This section explains the NAT feature on NSX Advanced Load Balancer Service Engine.
This feature is not supported for IPv6.
NAT will function in the post-routing phase of the packet path in the SE. It is recommended to check the SE default gateway (IP routing on Service Engine) feature. For more information, see Default Gateway (IP Routing on NSX Advanced Load Balancer SE).
Enabling IP routing on Service Engine and using the SE as the gateway is a necessary prerequisite to use the outbound NAT feature. Hence all necessary requirements for enabling IP routing on the Service engine is also applicable to the outbound NAT feature.
Outbound NAT is supported for TCP/ UDP, and ICMP flows.
NAT Guidelines
NAT is VRF-aware and must be programmed per SE group using a network service of Routing Service type. For more information, see Network Service Configuration.
NAT/ IP routing is supported on two-armed, no-access configurations of Linux server clouds and VMware clouds.
NSX Advanced Load Balancer supports NAT for VMware Cloud deployments in write access mode. For this feature to work on VMware write access clouds, at least one virtual service must be configured with the following configurations:
One arm (in the two-arm mode deployment) must be placed in the back end network. For this network, the SE acts as the default gateway.
The other arm is placed in the desired front end network.
The SE group of the network service must be in legacy HA (active/ standby).
The routing service must have enabled the routing set.
NAT functionality is done by Service Engine IP stack, so the
routing_by_linux_ipstackattribute of Routing Service must be set to False.Only DPDK-based SEs are allowed.
On VMware write access mode, the virtual service must be created. This virtual service creates the required Service Engines.
NAT IP of a NAT Rule cannot be the same as any interface IP present in the VRF. Such NAT IP will be ignored.
NAT IP is configured on an interface as a secondary IP. Hence different Service Engine groups can not share a NAT IP in a given VRF.
NAT Service
The diagrammatic representation of NAT service traffic initiated from inside to outside is as follows:
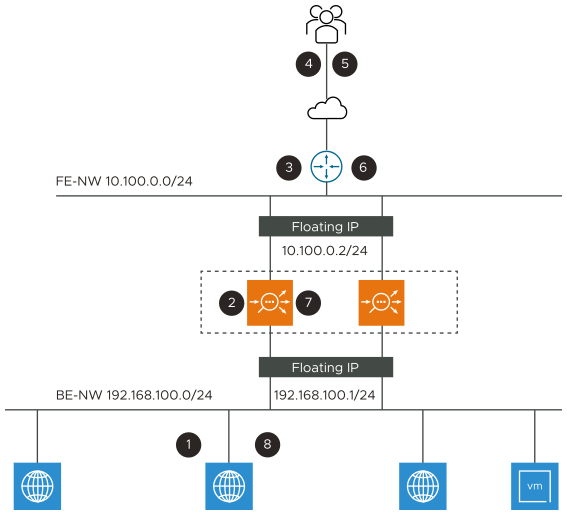
The flow details mentioned in the diagrammatic representation of NAT service traffic is from 1 to 8. The details of the flow are as follows:
Flow Count |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
The server ARP's for DG and gets MAC-A. The server sends IP packet to MAC-A. [S:IP-SX, D:IP-Ext] |
2 |
Service Engine creates a NAT entry since this is a new flow, does NAT of src-IP and sport and sends packet to router (MAC-R). [S:SE-NIP, D:IP-Ext] |
3 |
Router uses internet routing to forward to Ext. [S:SE-NIP, D:IP-Ext] |
4 |
Ext receives the packet sent by SX. [S:SE-NIP, D:IP-Ext] |
5 |
Packet received by destination. [S:IP-Ext, D:SE-NIP] |
6 |
Router ARP's for SE-NIP and SE-Active responds to ARP. [S:IP-Ext, D:SE-NIP] |
7 |
SE looks up NAT flow table and based on the match, it changes the dst-IP:port to real server IP port. [S:IP-Ext, D:IP-SX] |
8 |
SE does IP routing and sends packet to MAC-SX. [S:IP-Ext, D:IP-SX] |
The router acts as a front end floating IP for the SE group. SE backend network is not routable on the front end.
In the floating IP, the back end network is not routable on the front end.
