This section explains how to configure JWT validation through NSX Advanced Load Balancer using the UI and the CLI.
NSX Advanced Load Balancer supports the following JWT validation methods:
Manual upload of the JWKS keys
JWT Validation using JWKS keys
Claim-based validation using authorization rules under SSO Policy
Revocation using the authorization policies
JWT Validation Workflow
Communication between a client, an authorization server, and NSX Advanced Load Balancer during the JWT validation is as explained below:
The client sends an unauthenticated request to the authorization server.
The authorization server performs the authentication and issues a JSON web-based tokens.
The client sends a request to NSX Advanced Load Balancer virtual service to access the protected resource. The client request has JWT either in the URL query or against the authorisation header.
NSX Advanced Load Balancer validates the JWT in JWKS format using the public key of authorisation server that issued the JWT . If JWT is validated, NSX Advanced Load Balancer and provides access to the requested resource.
Configuring JWT Validation using the UI
To configure JWT validation through the NSX Advanced Load Balancer UI, follow the steps below:
Creating a JWT Server Profile
Navigate to .
Click CREATE.
Enter the Name of the Profile.
Specify the unique name of the token Issuer. This is applicable only for CLIENT_AUTH profile type.
-
Either paste the JWKS key set in the text box provided or click Import File to upload.
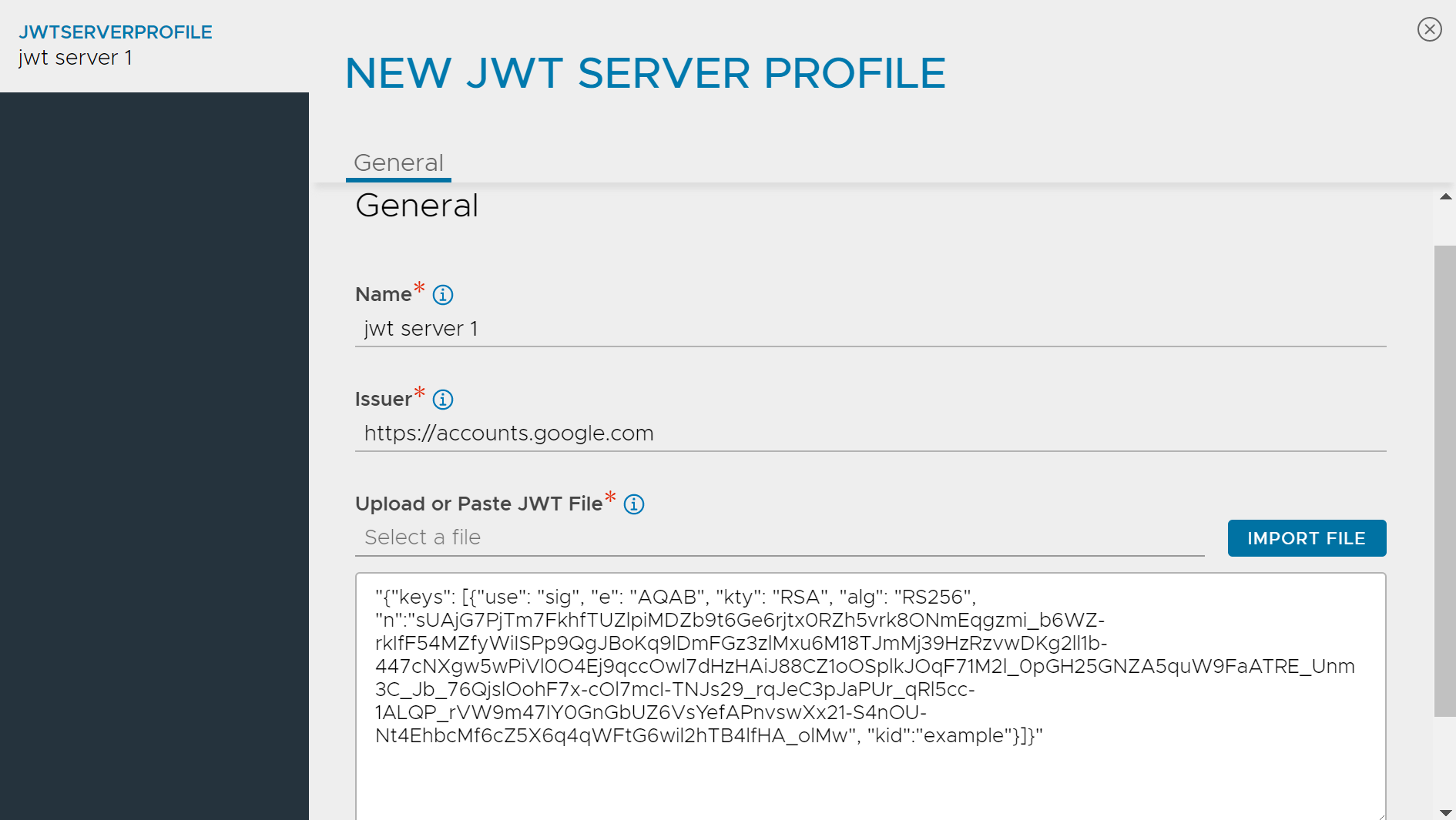
Click Save.
