This section provides an overview of workload traffic flows using HCX Network Extension with and without Mobility Optimized Networking.
Use Cases for Mobility Optimized Networking
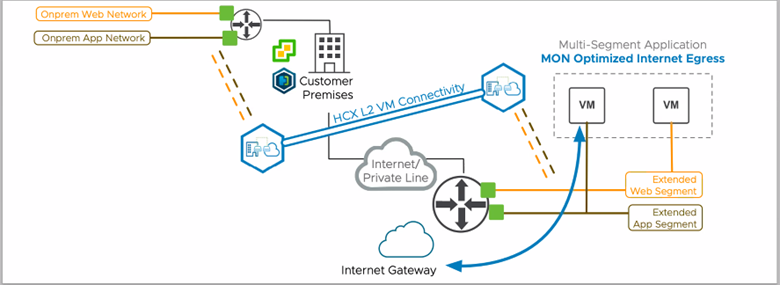
MON improves network performance and reduces latency for virtual machines that have been migrated to the cloud on an extended L2 segment. MON provides these improvements by allowing more granular control of routing to and from those virtual machines in the cloud.
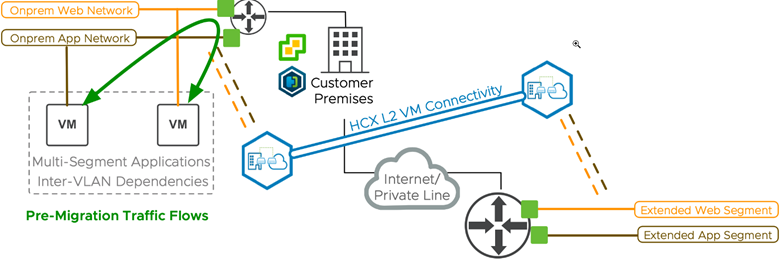
Without MON, HCX Network Extension expands the on-premises layer-2 network to the cloud SDDC while the default gateway remains at the source. The network tromboning effect is observed when virtual machines in the destination connected to different extended segments communicate.
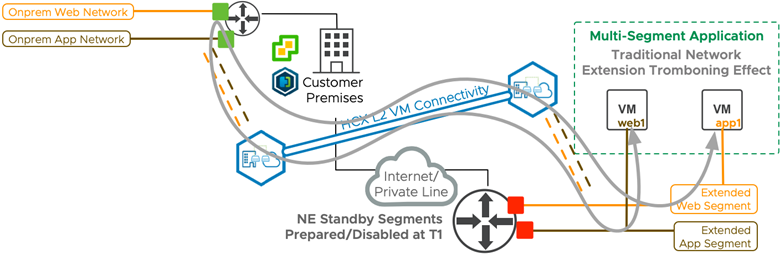
MON enables migrated virtual machines to reach segments within the SDDC without sending packets back to the source environment router.
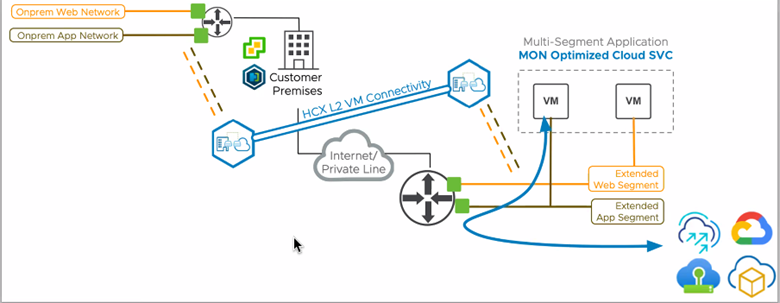
MON can be configured to allow migrated virtual machines to reach services hosted within a public cloud.
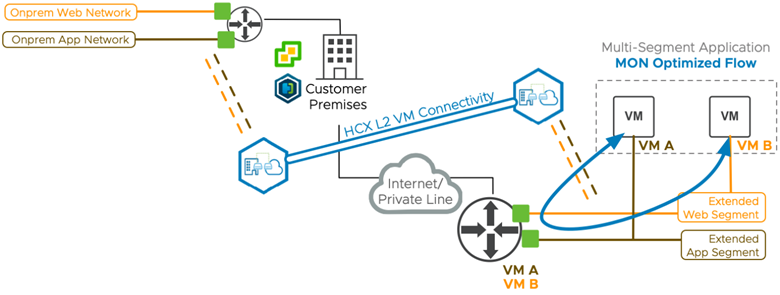
MON enables migrated virtual machines to use the SDDC Internet interface (with SNAT).
Mobility Optimized Networking Outcomes by Migration Type
HCX Bulk-migrated virtual machines are automatically MON-enabled in the SDDC.
HCX vMotion- and RAV-migrated virtual machines use the on-premises gateway until they are specifically configured to use the cloud gateway in the HCX UI/API.
Virtual machines attached to the segment prior to enabling MON use the on-premises gateway until they are specifically configured to use the cloud gateway in the MON interface.
Mobility Optimized Networking Operation
Network Extension with Mobility Optimized Networking provides the following functionality:
Enable or deactivate MON at the time of stretching a network.
Enable or deactivate MON for already extended networks.
Enable or deactivate MON on an individual VM basis for VMs residing on extended networks in the SDDC.
Display which VMs are using MON.
When using HCX to vMotion a VM, preserve existing network connections while providing the option to activate Mobility Optimized Networking on that VM after migration.
Configure MON Route Policy to define on-premises (non-SDDC) subnets or exception/deny subnets for local egress.
The following process explains what happens during the various phases of Mobility Optimized Networking.
Mobility Optimized Networking is enabled for an HCX extended segment.
HCX enables the network ID (gateway IP) in the SDDC Compute Gateway. It is enabled with a limited /32 255.255.255.255 network mask.
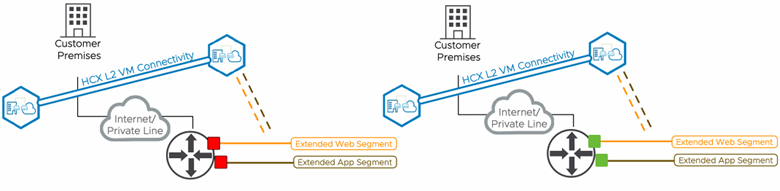
Static routes are added in the SDDC Compute Gateway for migrated virtual machines on HCX extended network.
HCX adds reachability information for the migrated virtual machine (in the form of a virtual machine specific static route) to the SDDC Compute Gateway, allowing reachability within the SDDC. This VM static route is not advertised to the on-premises environment. The HCX L2 path is used to reach subnets not in the SDDC.
Using SDDC forwarding technology, the virtual machine uses the SDDC Compute Gateway to reach the SDDC networks.
For reachability outside of the SDDC tier-1, the MON policy configuration is evaluated according to the MON policy configuration. Matching subnets are sent to the original premises router. Nonmatched subnets are sent to the SDDC tier-0 router. For more information on MON policy routes, see Mobility Optimized Networking Policy Routes.