This topic explains how AKO is deployed on vSphere with Tanzu with VDS.
AKO in vSphere with Tanzu
When using VDS as the networking option for vSphere with Tanzu (TKGs), AKO will automatically be deployed into the Supervisor cluster to handle L4 workloads in VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer. This para-virtualized AKO will manage the L4 workloads in both the Supervisor cluster and each of the workload clusters.
Additionally, AKO can be manually deployed through the helm into the workload cluster to support L7 Ingress workloads.
For more information, see Install NSX Advanced Load Balancer.
AKO Compatibility
When deploying AKO through helm in the workload cluster, the VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer version must be compatible with the AKO release. For more information, see Compatibility Guide for AKO.
Deployment Guide
AKO can be installed on any workload cluster through helm to handle the L7 Ingress workloads.
Deploying the NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controller
For more information on deploying the NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controller (or Cluster of Controllers), see Installing NSX Advanced Load Balancer in VMware vSphere Environments topic in the VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer Installation Guide.
Configuring vCenter Cloud on VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer
The point of integration with VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer and vCenter is called a cloud. For the vCenter environment, a vCenter cloud must be configured. For more information on configuring vCenter cloud, seeInstalling NSX Advanced Load Balancer in VMware vSphere Environments topic in the VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer Installation Guide.
Configuring VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer IPAM Profile
The VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer allocates IP addresses from a pool of IP addresses within the subnet configured. After creating the profile, modify the vCenter cloud and add the profile as shown below.
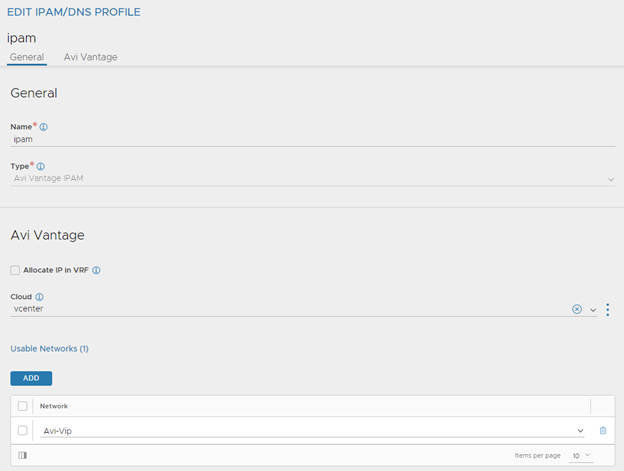
For more information, see Configuring NSX Advanced Load Balancer IPAM topic in the VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer Installation Guide.
Configuring VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer DNS Profile
AKO uses FQDN and path-based routing. It must be authoritative in the specified domain. After creating the profile, modify the vCenter cloud, and add the profile as shown below.
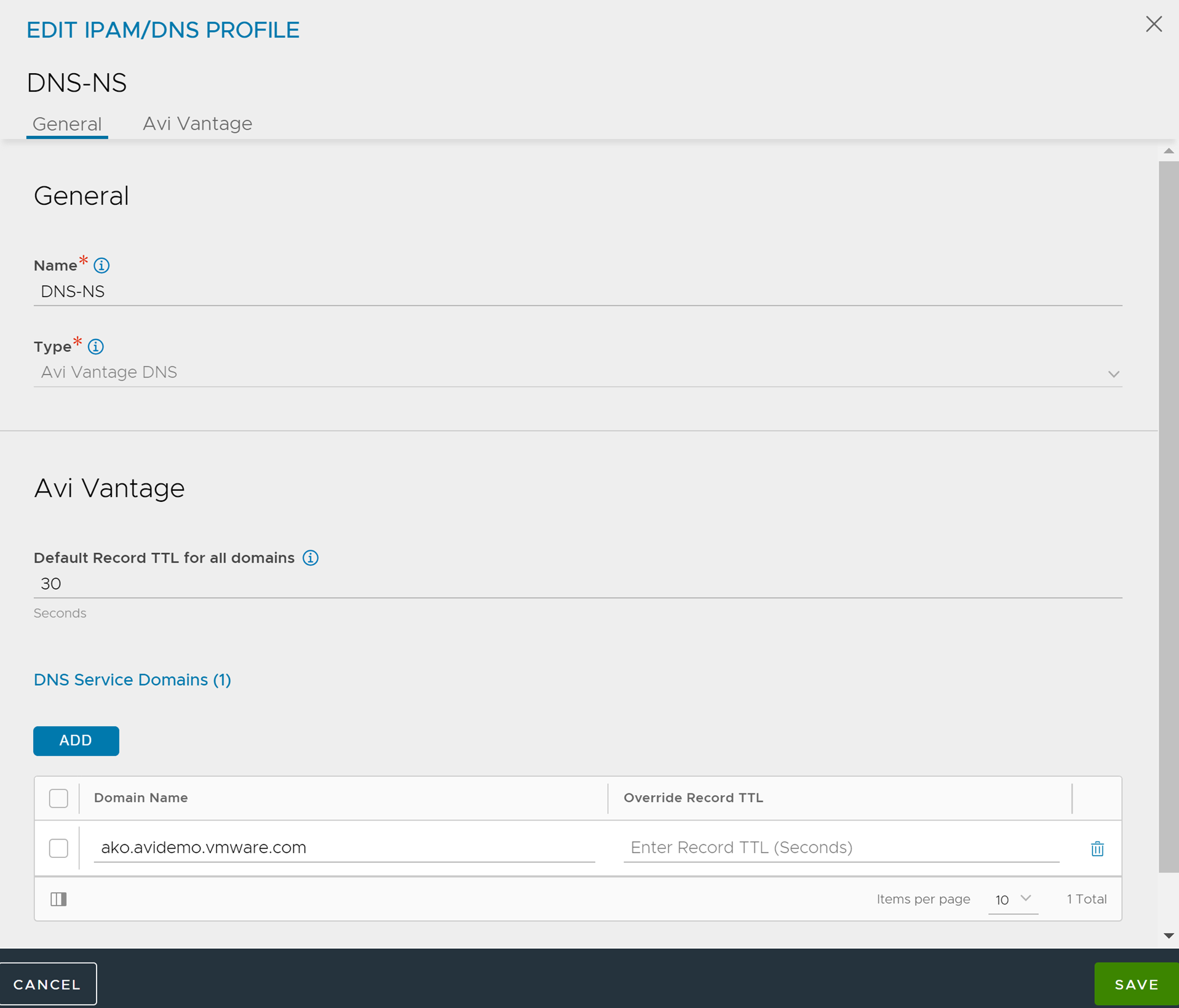
For more information, see Configuring NSX Advanced Load Balancer IPAM topic in the VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer Installation Guide.
Installing Helm on the Workload Cluster
Helm is an application manager that facilitates the installation of packages in a Kubernetes environment. AKO requires a helm for installation. For more information on install commands, see Installing Helm.
Pod Routing
Kubernetes Ingress traffic can be routed to the pods in the following ways:
ClusterIP
NodePort
NodePortLocal
ClusterIP
