Network Profiles are a sub-component of the Compute Profile. When a service mesh is created, the network profile configurations are used to connect the deployed HCX appliances.
Introduction to Network Profiles
Network Profiles can be pre-created in the Network Profile tab or they can be created during the Compute Profile configuration. A Network Profile contains:
-
One underlying vSphere Port Group (VSS or VDS) or NSX-based network.
-
IP address information: gateway IP, the network prefix and MTU, and DNS.
-
A pool of IP addresses reserved for HCX to use during Service Mesh deployments.
Characteristics of Network Profiles
Network Profile configurations are only used during Service Mesh deployments (IP addresses assigned to the IX and NE, and OSAM appliances).
The HCX Manager only uses a Management interface, it does not use other Network Profile networks.
A Compute Profile always includes one or more Network Profile.
When Service Mesh is deployed, every Network Profile that is included in the Compute Profile configuration is used.
When a Network Profile network is used in a Service Mesh, the HCX appliance consumes a single IP address out of the configured IP pool.
When a Network Profile is assigned to a specific HCX traffic type (the traffic types are explained in the next section), a single IP address is used. For example, if the same Network Profile is assigned for HCX Management and HCX Uplink, one IP address is used, not two.
A Network Profile can be used with multiple Compute Profiles.
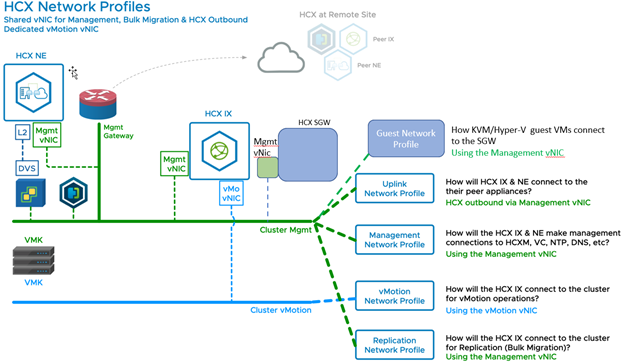
HCX Traffic Types
Consider the Network Profile traffic types are like a router's uplinks and downlinks. The HCX-IX (mobility) and the HCX-NE (extension) appliances have "uplinks" and "downlinks". The HCX "uplink" is used to connect the IX or NE to its remote peer, the "downlink" traffic types (Management, vMotion, Replication) connect the IX or NE to the local environment.
HCX Network Profile Types |
Description |
|---|---|
HCX Uplink |
Used by Service Mesh components to reach their peer appliances.
Important:
When destination HCX systems need to be reachable over the Internet, use the Uplink Network Profile to assign the Public IP addresses. Destination NAT configurations are not supported. The source HCX systems don't need Public IP addressesand can be configured using traditional SNAT. |
HCX Management |
Used by Service Mesh components to connect to HCX Manager, vCenter Server, NTP, DNS. |
HCX vMotion |
Used by Service Mesh components to connect to the ESXi cluster for vMotion-based services. |
HCX Replication |
Used by Service Mesh components connect to the ESXi cluster for Replication-based services.
Note:
This NP type is compatible with ESXi vSphere Replication VMkernel traffic but cannot be used for vSphere Replication NFC VMkernel traffic. |
HCX Guest Network |
In OSAM deployments, used by the Service Mesh Sentinel Gateway to connect to the Sentinel agents. |
HCX Traffic Types and HCX Appliances
The table describes which NP traffic types are used by the different HCX appliances.
One IP address is assigned per traffic type.
(For example, if all HCX-IX traffic types are configured to use a single network, a single vNIC with a single IP address is assigned. If a dedicated network is configured for each possible IX traffic type, then the HCX-IX uses four vNICs with an IP in each network. These wiring variations are described in the examples section, after the table.
HCX Appliance |
Traffic Types Used |
|---|---|
HCX-IX (Migrations, DR) |
|
HCX-NE (Network Extension) |
|
HCX-WO (WAN Optimization) |
|
HCX-Sentinel Gateway (OSAM) |
|
HCX-Sentinel Data Receiver |
|
Network Profile Configuration Examples
The following examples depict how the HCX Service Mesh appliances might be wired up.
