Defining Workload Management Rules
You can define workload management rules for both queries and for idle sessions.
Defining Workload Management Rules for Queries
Query assignment rules enable you to configure which resource group a transaction uses before the transaction begins. Workload rules monitor additional conditions for queries, such as the amount of CPU time or disk I/O consumed, and enable you to cancel a running query or (for Greenplum version 6.8 or later) move a query to a different resource group after it has started. You configure both types of rule on the Workload> Workload Mgmt page using the same rule interface.
Transactions are first matched to a configured rule using any combination of user-defined query tags, the current role in the database session, or the resource group originally used for the transaction. When no rule matches, the transaction remains assigned to the role’s default resource group. See About Assignment Rules for more information about assignment rules.
A rule that provides additional conditions acts as a query assignment rule, and determines the resource group where the statement should run.
A rule that provides additional conditions such as a maximum CPU time, Disk I/O, planner cost, or slices used, is a workload rule. With workload rules, Command Center monitors the query to evaluate those conditions. If all conditions are met, the workload rule action is performed.
A additional configuration parameter, wlm_short_query_threshold, is provided to ensure that only queries that run for the configured number of seconds are canceled or moved according to workload rules. This can help in preventing Command Center from applying workload rules to short-running queries. See Greenplum Command Center Parameters for information on changing these parameters.
If Command Center cannot successfully apply any rule’s action (for example, if an attempt to move a query to another resource group fails due to resource availability), then the action is retried 2 times, after waiting a minimum of 15 seconds between attempts. You can configure the wait interval by using the wlm_query_cooldown_time configuration parameter.
-
To edit an existing query rule, click EDIT next to the rule definition to open the Workload Management Rules editor.
-
To delete a query rule, click EDIT next to an existing rule and then click DELETE in the Workload Management Rules editor.
-
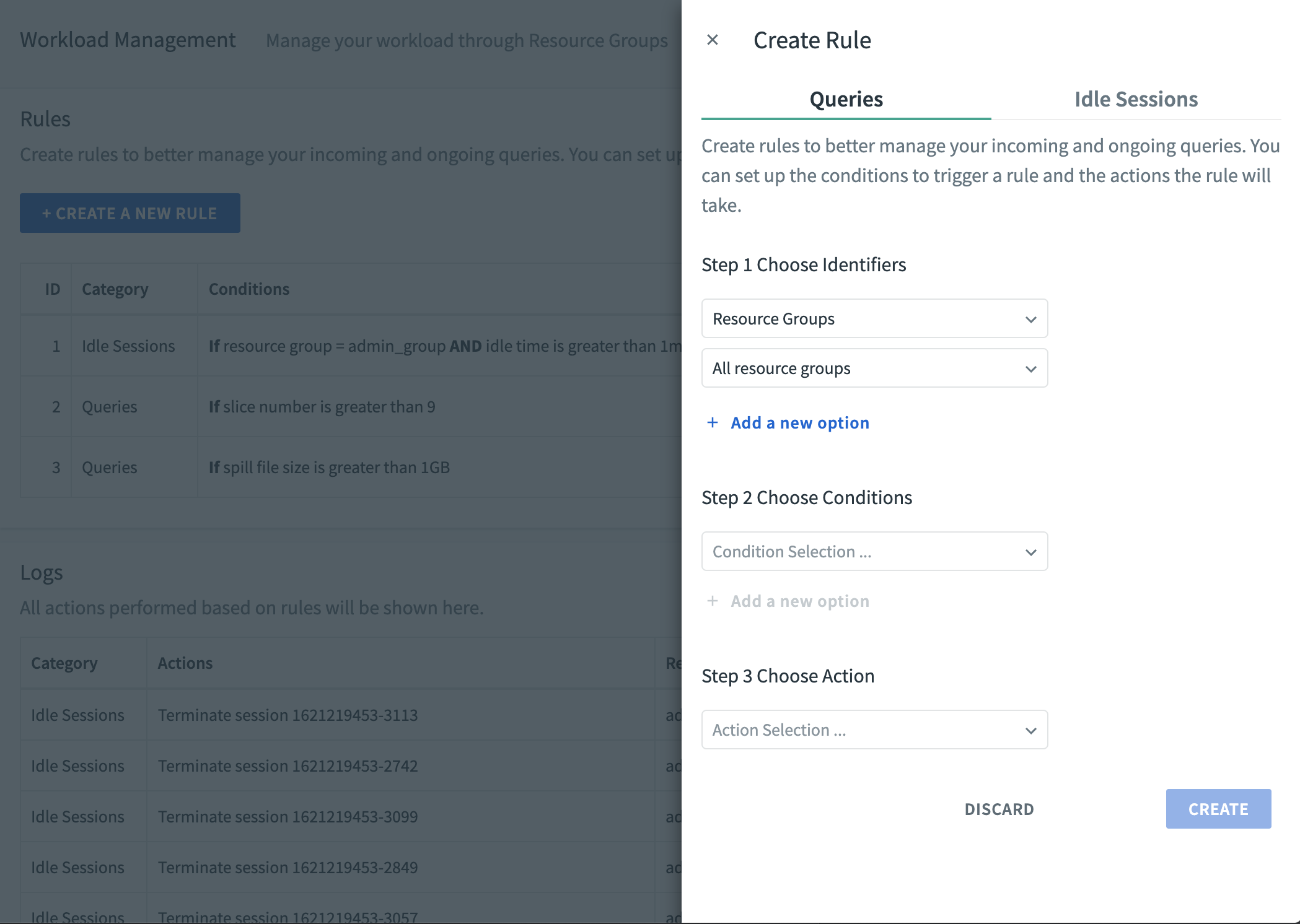
To create a new query rule, click CREATE A NEW RULE and fill in the fields in each section.
-
Choose one or more identifiers to match queries to the rule. By default, rules are applied to all resource groups. Click Add a new option to include additional identifiers to filter based on query tags and/or database role. Note that queries are matched to a rule only if all of the configured identifiers match.
Resource Groups
Choose a resource group name from the list, or accept the default All resource groups to match the rule with any available resource group. Note that if you remove the Resource Groups identifier from your rule, Command Center still uses All resource groups as the default identifier for matching a query’s resource groups.Query Tags