In ClusterIP mode, the VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer SEs will route directly to the Pod IPs. For this to work, the VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer will configure static routes on the SEs for the internal Kubernetes cluster network. With this design, VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer can check health of each pod individually and provide application persistence at the application level. However, this design requires a new SE Group per cluster since each SE Group will have its own static routes to each Kubernetes cluster. Additionally, the VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer SEs must have a vNic in the Kubernetes node network.
NodePort
In NodePort mode, the VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer SEs will route to the Kubernetes service. No static routes are required, as the service will be externally reachable through the NodePort. This design allows for the reuse of the SE Group since no static routes to the Kubernetes nodes are required. However, this design limits monitoring and persistence because most of this is handled by kube-proxy.
NodePortLocal
In NodePortLocal mode, the VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer SEs will route directly to the pods through a nodeport. Each pod is directly exposed as a NodePort. No static routes are required with this design since the NodePorts are externally routable. Additionally, this design will allow the reuse of SE Groups.
Installing AKO on the Workload Cluster
AKO is installed through helm using a values.yaml file with various parameters specific to the environment. For more information, see values.yaml. When using VDS in the TKGs environment, the below parameters must be configured:
AKOSettings.clusterName: cluster-1. Create a Unique cluster name for each cluster.
AKOSettings.layer7Only: true. Set this to
true. The VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer will handle the L7, and VDS will still handle the L4.NetworkSettings.vipNetworkList: Define the VIP Network List.
L7Settings.serviceType: Set this to either ClusterIP (default) or NodePort.
ControllerSettings.serviceEngineGroupName: Default-Group
ControllerSettings.controllerVersion: 22.1.2
ControllerSettings.cloudName: vcenter-cloud
ControllerSettings.controllerHost: ‘’
ControllerSettings.tenantName: admin
Avicredentials.username: username
Avicredentials.password: password
After configuring the necessary parameters in the values.yaml file, install AKO using the following command:
helm install ako/ako --generate-name --version 1.10.1 -f values.yaml namespace=avi-system
For complete installation steps, see Install Avi Kubernetes Operator.
Validating the AKO Installation
This optional step will validate the AKO pod running in the avi-system namespace. Use kubectl get pods -n avi-system command to show ako-0 pod. Below is an example of the output:
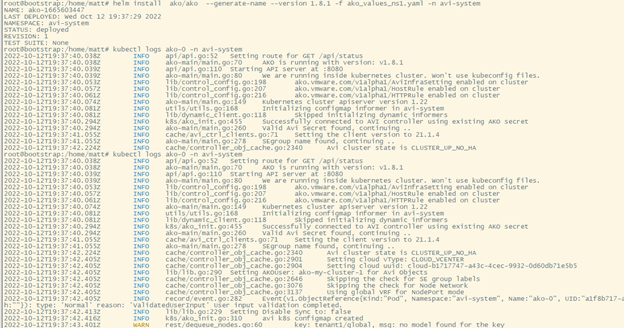
Deploying an Ingress
AKO is now installed and configured for L7 Ingress. After creating the first ingress, the appropriate objects are created in the NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controller and an SE is automatically be deployed (if not configured already) to handle the L7 load balancing.