple lines. The darker or more intense the purple line indicates that more roams have happened.
If you hover your mouse over the purple line, you can see the number of roams in the past 2 weeks. The ROAMING button will have a dark background and light lettering if roaming is OFF, and vice versa if roaming is ON.
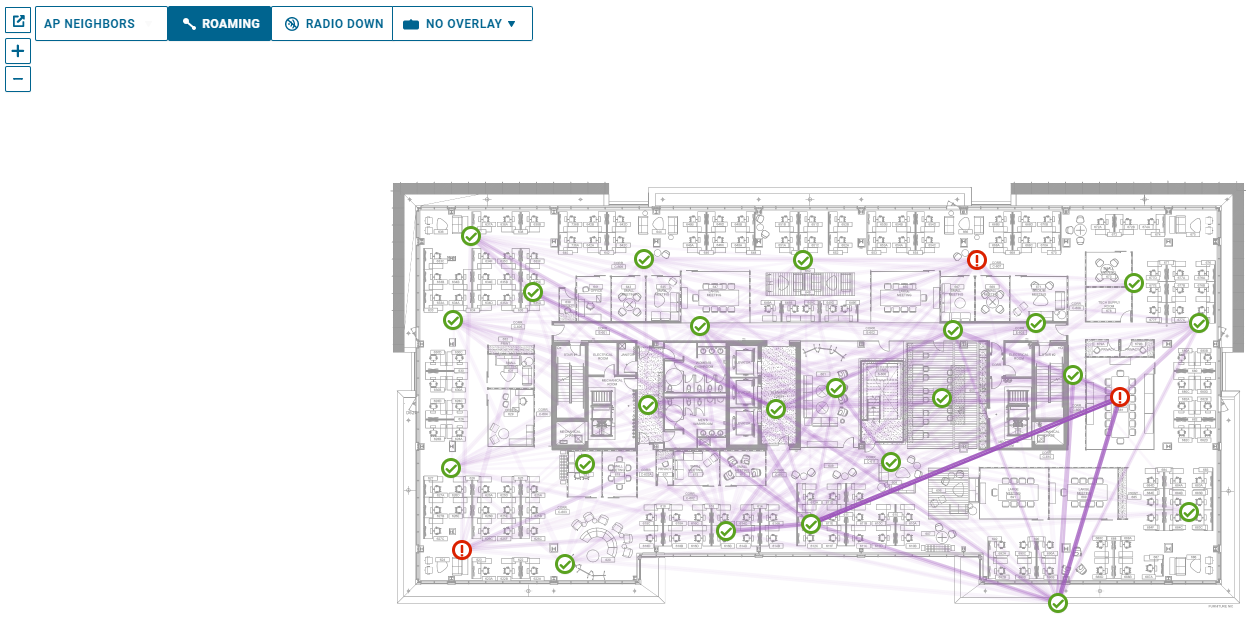
The roaming pattern can highlight the following issues:
An AP misconfigured or malfunctioning - An AP with no roams to/from it, but the expected behavior is APs with many roams.
Too much coverage - APs covering too much area. When clients roam to another AP skipping APs in between.
Unexpected roaming behavior - Clients roaming from an indoor AP to an outdoor AP and back to an indoor AP (outdoor AP providing too much coverage indoors).
Unused/Unnecessary APs - APs with no roams and no issues other than maybe it is not necessary or overkill on coverage.
APs misnamed or misplaced on a map - If all the roams to/from an AP on the map look out of place, the AP may have been named incorrectly on install, or placed incorrectly on the map.
You can also filter the map to show just a specific client's roaming pattern. To view a specific client’s roaming pattern, click the Filters tab, enter client's information (MAC, hostname, IP, and so on), and click APPLY. A 2-week roaming pattern for the specific client is displayed.
Channel Planning
AP Channel is one of the overlays you can use on the floor maps. This will show the last seen channel for each AP radio on the map.
