The NSX Advanced Load Balancer provides many features to help understand the utilization of SSL traffic and troubleshoot SSL-related issues.
Visibility and Security Insights
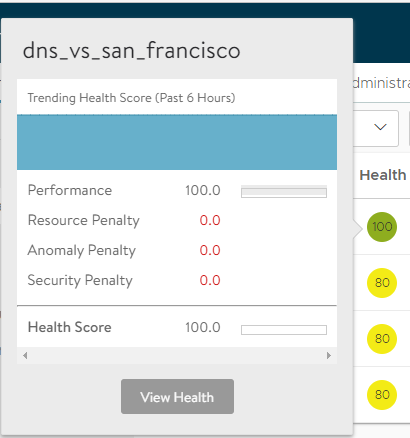
The NSX Advanced Load Balancer provides many useful data points and metrics for virtual services. Some features are valuable for digging deeper into the SSL-termination process.
Navigate to the Security tab of the virtual service to view its SSL and DDoS insights. SSL misconfigurations or issues, such as an expiring SSL certificate, are highlighted on this page. It is also shown in the health score of the virtual service, incurring a security penalty. In ideal cases, the security penalty must be zero, which means that it is not detracting from the health or risk of a virtual service. A non-zero security penalty must be investigated and remediated. Security insights specific to SSL are shown on the left tiles:
SSL Distribution
SSL Score
SSL Distribution Insights
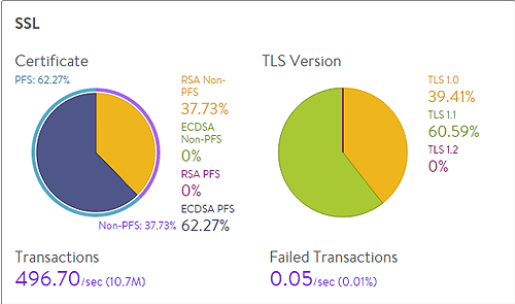
The SSL section in Security tab of the virtual service shows the most relevant SSL data about client connections terminated on NSX Advanced Load Balancer for the selected period. If SSL termination is not being performed on the virtual service, this section will have no data.
- Certificate
-
Breaks down the certificate types used by clients during the negotiation phase of SSL session setup. A virtual service can be configured to accept both RSA and EC certificates. The NSX Advanced Load Balancer negotiates whichever type the client supports, with EC as the preference for clients that support both. Depending on the cipher negotiated by the client, RSA and EC can be negotiated with or without perfect forward secrecy.
- TLS Version
-
Displays the TLS versions negotiated by clients.
- Transactions
-
The average transactions per second (TPS) for new connections negotiated within the time period. This metric includes both new and reused transactions. This metric is further broken down through the Transactions metric tile from the SSL section of the sidebar tiles, which further breaks down this number.
- Failed Transactions
-
Number of unsuccessful transactions. Typically, transactions can fail either due to clients terminating the negotiation midstream, or because the client and the NSX Advanced Load Balancer cannot agree on a mutually supported cipher or TLS version. To view individual failed transactions, access the logs page of the virtual service.
SSL Score
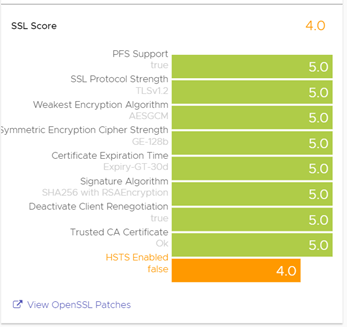
The SSL Score section in the Security tab of the virtual service shows the major factors affecting the SSL Score penalty. Any penalty here is multiplied by 5 when viewed in the virtual service health score. For example, if a site does not use a trusted certificate, it carries a local penalty of 4. This incurs a Security Penalty of 20 against the virtual service health score.
- PFS Support
-
Negatively impacts the security score of a virtual service by reducing it if PFS-capable ciphers are not enabled in the SSL profile for the virtual service.
- SSL Protocol Strength
-
Reduces the score if an insecure SSL/TLS version is enabled.
- Weakest Encryption Algorithm
-
Reduces the score if a weak encryption algorithm is enabled in the SSL profile. For more insights on how weak encryption algorithm affects the health score, see the security score of the SSL Profile.