Associating the JWT Server Profile with the Authentication Profile
Navigate to .
Click CREATE.
Enter the NAME of the Authentication Profile.
Select the Type as JWT Validation.
-
From the dropdown menu, select the JWT Server Profile that was created.
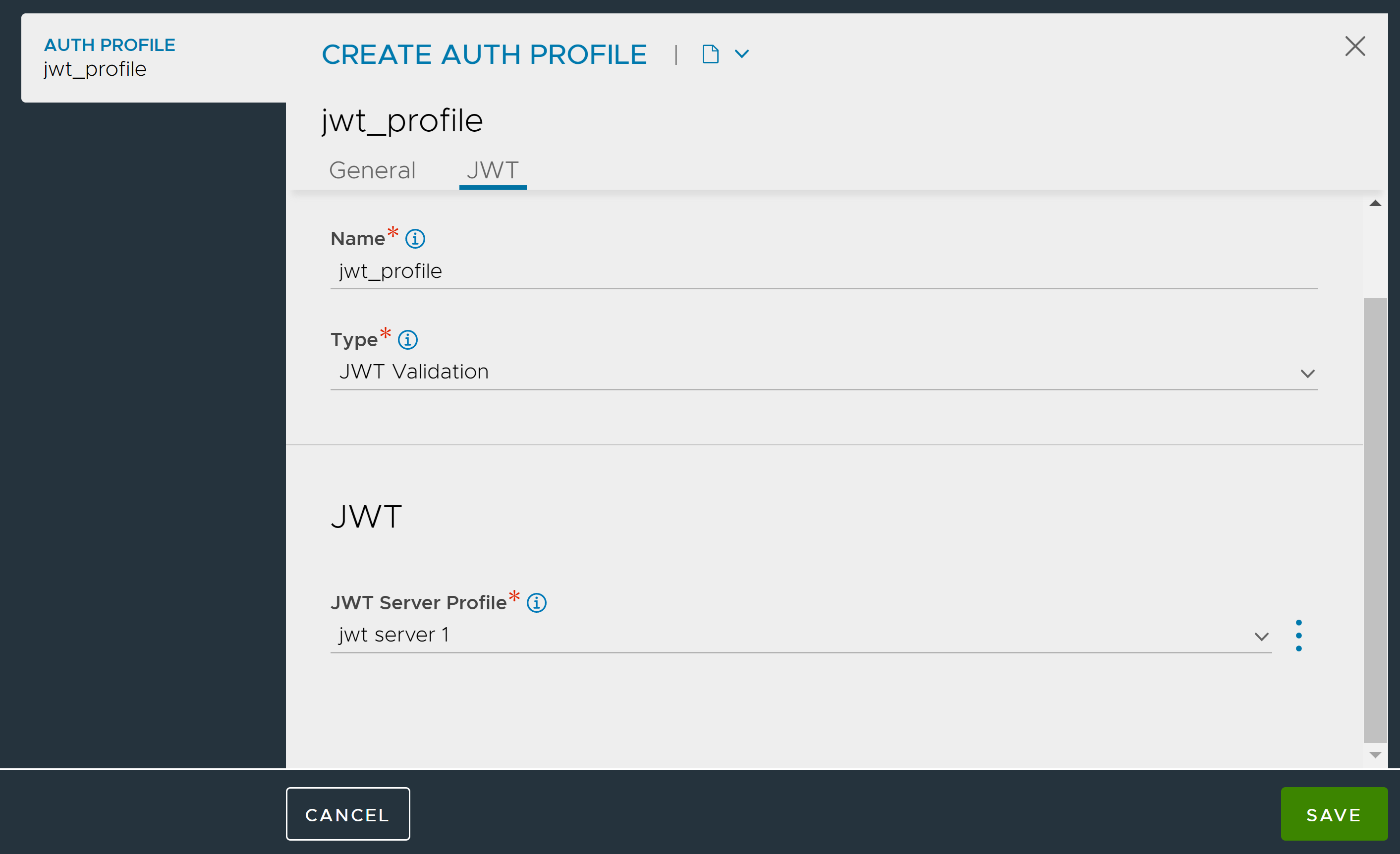
Click Save.
