The infrastructure providing network connectivity to an HCX deployment (the Underlay) must meet the minimum requirements. The underlay includes any intermediate system that is customer managed, cloud provider managed, or part of an Internet service provider network.
What Is the Network Underlay
A network underlay provides the physical or logical connectivity on which HCX transport packets are tunneled, where an HCX transport packet contains an overlay header. The underlay network does not need to know that it is carrying HCX transport packets. This includes the physical routing infrastructure on the customer data center and (if applicable) the cloud provider infrastructure, and any physical network services joining the connected locations.
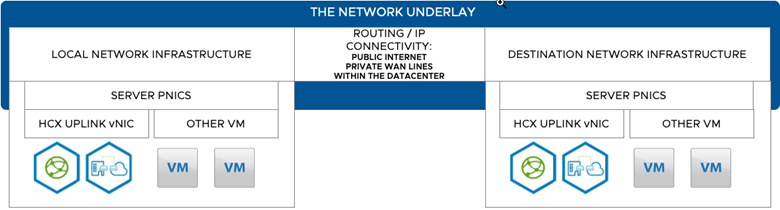
A network underlay can vary from high-bandwidth low-latency private paths between server racks in a data center, to lower-bandwidth higher-latency Internet based connectivity. In this document, the term "network underlay" encompasses all elements that affect the performance characteristics of an underlay, including the servers and network devices and connections between the vSphere environments. The network underlay requirements must be satisfied when considering all elements of the underlay.
VPN Based Network Underlays
Virtual Private Networks are frequently used for creating secure network connection to private and public vSphere clouds over the Internet. SDWAN and custom tunneling solutions are used over the internet to improve data traffic transmissions. The SDWAN, VPN, and other tunneling solutions are collectively referred to as VPN in this document.
The network underlay includes connections with VPN configurations. The network underlay requirements must be satisfied when considering all elements of the underlay.

General Network Underlay Requirements
HCX supports multiple uplinks and each uplink can be connected to a different network underlay. Examples of different network underlays include private line, public Internet, and multi-homed connectivity.
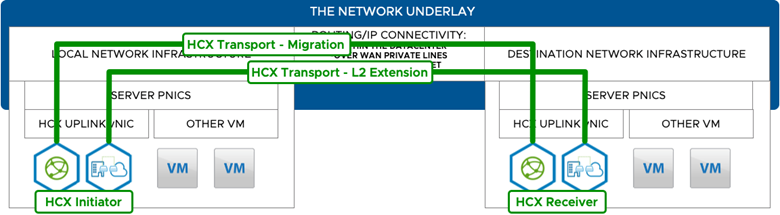
The following table summarizes the requirements from the Network Underlay to use the HCX migration and extension services:
This table applies to HCX Migration and Extension Overlays (HCXService Mesh appliances).
This table does not apply to HCX Connector or HCX Cloud Manager or the management connections.
HCX Requirement ID |
Requirement Summary |
Requirement Details |
|---|---|---|
hcx-overlay-req-1 |
IP Addressing & IP Reachability |
Requires a valid IP address and IP connectivity for end to end communication between the HCX Uplink IP at the source site and the destination site. |
hcx-overlay-req-2 |
Bandwidth, Loss and Latency, MTU |
All underlays must comply with minimum parameters requirements for services to be supported at the minimum performance level. The minimum requirement applies to all network underlays and is provided in the next table. MTU configuration must be applied to the HCX Site Resource Profile prior to deploying the IX/WO appliances. If the MTU is changed on existing appliances, the appliances must be redeployed.