NAT requires the following configurations at various points in the network:
On the NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controller, you can Enable IP Routing in the Service Engine group (only Legacy HA) in Advanced tab configuration.
On the front end router, configure static routes to the back end server networks with the next-hop as floating IP in the front end network.
On the back end router, configure the SE’s floating IP in the back end server network as the default gateway.
Configuring NAT Policy using UI
The following are the steps to configure NAT policy:
Navigate to . Click CREATE.
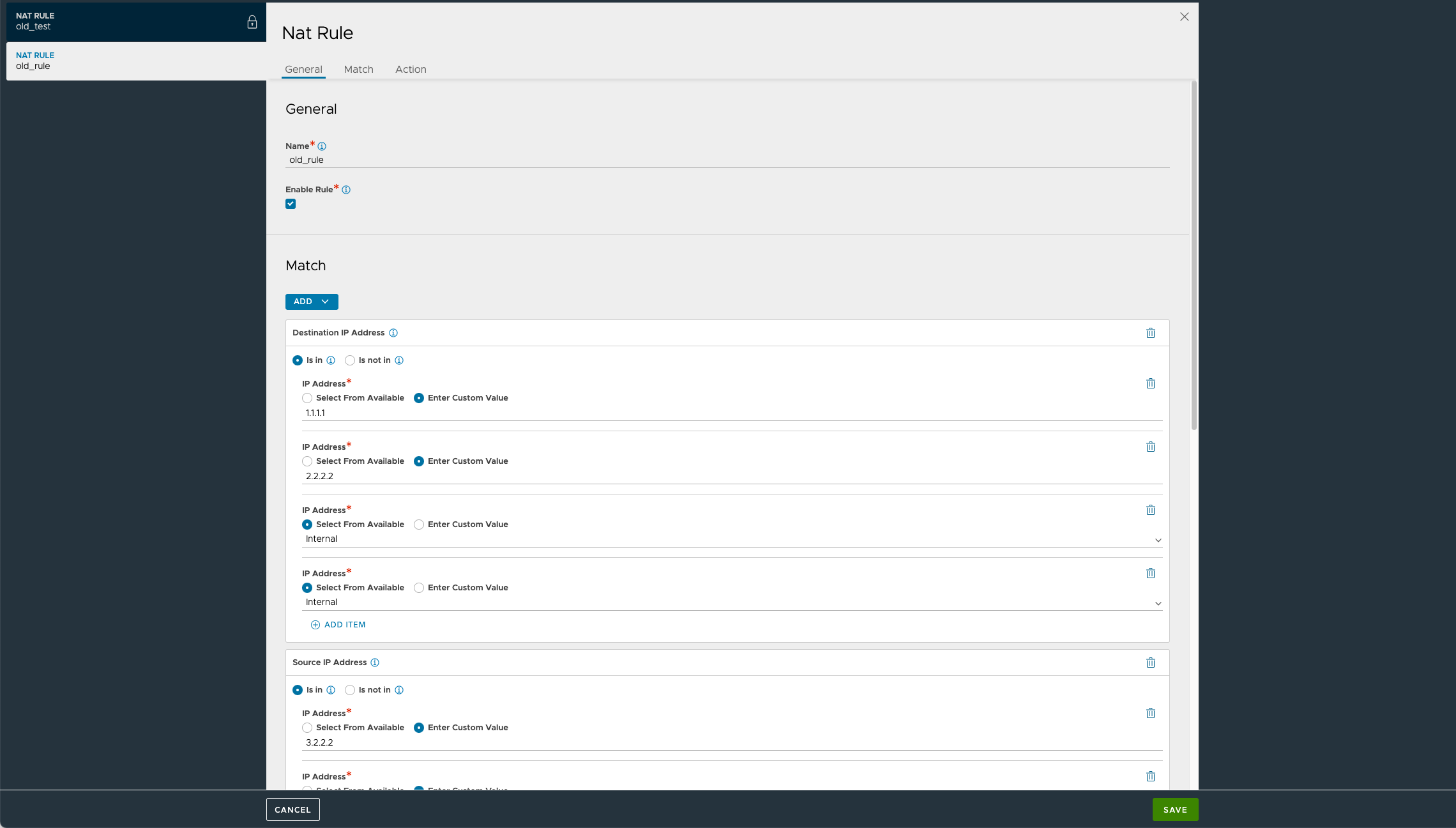
Specify the name of the NAT policy.