To quickly visualize the channel plan for the floor, select the Overlay tab and choose AP Channel (Last Seen). You can spot APs next to each other that are on the same channel which may point to static planning issues, RRM/ARM issues, or potential noise/interference issues on the channels the APs are avoiding.
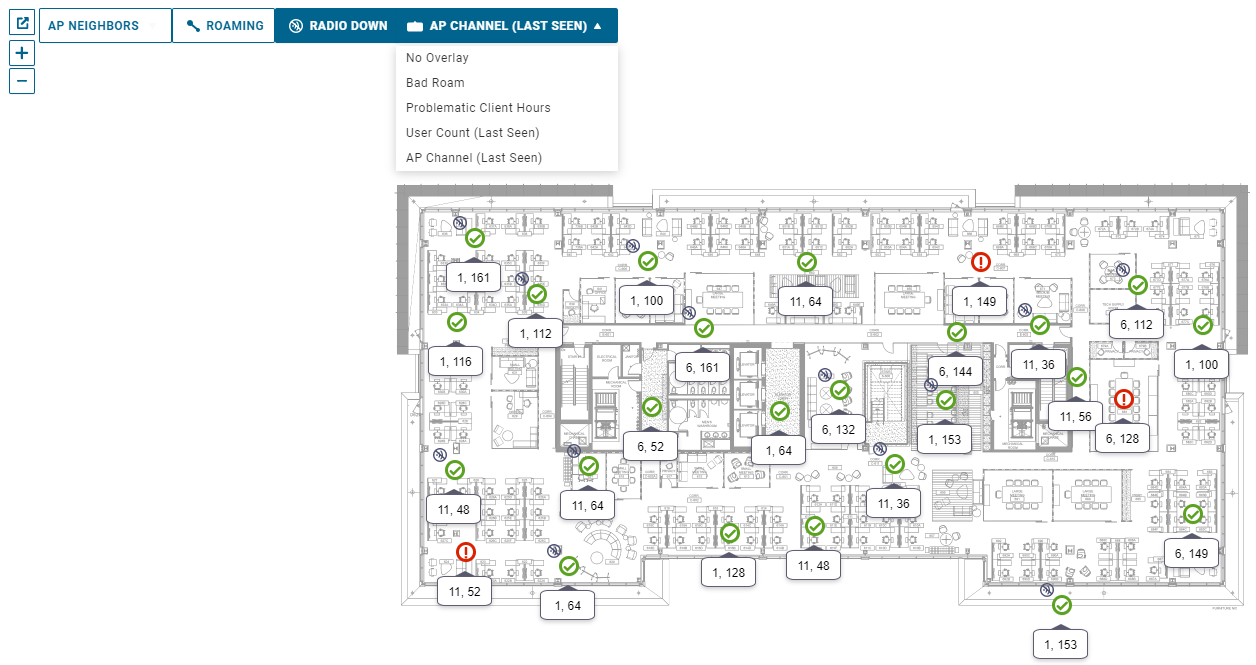
Other overlays that can be used include:
Problematic Client Hours - Highlights hot spot areas of concern by showing the total number of client hours that have had performance issues next to the APs.
User Count - Shows the last seen user counts on each AP, and highlights higher density areas, or APs near each other that are not load balancing as expected, based on client counts.
Bad Roam - Lists the number of bad roams to that AP and highlights systemic roaming issues that should be addressed.
Additional Insights
Some additional insights into the performance across the floor map can be seen by using the Root Cause filters. Applying a Root Cause filter will only show the APs on the map that have seen clients with the selected root cause issues in the last two weeks. For example, selecting the High Channel Utilization Root Cause filter will show the APs that have had client performance issues due to high channel utilization. If you also enable the Problematic Client Hours overlay, you will be able to see which APs have the most issues with that specific Root Cause. You can also sort the APs in the list on the right pane based on the percentage of issues.
To apply the Root Cause filter, select the Filters tab in the top right and then select a Root Cause from the drop down list, and click APPLY.