Creating the SSO Policy
To create the SSO Policy,
Navigate to .
Click Create.
Enter the Name of the SSO Policy.
Select JWT as the Type of SSO Policy.
-
Select the JWT Auth Profile to use for validating users.
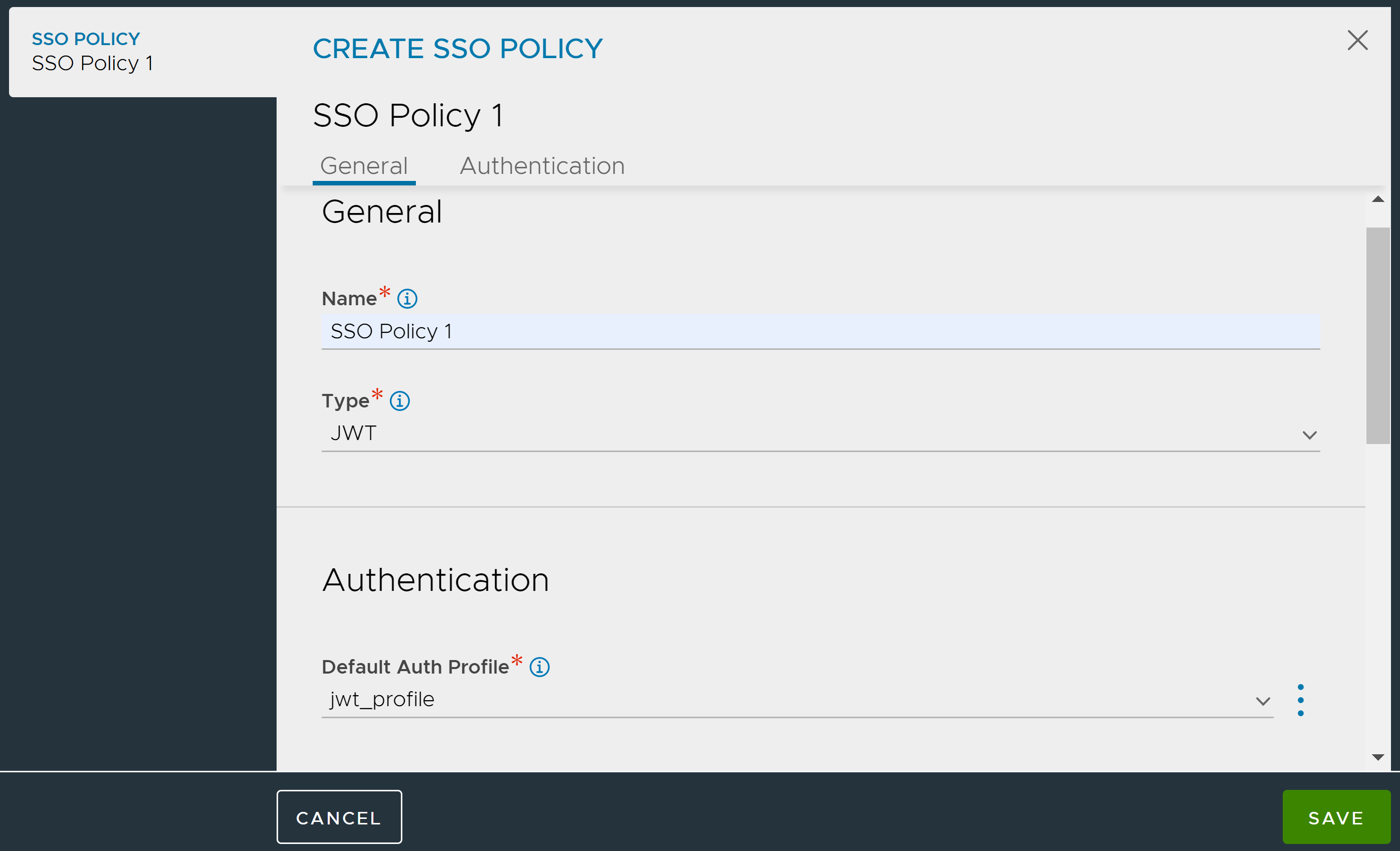
Under Authentication Rules, click Add and configure the Authentication Rules as required.