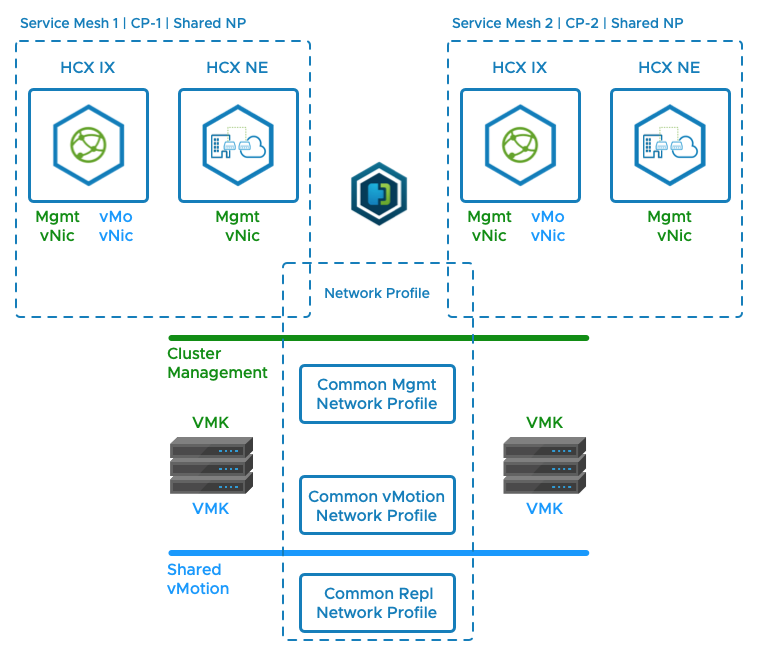
In fully private HCX deployments where the environments are inside of the same private network, it is typical for the source HCX and the destination HCX network profiles to be structured identically.
It is possible (and common) for the Network Profile configurations to differ at the source and destination when they are separated by the Internet. The reason for this is that the destination HCX Service Mesh appliances must have an HCX Uplink network profile with Public IP assignments (this requirement is not true at the source, where internal addresses can use source NAT for Internet access).
HCX Network Configuration 1 - Shared Management, Replication and Uplink with Dedicated vMotion
-
This configuration trades the benefits gained from separation of traffic to simplify deployments. The same network is selected for Management, Uplink and Replication traffic.
-
This configuration requires the management IP addresses assigned to destination HCX appliances at the destination to be fully reachable from the source HCX appliances without NAT translation. Because of this requirement, this configuration is most typical in HCX deployments fully within a private network.