Enter one or more query tags to match against thegpcc.query_tagsparameter in the Greenplum Database session. A query tag is a user-defined <name>=<value> pair. Separate multiple query tags with semicolons. See Defining and Setting Query Tags for more information about query tags.Role
Enter a role name in the field to match the rule with a role of the same name in the database session. -
To create a query assignment rule, define no additional conditions for the rule (skip to the next step). To create a workload rule, choose one or more conditions that a matched, running query must meet before the selected action is performed. Click Add a new option to specify multiple conditions, all of which much apply before any action is taken.
CPU Skew - The threshold value for CPU skew and the maximum amount of time – in seconds, minutes, or hours – the query can run at that skew threshold value.CPU Time The maximum amount of CPU time that the query consumes, specified in seconds, minutes, or hours.
Planner Cost
The query planning cost assigned to the query. Specify two separate values in the fields. The first field, ORCA cost, indicates the maximum Pivotal Query Optimizer (GPORCA) planning cost for the query. The second field, Planner cost, indicates the maximum Postgres Planner cost for the query, used only if the query falls back to using the Postgres Planner instead of GPORCA. Note that the two optimizers use different cost models, as well as different algorithms, to determine the cost of a query execution plan. See Query Profiling in the Greenplum Documentation for more information.Both planner cost values are required, because you cannot predict which planner will be chosen for a particular query.
Query Running Time
The maximum total running time for the query, specified in seconds, minutes, or hours.Slice Number
The maximum number of slices allocated by the query planner to execute the query in parallel on different segments.Spill File Size
The maximum value of a query’s spill file size, specified in MB, GB, or TB.Total Disk I/O
The maximum total disk I/O that the query performs, specified in MB, GB, or TB. Note that Command Center can only make an approximate estimate of the actual I/O used by a query, so actual usage may ocassionaly exceed the configured value. -
Choose an action to perform when a query is matched to the rule and all conditions apply. For query assignment rules (rules that have no additional conditions), chose Move to another resource group.
Cancel query
Cancel the query that matches all of the configured conditions. You must specify at least one condition (creating a workload rule) to trigger this action.Move to another resource group
For a query assignment rule, this action defines the resource group where the query executes. If Command Center matches the rule based on the query tags and/or role identifiers for the rule, the configured source group is used to execute the query.For a workload rule that configures one or more conditions, this action moves the running query to the specified resource group if all of the configured conditions are met. Note that moving an active query as part of a workload rule is supported only when using Greenplum version 6.8 or later. You can create a workload rule with this action in earlier versions of Greenplum, but the rule will be created in the Inactive state.
