The cloud file system provides cloud storage for snapshot replication that enables disaster and ransomware recovery on a recovery SDDC.
Summary
| Cloud File System Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Details | Shows the name of the cloud file system and the availability zone where you deployed it. |
| Capacity | Protected capacity. The billable amount of storage capacity used by protected VMs and their snapshots. |
| Protected sites | Lists the number of protected sites (on-premises or VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC) replicating snapshots to this cloud file system. |
| Protection | The Protection panel shows the following information:
|
| Recovery |
The Recovery panel shows the following information:
|
Capacity Utilization and Storage Space Reclamation
On the cloud file system, capacity usage is computed as part of a background storage space reclamation job that runs every 13 hours. When a large amount of data gets added to or removed from the cloud file system, storage space reclamation can take a long time, so storage capacity might not get updated in 13 hours. You would see old space usage in the UI, and VMware Live Cyber Recovery charges based on space usage information.
For example, if a large amount of data gets written to the cloud file system, space reclamation might run longer and you won't be charged for this new data until the space reclamation job is completed.
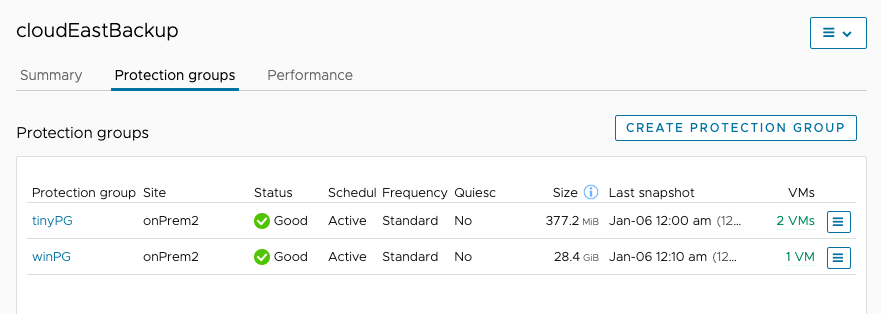
Protection Groups
The Protection groups tab for a cloud file system shows all protection groups that are replicating VM snapshots to the selected cloud file system. The list displays protection groups by name and shows their status, schedule, frequency, and other useful information.
Performance
You can view the following performance information about a cloud file system and any VMs running live on it:
| Live VM performance | Description |
|---|---|
| IOPS |
Input/Output Operations Per Second (IOPS) measures the number of read and write commands a storage device or medium completes every second for all workloads on the cloud file system datastore. IOPS also indicates the average KiB size for each read or write operation, measured in Kibibytes (KiB). |
| Throughput |
The data transfer rate to and from the cloud file system datastore, measured in kibibytes (KiB) or Mebibytes (Mibs). Measures the total amount of data that moves along the network path. |
| Latency |
The time it takes for an IOPS request to complete, measured in milliseconds (ms). |
| Cache hit rate |
A measurement of how many content requests the cloud file system NVMe cache can fulfill successfully, compared to how many requests it receives. A cache hit ratio of 90% and higher means that most of the requests are satisfied by the cache. A value under 80% indicates a working set that is substantially larger than supported by the cache. |
| Replication throughput |
The current data transfer rate of all currently running snapshot tasks replicating to the cloud file system datastore, measured in kibibytes (KiB). Measures the total amount of data that moves along the network path. |