The NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controller is the management and orchestration engine for NSX Advanced Load Balancer ADC.
To provide HA and resilience, it is recommended to deploy a cluster of three Controller instances. Once the Controller cluster is formed, the controllers synchronize the state, irrespective of the Controller instance used to configure NSX Advanced Load Balancer features or retrieve operational data.
For more information about Controller cluster architecture, see High Availability for NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controllers.
In AWS environments, AWS Availability Zones (AZs) provide redundancy and separate fault domains. All AWS regions support a minimum of two AZs. To leverage the HA provided by AWS AZs, it is recommended to deploy different Controller instances of a cluster in different AZs.
Managing an NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controller Cluster across AZs
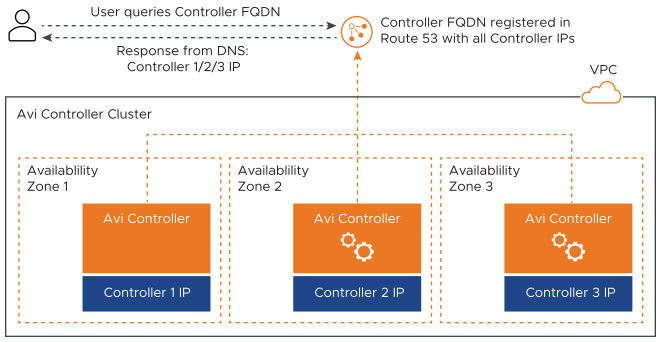
Each NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controller will receive an IP address from a different subnet given that an AWS subnet does not span across AZs.
In this scenario, it is recommended to create a FQDN in AWS Route 53, and associate all three Controller IPs with this FQDN. In addition, Route 53 health checks can be used in conjunction with multivalue routing when the FQDN is added to a public zone. This ensures that only healthy Controller IPs are returned.