|
hcx-overlay-req-3 |
Source Network Address Translation (SNAT) |
SNAT is not required, but can be used to translate HCX Uplink private IP packets to public IP addresses for connections over the Internet. SNAT can only be applied to the HCX Initiator (the HCX source appliances). |
hcx-overlay-req-4 |
Destination Network Address Translation (DNAT) Load Balancing Reverse Proxy |
Inbound DNAT, load balancing, or reverse proxy configurations in the underlay are not supported for the HCX Migration and Extension Transport tunnels. |
hcx-overlay-req-5 |
VPN |
Any VPN configuration in the network path is treated agnostically as an underlay, and is supported while the measured underlay parameters meet the documented requirements. Any additional encapsulation and performance degradation, overhead, or cost in addition to the characteristics of the underlay they ride on must be considered when measuring underlay outcomes. HCX does not support VPN configurations where the NSX Tier-0 router provides the VPN termination AND connectivity to the HCX Manager uplinks through NSX Service Insertion. |
Minimum Network Underlay Requirements for HCX
HCX has network underlay minimums for HCX migration and disaster recovery operations. HCX operations with lesser performance than the minimum values are not supported.
The table below lists the minimum requirements for individual operations at minimum performance. For vMotion and Replication Assisted vMotion, the bandwidth requirement varies based on whether the WAN-Optimization service is running in the Service Mesh for the site pair. WAN Optimization can improve the network performance through a combination of deduplication, compression, and line conditioning techniques..
In addtion to activating the WAN Optimization service in the Service Mesh, review these additional considerations related to network bandwidth performance:
-
Minimizing latency, loss, jitter can result in improved migration performance outcomes.
-
Parallel HCX operations (migration and extension) can result in increased bandwidth requirements.
| Network Parameter |
HCX vMotion (IX) |
HCX Assisted vMotion (Direct) | Replication Assisted vMotion |
Bulk Migration & DR (Protection) |
OS Assisted Migration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min Bandwidth (Mbps) |
150 with WAN Optimization 250 without WAN Optimization |
250 | 150 with WAN Optimization 250 without WAN Optimization |
50 |
50 |
| Min MTU (bytes) (1350 if version < HCX 4.2) |
1150 |
1500 | 1150 |
1150 |
1150 |
| Max Packet Loss (%) |
0.1 |
0.1 | 0.1 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
| Max Latency (ms) |
150 |
150 | 150 |
150 |
150 |
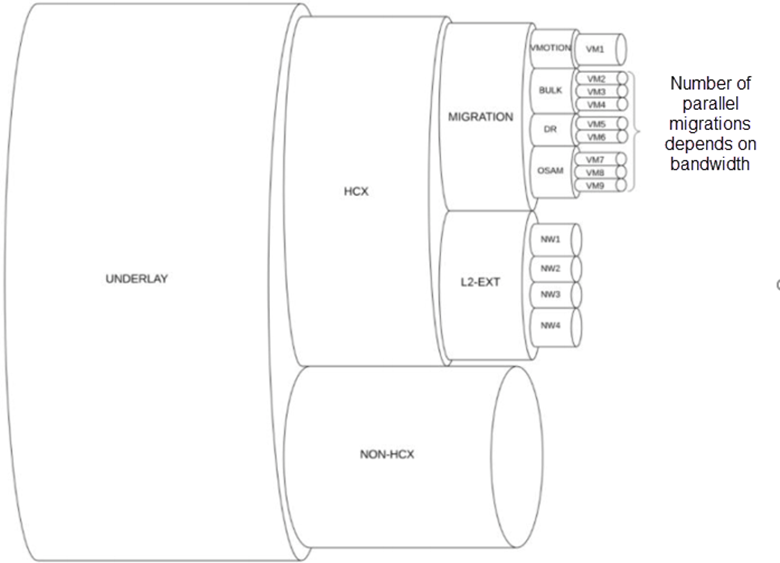
Bandwidth distribution with HCX Manager on a network underlay can be visualized as a set of nested pipes, where the underlay network is the main channel. HCX Manager and non-HCX Manager traffic is carried through main channel. Migration and Network Extension traffic can be thought of as separate pipelines through the site manager channel. The Network Extension pipe provides the throughput for all the extended network traffic. The migration pipe handles the vMotion, Bulk, Protection, and OS Assisted Migration service traffic.
The number of parallel migrations allowed depends on the bandwidth of the migration pipe.