Check Enable Rule box.
Specify the Destination and Source IP address in the Match tab.
Under the Action tab, select the Type.
- Dynamic IP and Port:
-
This option helps Source IP NAT with Port-Address Translation for packets originating from the Internal Network. This applies to TCP, UDP, and ICMP protocol packets.
- Dynamic IP and Preserve Port
-
This option (supported from NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controller version 22.1.6) helps in preserving the source-port of packet coming from Internal Network. So, this action does only Source NAT of the IP without doing the Port-Address Translation.
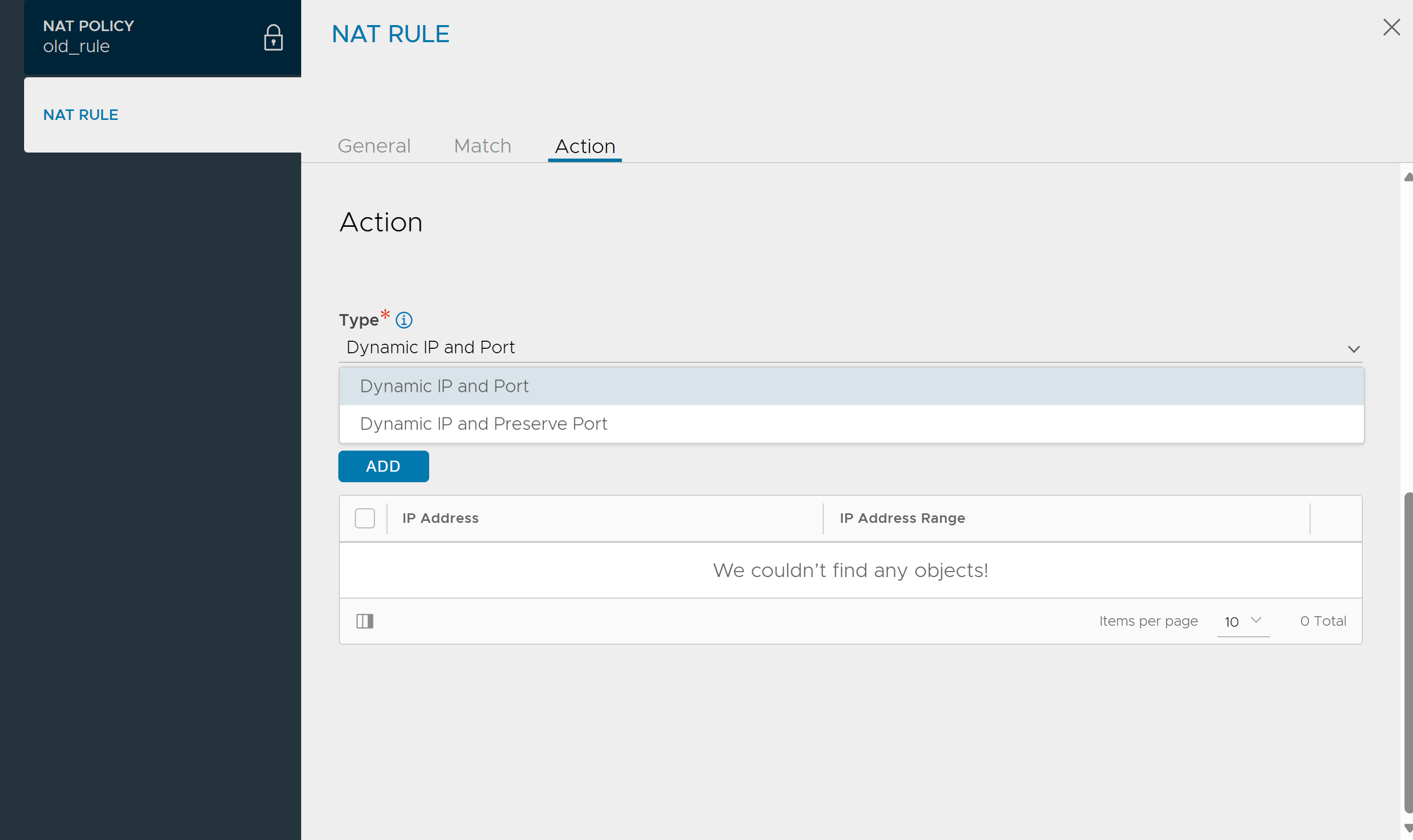
Note:The Dynamic IP and Preserve Port Action Type is applicable only for matching rules, specifically for UDP traffic.