- Symmetric Encryption Cipher Strength
-
Reduces the score if the cipher suite uses an encryption algorithm that is considered insecure by the NSX Advanced Load Balancer.
- Certificate Expiration Time
-
Reduces the score if the certificate is about to expire or has already expired.
- Signature Algorithm
-
Reduces the score if weak hashing algorithms such as md5 or SHA1 are enabled in the SSL profile of the virtual service.
- Disable Client Renegotiation
-
As a best practice, the NSX Advanced Load Balancer turns off client SSL renegotiation. This field is non-configurable and therefore does not impact the security score.
- Trusted CA Certificate
-
Reduces the score if the virtual service uses a self-signed certificate.
DDoS Insights
The DDoS section on the right of the default security page breaks down distributed denial of service data for the virtual service into the most relevant layer 4 and layer 7 attack data.
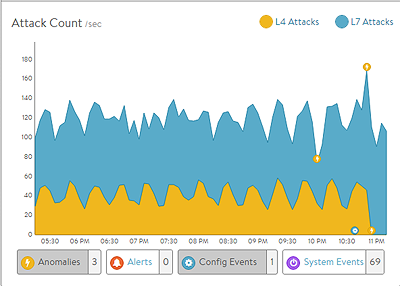
- L4 Attacks
-
The number of network attacks per second, such as IP fragmentation attacks or TCP SYN flood. For the example shown here, each unacknowledged SYN is counted as an attack. (This is the classic signature of the TCP SYN flood attack, a large volume of SYN requests that are not followed by the expected ACKs to complete session setup.)
- L7 Attacks
-
The number of application attacks per second, such as HTTP SlowLoris attacks or request floods. For the example shown here, every request that exceeded the configured request throttle limit is counted as an attack. (See the application profile’s DDoS tab for configuring custom layer seven attack limits.)
- Attack Duration
-
The length of time during which an attack occurred.
- Blocked Connections
-
If an attack was blocked, this is the number of connection attempts blocked.
- Attack Count
-
Shows attacks plotted in a graph over time.
Application Logs
Navigate to the Logs tab of the virtual service to view details of individual connections and requests. The NSX Advanced Load Balancer captures many metrics, including several that are not shown in the UI, such as ciphers. Export the logs or filter for additional metrics, if needed.
Version
Certificate type
Cipher
PFS
SSL session ID / TLS ticket
In the Log Analytics tile, click the SSL tile to see a summary of the SSL data for the selected logs.
SSL Ciphers
Navigate to to view a basic rating system that indicates the performance, compatibility, and security of the ciphers and their order. The rating is a quick and easy way to assess the results of the cipher settings.
SSL Certificates
Navigate to to display all the available certificates. This view breaks down the type of certificate and provides a simple color code to indicate the status. For example, a certificate turns yellow if the certificate is going to expire soon and red when it has expired. Certificate chain issues can also be viewed.
Troubleshooting
The tools mentioned in this topic can prove valuable for troubleshooting common SSL-related issues. Some common issues are:
Certificate Expiration
When a certificate expires, the virtual service incurs a Security Penalty. This is visible in the Security page of the virtual service and the SSL/TLS Certificates page. For more information on enabling proactive certificate expiration notifications, see the Notification of SSL Certificate Expiration topic in the VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer Configuration Guide.
SSL Version Related Threats
Periodically, new vulnerabilities to SSL and TLS, such as Heartbleed and Drown attacks, are announced. Many of these vulnerabilities target older versions of SSL, which are not enabled on the NSX Advanced Load Balancer. To disable additional versions, such as TLS 1.0, navigate to the SSL profile and make the change. It is equally important to understand the impact of the change on existing users. You can take a look at the Security Insights or the Logs page to get information on a number of users negotiating through TLS 1.0, versions of browsers used by them, and if those browsers support newer versions of SSL/TLS.
Incompatible Ciphers
A number of issues can cause this error. The virtual service logs are captured for any possible SSL incompatibilities. A common cause for this error is the application of an SSL profile that only enables EC ciphers, to a virtual service that has been configured with an RSA certificate.