Under Authorization Rules, click Add and configure the Authorization Rules as required.
Click Save.
Configuring the Virtual service
Associate the SSO Policy and the JWT service configuration to the virtual service.
Navigate to .
Click on CREAT VIRTUAL SERVICE.
Select Advanced Setup.
Configure Step 1: Settings as required and click Next.
Under Step 2: Policies, click Access.
Under the Access tab,
Select JWT as the Access Policy.
Select the SSO Policy created with the JWT Profile to be associated wih this virtual service.
Specify the SSO Audience that uniquely identifies the resource server.
Select the Token Location to define whether to look for the JWT in the Authorization Header or URL Query.
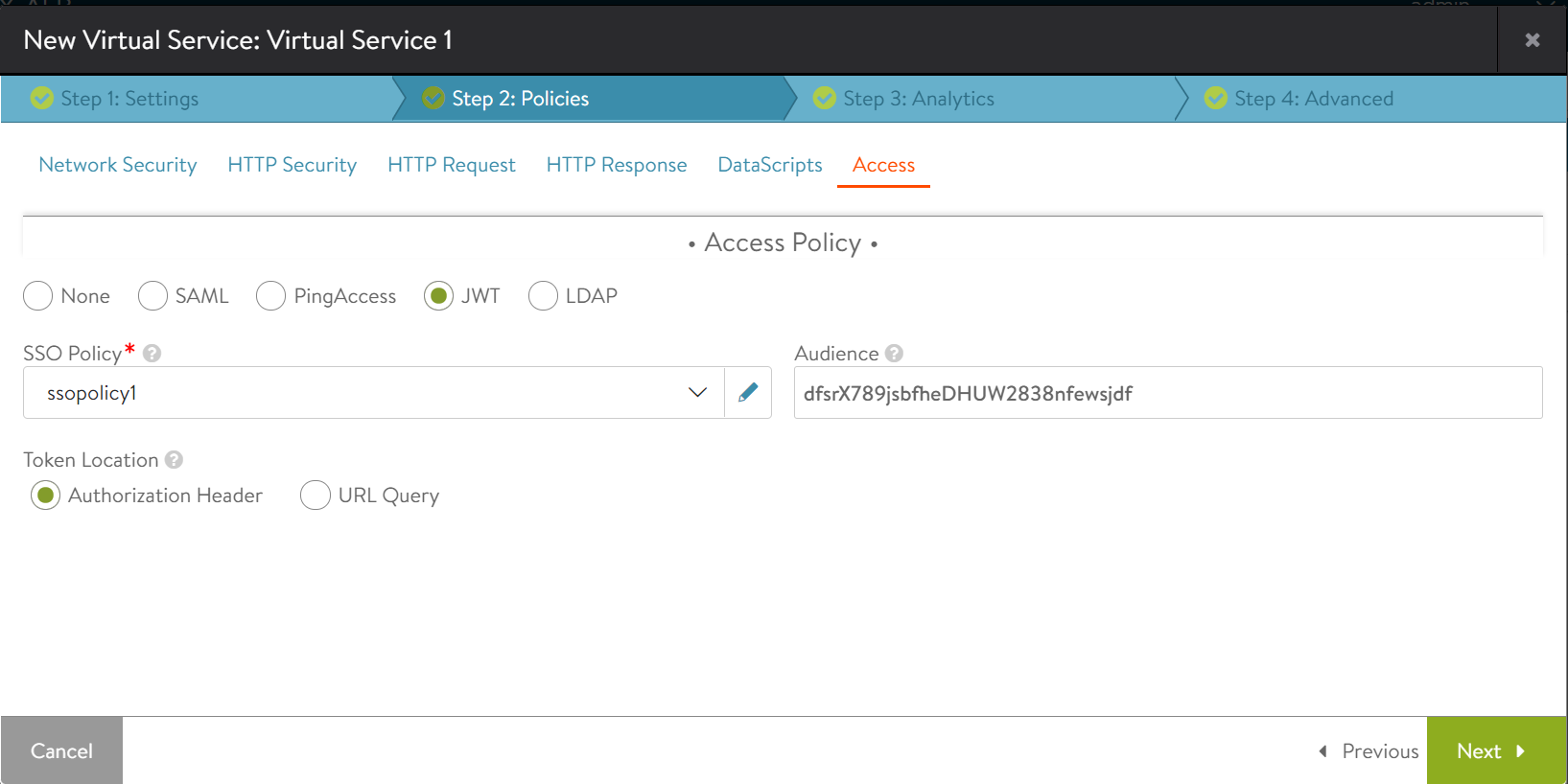
Configure the other details for teh virtual service and click Save.
Configuring JWT Validation using CLI
To configure the JWT Validation using CLI, run the following commands:
Creating a JWT server profile : Login to NSX Advanced Load Balancer CLI and use the configure jwtserverprofile <profile name> command to provide values for various attributes.
[admin:controller]: > configure jwtserverprofile jwtserver1 [admin:controller]: jwtserverprofile> issuer https://accounts.google.com [admin:controller]: jwtserverprofile> jwks_keys "{"keys": [{"use": "sig", "e": "AQAB", "kty": "RSA", "alg": "RS256", "n":"sUAjG7PjTm7FkhfTUZlpiMDZb9t6Ge6rjtx0RZh5vrk8ONmEqgzmi_b6WZ-rkIfF54MZfyWiISPp9QgJBoKq9lDmFGz3zlMxu6M18TJmMj39HzRzvwDKg2ll1b-447cNXgw5wPiVl0O4Ej9qccOwl7dHzHAiJ88CZ1oOSplkJOqF71M2l_0pGH25GNZA5quW9FaATRE_Unm3C_Jb_76QjslOohF7x-cOl7mcI-TNJs29_rqJeC3pJaPUr_qRl5cc-1ALQP_rVW9m47IY0GnGbUZ6VsYefAPnvswXx21-S4nOU-Nt4EhbcMf6cZ5X6q4qWFtG6wil2hTB4lfHA_olMw", "kid":"example"}]}" [admin:controller]: jwtserverprofile> [admin:controller]: jwtserverprofile> save +------------+----------------------------------------------------+ | Field | Value +------------+-----------------------------------------------------+ | uuid | jwtserverprofile-e1c8f0c2-b38c-41f4-bf1e-0f55e282797e | name | jwtserver1 | jwks_keys | {"keys": [{"use": "sig", "e": "AQAB", "kty": "RSA", "alg": "RS256", "n":"sUAjG7P | jTm7FkhfTUZlpiMDZb9t6Ge6rjtx0RZh5vrk8ONmEqgzmi_b6WZ-rkIfF54MZfyWiISPp9QgJBoKq9lD | | | mFGz3zlMxu6M18TJmMj39HzRzvwDKg2ll1b-447cNXgw5wPiVl0O4Ej9qccOwl7dHzHAiJ88CZ1oOSpl | | | kJOqF71M2l_0pGH25GNZA5quW9FaATRE_Unm3C_Jb_76QjslOohF7x-cOl7mcI-TNJs29_rqJeC3pJaP | | | Ur_qRl5cc-1ALQP_rVW9m47IY0GnGbUZ6VsYefAPnvswXx21-S4nOU-Nt4EhbcMf6cZ5X6q4qWFtG6wi | | | l2hTB4lfHA_olMw", "kid":"example"}]} | issuer | https://accounts.google.com | tenant_ref | admin +------------+---------------------------------------------------+ [admin:controller]: >Associate the JWT server profile created in the previous step to the authentication profile:
[admin:controller]: > configure authprofile authprofile1 [admin:controller]: authprofile> jwt_profile_ref jwtserver1 [admin:controller]: authprofile> type auth_profile_jwt [admin:controller]: authprofile> save +-----------------+-----------------------------------------------+ | Field | Value +-----------------+------------------------------------------------+ | uuid | authprofile-e1b763d6-bbd0-4a70-9a9b-95ab60e72e11 | name | authprofile1 | type | AUTH_PROFILE_JWT | jwt_profile_ref | jwtserver1 | tenant_ref | admin +-----------------+------------------------------------------------+ [admin:controller]: >
Create an SSO policy using the configure ssopolicy
<sso policy name>command. Associate this SSO policy with the authentication policy created in the previous step and set the type for the authentication policy assso_type_jwt.[admin:controller]: > configure ssopolicy ssopolicy1 [admin:controller]: ssopolicy> authentication_policy default_auth_profile_ref authprofile1 [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy> save [admin:controller]: ssopolicy> type sso_type_jwt [admin:controller]: ssopolicy>save +----------------------------+------------------------------+ | Field | Value | +----------------------------+------------------------------+ | name | ssopolicy1 | | authentication_policy | | | default_auth_profile_ref | authprofile1 | | type | SSO_TYPE_JWT | +----------------------------+-----------------------------+
Associate the SSO Policy and the JWT virtual service configuration to the virtual service.Set the value of