-
Click CREATE to create the new rule, or DISCARD to dismiss the window without creating the rule.
-
-
Use the Active/Inactive toggle to make a rule active or inactive.
Defining Workload Management Rules for Idle Sessions
You can create a workload rule that terminates an idle session associated with a particular resource group once the session has been idle for a specified number of seconds, minutes, or hours. If all conditions are met, the workload rule action is performed.
-
To edit an existing idle sessions rule, click EDIT next to the rule definition to open the Workload Management Rules editor.
-
To delete an idle sessions rule, click EDIT next to an existing rule and then click DELETE in the Workload Management Rules editor.
-
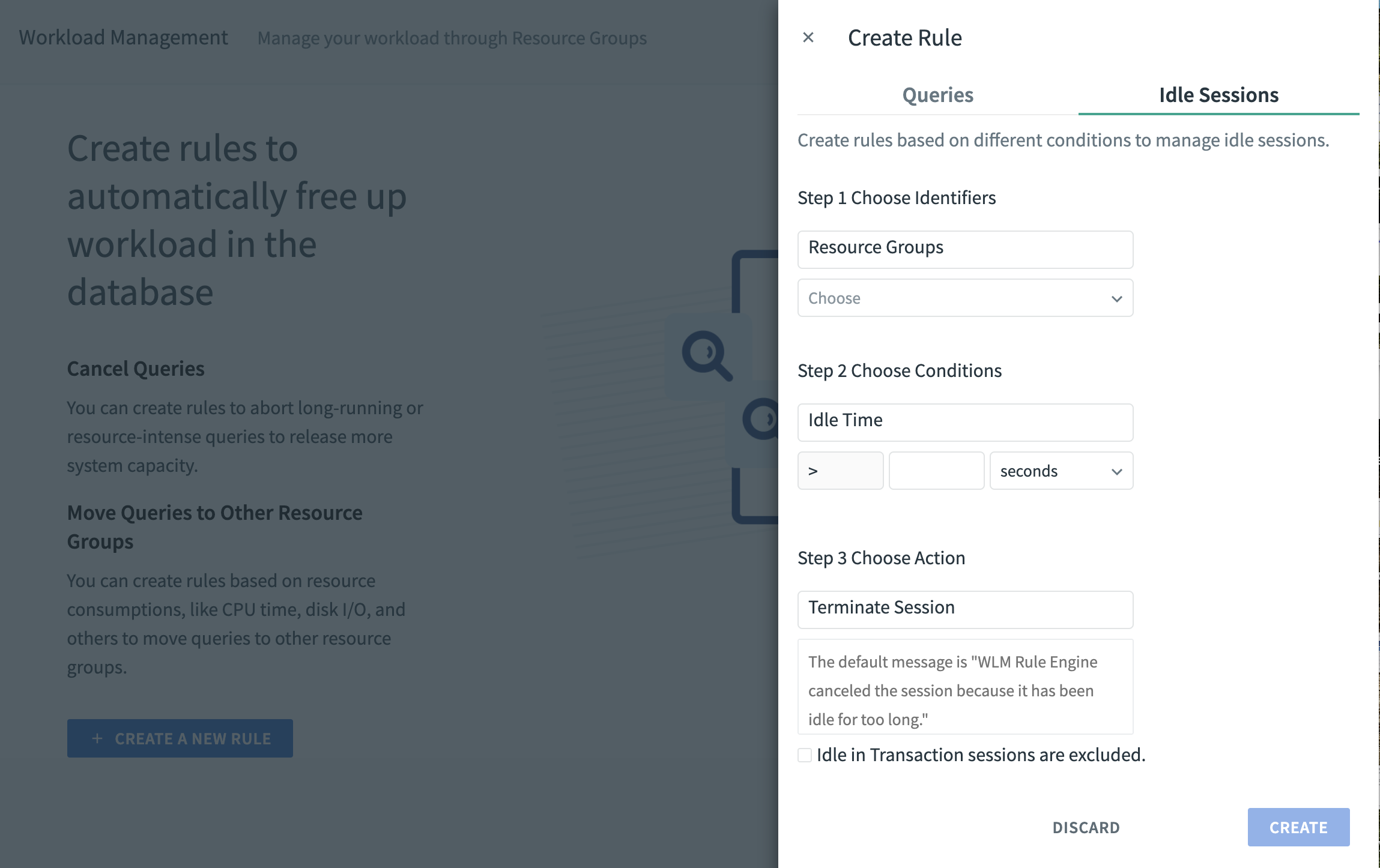
To create a new idle sessions rule, click CREATE A NEW RULE and fill in the fields in each section.
