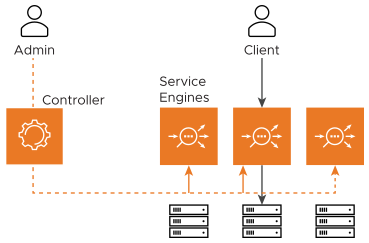
The NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controller is the single point of management and control. It is typically deployed as a three-node cluster to ensure high availability.
The Controller implements the control plane. A single NSX Advanced Load Balancer deployment is managed from this Controller Cluster (identified by FQDN and or cluster IP address), regardless of the number of applications being load balanced or the number of NSX Advanced Load Balancer Service Engines (SEs) required.
The Controller places virtual services on SEs to load balance applications, regardless of whether the SEs were created automatically (write-access mode) or manually (no-access mode). For a higher degree of automation, a Controller is deployed in a write-access deployment, allowing it to work with the underlying orchestrator to launch new SEs in response to events such as creating a new virtual service or increase in application load above a threshold level. The Controller's REST API provides visibility to all configured applications (virtual services) and enables complete application lifecycle automation.
Control Plane High Availability
In a production deployment environment, the best practice to ensure high availability is to deploy a set of three NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controllers as a High Availability (HA) cluster. In a cluster deployment, one of the Controllers is the leader and performs load balancing and configuration management for the cluster. The other two Controllers are the followers; they collaborate with the leader to perform data collection from Service Engines and process analytics data.