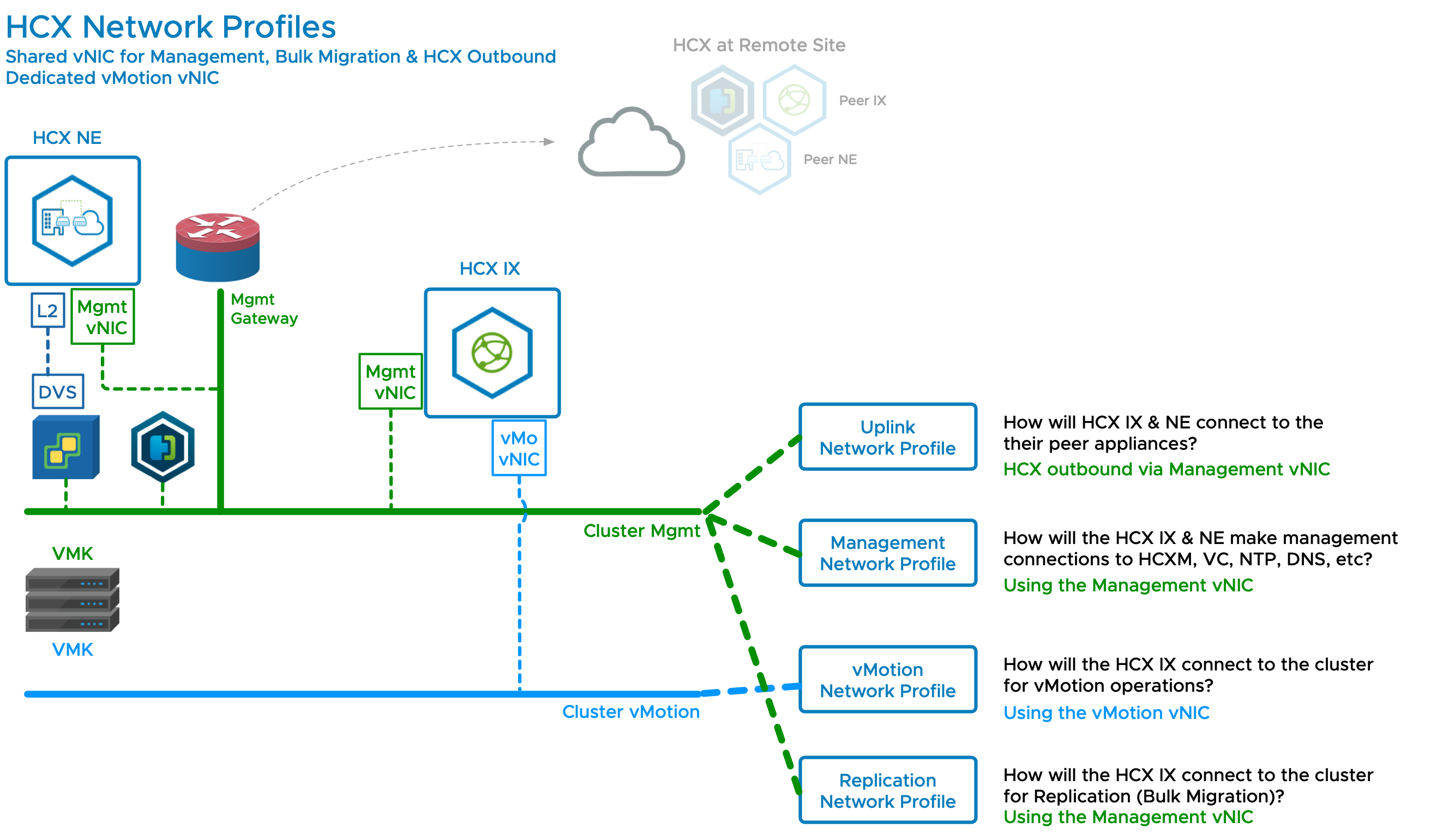
HCX Network Configuration 2 - Dedicated Replication Network
Configuration 2 adds a dedicated network for the Replication traffic (HCX Bulk Migration).
This configuration variation is only possible when the cluster hosts use a dedicated Replication VMkernel network (the option to add a Replication VMkernel adapter was added in vSphere 6.0, so it is not as common as having a vMotion VMkernel adapter).
Separating the replication traffic is a recommended practice. This configuration is used when a dedicated replication VMkernel interface is available.
-
Important:
In deployments where ESXi servers use a dedicated VMkernel configuration for vSphere Replication services, the HCX Interconnect uses a Network Profile configuration dedicated to the vSphere Replication traffic. This configuration does not include the vSphere Replication NFC traffic. HCX always uses its Management interface for vSphere Replication NFC traffic.
