This section focuses on the following upgrade scenarios using the NSX Advanced Load Balancer UI.
Upgrading a global app on specific servers — The Member Disable-Enable Option
Upgrading a global app pervasively — The Global Service Disable-Enable Option
Upgrading all global apps at a specific site — The Site Disable-Enable Option
The same operations are possible from the CLI and REST API.
Upgrade actions described below are GSLB operation actions, not GSLB configuration-changing options. In-flight connections to a VIP or virtual service at a site are not affected. This could be addressed by changing the DNS TTL, but some intermediate DNS cache may not honor the TTL; traffic may continue to arrive at the erstwhile VIP.
Upgrade a Global App on Specific Servers — The Member Disable-Enable Option
When it is time to upgrade a generally sound global application to fix bugs or add features, we use this option. It is graceful and non-disruptive. The fact that multiple sites are already delivering the service suggests that one site’s service can be turned off and upgraded while traditional service from N-1 remaining sites continues. This is the classical rolling upgrade scenario.
On the GSLB leader, on a site-by-site basis, use the GSLB pool editor to deselect the Enabled option of the relevant pool member (gs11 in the case of below screenshot).
A member virtual service must be upgraded after it has reached an inactive state.
Make required changes to the application on the servers within that virtual service’s server pools, re-launch the application, and then select Enabled option.
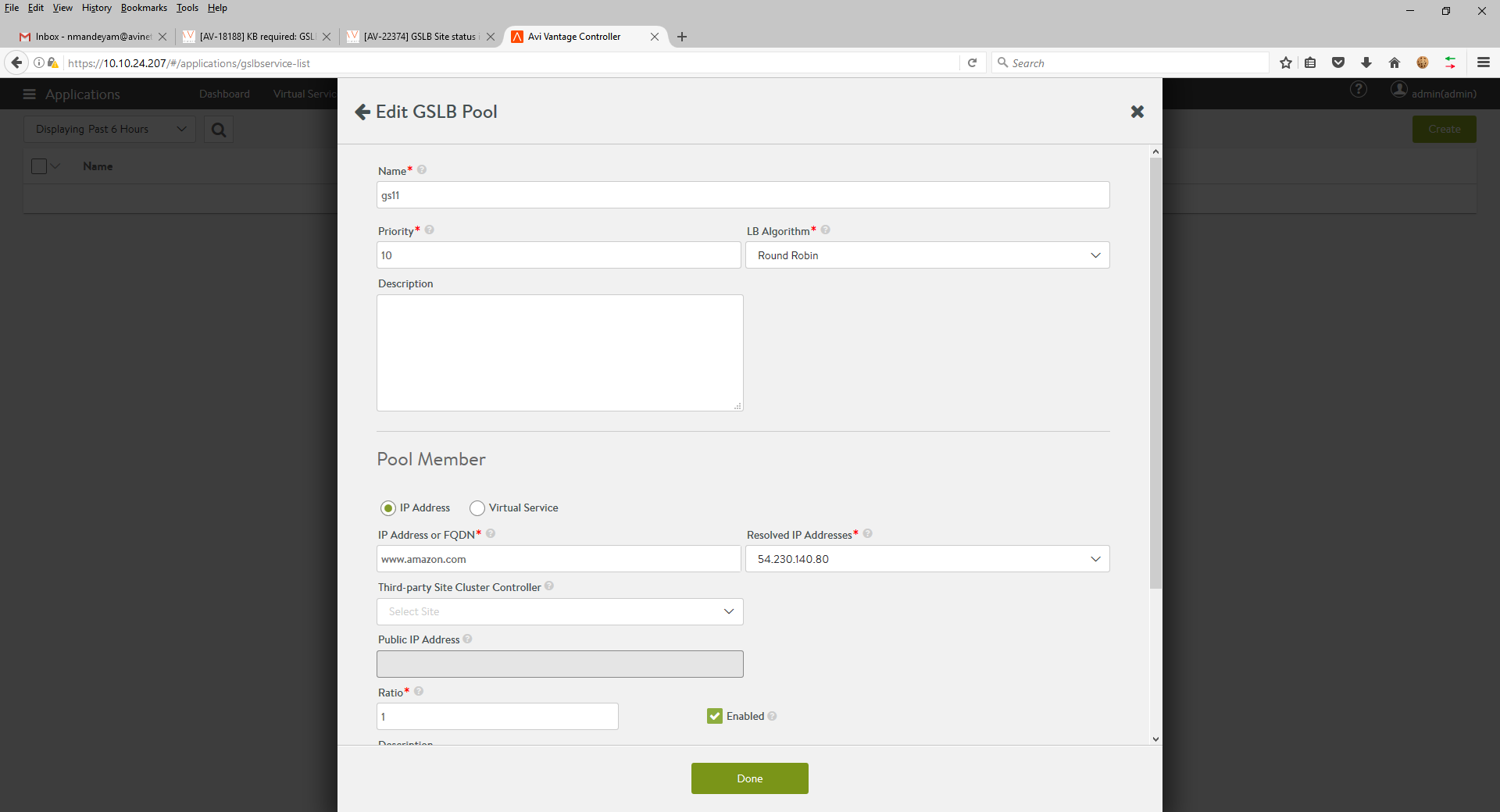
Disabling the GSLB pool member causes NSX Advanced Load Balancer to change the global DNS (the member’s IP address is withdrawn) such that traffic to the member virtual service (gs11 in this case) ceases. Traffic remains distributed across the remaining sites that host the application.
Upgrade a Global App Pervasively — The Global Service Disable-Enable Option
In some cases, a global application needs to be suspended immediately and pervasively, for example, until some bug or security breach has been addressed at all participating sites. In this scenario, instead of disabling one member at a time as described above, we might want all members to stop at once, using the global-service-disable option.
On the GSLB leader, navigate to . Select the application that needs to be disabled. Click the Disable button. Do not click Delete, as that would permanently remove the global service from the system configuration.
The NSX Advanced Load Balancer changes the global DNS configuration such that the FQDN is withdrawn.
Upgrade All Global Apps at a Specific Site — The Site Disable-Enable Option
Imagine a bank of servers housing all of the enterprise’s virtualized global applications. If data center space is tight, upgrading them to next-generation servers demands a forklift upgrade. Running these global apps simultaneously on the old bank while also launching them on the new bank is not feasible. Downtime at the site is unavoidable, and during it, client load must be served by the remaining GSLB sites.
On the GSLB leader, navigate to . Check the sites on which you want all GSLB apps disabled and click Disable button. Do not click Delete, as doing so would permanently remove the identified sites from the GSLB configuration.
The NSX Advanced Load Balancer changes the global DNS such that the IP addresses of all virtual services at the identified sites participating in all global applications are withdrawn. Local applications are not affected. Responses to requests for the FQDN of global applications will contain the IP addresses of virtual services running on N-1 remaining GSLB sites.
The leader site cannot be disabled. To overcome this limitation, leadership must be passed over to a site that has already been upgraded. The former leader can then be disabled.
Once a site is re-enabled, NSX Advanced Load Balancer resynchronizes all relevant information to the newly enabled site.