Click Save after specifying the necessary details.
Configuring NAT Policy using CLI
You can configure NAT policy as follows:
Assume 10.100.0.78 is the destination-IP on which the server is trying to reach, 10.100.0.26 is the NAT IP. This IP is owned by Service Engine. Note that the NAT IP has to be configured as a static route on the front end router with next-hop as front-end floating-interface-ip (10.100.0.2) of the SE.
configure natpolicy nat-policy-default-group-global rules index 1 enable name rule1 match source_ip match_criteria is_in addrs 192.168.100.21 ranges begin 192.168.100.2 end 192.168.100.10 save prefixes 192.168.100.1/24 save destination_ip match_criteria is_in addrs 10.100.0.78 save services destination_port match_criteria is_in ports 80 ports 443 save source_port match_criteria is_not_in ports 800 save save save action type nat_policy_action_type_dynamic_ip_port nat_info nat_ip 10.100.0.26 save save save saveAssume that the Service Engine Group name is set to DefaultGroup with SE-interfaces present in VRF global.
Create a NetworkService that has a NAT policy.
configure networkservice nat-policy-default-group-global vrf_ref global se_group_ref Default-Group service_type routing_service routing_service enable_routing nat_policy_ref nat-policy-default-group-global save saveConfigure ServiceEngineGroup in Legacy-HA and EnableRouting with floating interface IP, as mentioned. For more information, see Default Gateway (IP Routing on NSX Advanced Load Balancer SE).
If explicit
destination_portorsource_portmatch_criteriaare not specified by default, then all the ports in the range 1-65535 are allowed.For explicit
match-criterionconfiguration, in the case of bothdestination_portandsource_portmatch criteria, a maximum of eight port configurations are allowed.
Outbound NAT Use Case
NAT policy configuration can be used in router mode when NSX Advanced Load Balancer SE floating IP is configured as default gateway on the backend server and the backend subnet is not routable externally. NSX Advanced Load Balancer will perform in parallel source IP NAT for backend server outbound traffic and proxy service for inbound traffic.
Debugging Commands
The following are the available debugging commands to get the information of the NAT flows/ statistics:
[admin:localhost.localdomain]: > show serviceengine Active_Standby-se-xyjud nat nat-flows Show NAT flow information natpolicystats show NAT policy stats natstat Show NAT statistics
The statistics are available using CLI.
Match Criteria
The following match criteria options are supported:
Match source IP address
Match source IP address range
Match source IP address group
Match source IP prefix
Match source ports. Port range is not supported.
Match destination IP address
Match destination IP address range
Match destination IP address group
Match destination IP prefix
Match destination ports
For every option, is not option is available. This option can be used to exclude packets having certain parameters from matching the rule.
Match Operations
If two or more of the same parameters are used as match criteria, then OR operation is used for matching.
Example:
match source_ip match_criteria is_in addrs 192.168.100.21 ranges begin 192.168.100.2 end 192.168.100.10
This will match if the source IP is 192.168.100.21 or if the source IP falls in the range of 192.168.100.2 - 192.168.100.10.
If two different parameters are used in the match criteria, then AND operation is used for matching.
Example:
match source_ip match_criteria is_in addrs 192.168.100.21 ranges begin 192.168.100.2 end 192.168.100.10 destination_port match_criteria is_in ports 80
This will match if the source IP is 192.168.100.21 or if the source IP falls in the range of 192.168.100.2 - 192.168.100.10 and if the destination port is 80.
If there are multiple rules configured, the rules are evaluated in the ascending order as indexed. The evaluation stops on the first match. No subsequent rules are checked if a packet already matches a rule.
Action Options
NAT IP can be NSX Advanced Load Balancer VIP, floating interface IP, or IP address in the subnet of SE interface. NAT IP cannot be SE interface IP.
NAT IP range.