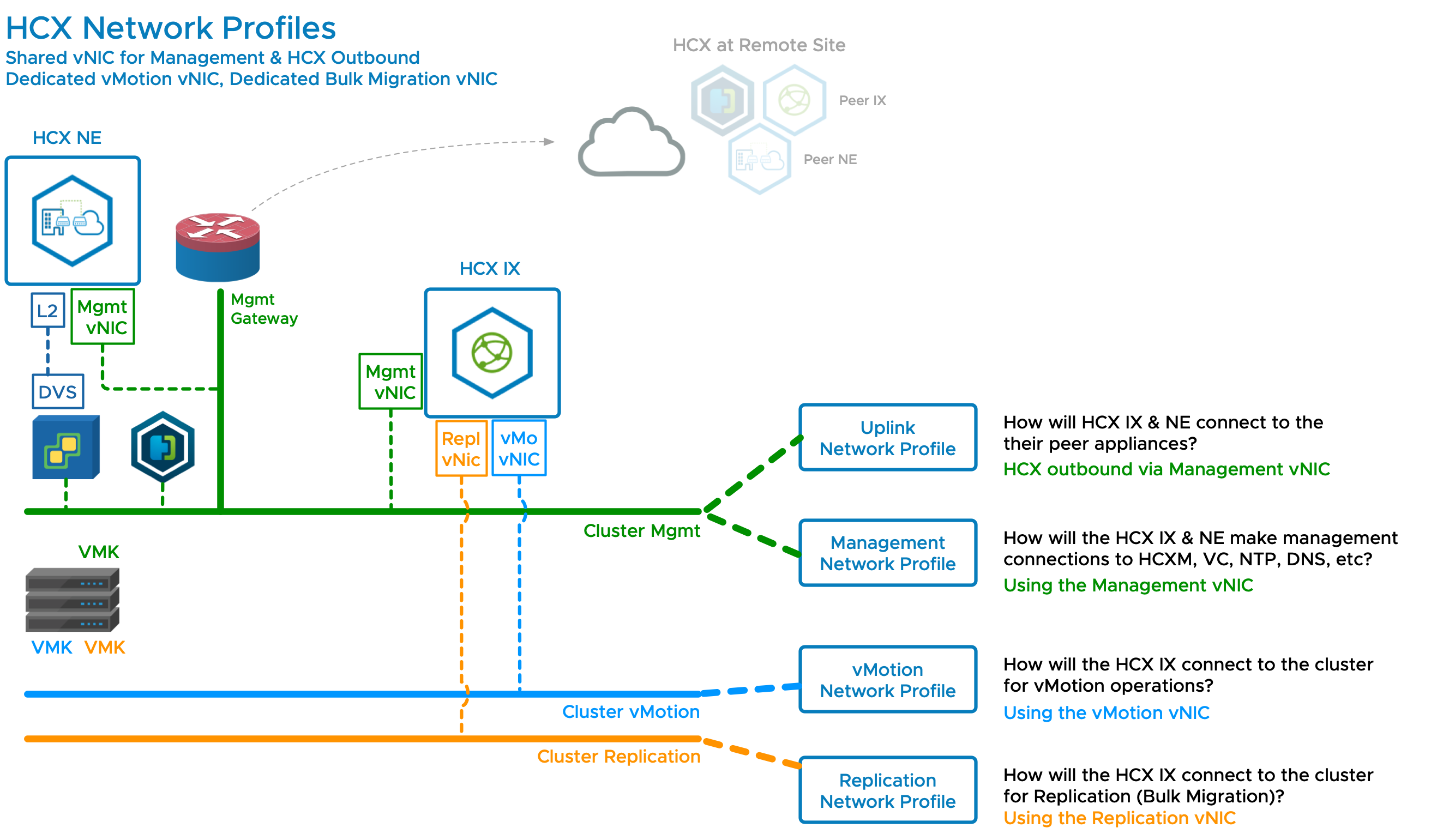
HCX Network Configuration 3 - Dedicated Uplink Network
Configuration 3 adds a dedicated network for HCX Uplink traffic (HCX Service Mesh Transport traffic).
This configuration trades simplicity of deployment (see configuration 1) for the benefits of separating the uplink and the management traffic.
A dedicated uplink network is a good way to isolate the migration traffic for applying Qualityof Service (QoS).
A dedicated uplink can be used to consume bandwidth/networks dedicated to the migration project.
For deployments over the Internet:
Public IP addresses are assigned at the destination using the HCX Uplink network profile.
The source HCX appliances can use traditional Internet SNAT to securely connect to the destination public IP addresses using strong encryption.
Public cloud providers leverage this configuration to make HCX services easy to deploy before dedicated private circuits become available.