-
Choose a resource group name from the list.
-
Choose an idle time for the session – in seconds, minutes, or hours.
-
In the box under Terminate Session, enter a message to print to the log file and to the console where the session is running. If you do not enter anything, the default message “WLM Rule Engine canceled the session because it has been idle for too long” will be printed.
-
To exclude Idle in Transaction sessions from the new rule, click the checkbox labeled “Idle in Transaction sessions are excluded.”
-
Click CREATE to create the new rule, or DISCARD to dismiss the window without creating the rule.
-
Defining and Setting Query Tags
A query tag is a user-defined <name>=<value> pair, set in the Greenplum Database gpcc.query_tags parameter in the Greenplum Database session. The gpcc.query_tags parameter is defined when the gp_wlm database extension is enabled in the postgres database. If you try to set query tags when the gp_wlm extension is not enabled, you get an unrecognized configuration parameter error. To see if the extension is enabled, run the following command.
$ psql postgres -c "\dx"
List of installed extensions
Name | Version | Schema | Description
--------+---------+--------+--------------------------------------
gp_wlm | 0.1 | gpcc | Greenplum Workload Manager Extension
(1 row)
When you submit a transaction and the gp_wlm extension is enabled, Greenplum Database calls the gp_wlm extension to determine the resource group for the transaction. The extension evaluates the current role and query tags set in the session against the rules you have defined in Command Center. If there is a match, the extension returns the rule’s resource group. If there is no match, Greenplum Database assigns the transaction to the role’s default resource group.
The following command, executed in the Greenplum Database session, sets the appName and appUser query tags to “tableau” and “bi_sales”, respectively.
=# SET gpcc.query_tags TO 'appName=tableau;appUser=bi_sales';
To match a rule, all tags in the rule’s query tag field must be present in the gpcc.query_tags parameter in the database session. The order of the tags is not significant, and the gpcc.query_tags parameter can have a superset of the tags defined in the queryTags value.
When query tags are surrounded by single quotes and those tags have been set by the PGOPTIONS parameter, the single quotes become part of the query tags. In this case, Command Center ignores the single quotes, rather than processing them as part of the query tag name – which would cause resource group assignment rules to fail.
If you set the gpcc.query_tags parameter inside of a transaction, you must commit the transaction before the new query tags are used to evaluate assignment rules.
You can set the value of the gpcc.query_tags parameter using the SET command, as in the example above, or as a connection parameter with database clients that support it, such as psql. Following are two examples that show how to specify query tags on the psql command line.
$ PGOPTIONS="-c gpcc.query_tags=appName=tableau;appUser=bi_sales" psql
$ psql postgresql://mdw:5432/postgres?options="-c gpcc.query_tags%3DappName%3Dtableau;appUser%3Dbi_sales"
In the second example, it is necessary to code the equals signs as %3D to prevent psql from interpreting the query tags as command-line arguments.
psql -c command does not work because resource group assignment occurs before the command specified with the
-c option is executed. For example, this command will not have the desired effect.
psql -c “SET gpcc.query_tags TO ‘appName=tableau;appUser=bi_sales’; SELECT * FROM sales_data;”
Monitoring Workload Rules
The Logs section displays a row of information for each instance where a query or idle session both matched a workload rule and triggers the workload rule conditions to perform an action. Note that query assignment rules are not currently logged in this section.
Columns of the log entry provide details about how the rule was applied:
Actions Summarizes the rule actions that were taken for the specified query ID.
Resource Group The resource group that matched the query or idle session rule.
Role The database role of the query session.
Rule The ID number of the rule. This ID matches an ID from the list of Rules on this page. Place your cursor over the ID to display a summary of the rule conditions that were in effect when the action was triggered.
Status Indicates whether the rule’s action succeeded or failed.
Execution Time The time when the rule action was performed.