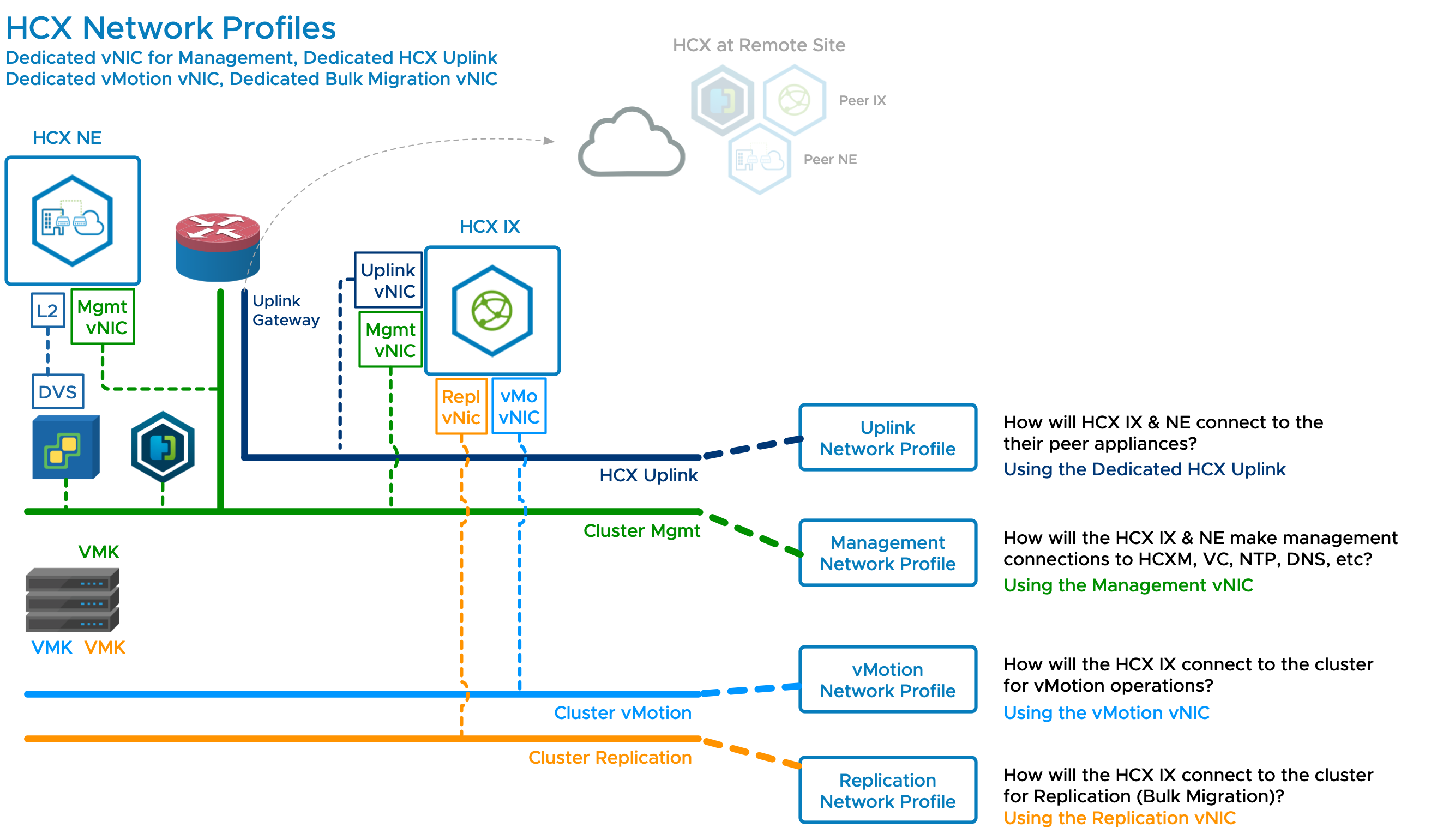
HCX Network Configuration 4 - OS Assisted Migration Using Guest Network
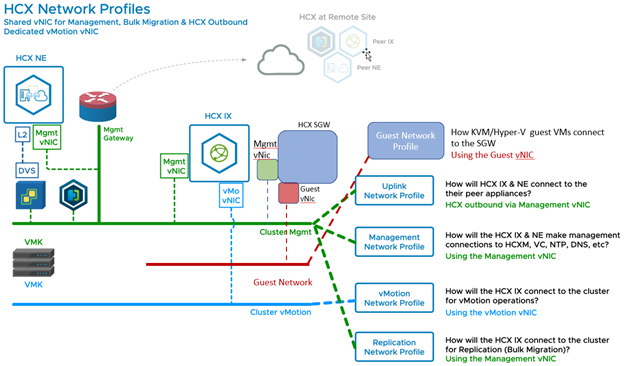
HCX Network Configuration 5- OS Assisted Migration Using Management Network
Configuration shows OS Assisted Migration networking when using the Management Network for the Guest Network function.