jwt_locationasjwt_location_authorization_header, if the JWT is sent as Bearer Token in the authorization header.[admin:controller]: > configure virtualservice virtualservice1 [admin:controller]: virtualservice> [admin:Charitha-controller]: virtualservice> sso_policy sso_policy (submode) sso_policy_ref The SSO Policy attached to the virtualservice. [admin:controller]: virtualservice> sso_policy_ref WORD The SSO Policy attached to the virtualservice. [admin:controller]: virtualservice> sso_policy_ref ssopolicy1 [admin:controller]: virtualservice> jwt_config audience Uniquely identifies a resource server. This is used to validate against the aud claim. jwt_location Defines where to look for JWT in the request. jwt_name Name by which the JWT can be identified if the token is sent as a query param in the request url. [admin:controller]: virtualservice> jwt_config audience WORD Uniquely identifies a resource server. This is used to validate against the aud claim. [admin:controller]: virtualservice> jwt_config audience dfsrX789jsbfheDHUW2838nfewsjdf [admin:controller]: virtualservice:jwt_config> jwt_location jwt_location_ jwt_location_authorization_header JWT sent in the authorizarion header of the request as a bearer token. jwt_location_query_param JWT sent in the request query params. [admin:controller]: virtualservice:jwt_config> jwt_location jwt_location_authorization_header [admin:controller]: virtualservice:jwt_config> save
Select
jwt_location_query_paramsas the value for jwt_location, if the JWT is sent in the URL as a query parameter.[admin:controller]: > configure virtualservice virtualservice1 [admin:controller]: virtualservice> [admin:Charitha-controller]: virtualservice> sso_policy sso_policy (submode) sso_policy_ref The SSO Policy attached to the virtualservice. [admin:controller]: virtualservice> sso_policy_ref WORD The SSO Policy attached to the virtualservice. [admin:controller]: virtualservice> sso_policy_ref ssopolicy1 [admin:controller]: virtualservice> jwt_config audience Uniquely identifies a resource server. This is used to validate against the aud claim. jwt_location Defines where to look for JWT in the request. jwt_name Name by which the JWT can be identified if the token is sent as a query param in the request url. [admin:controller]: virtualservice> jwt_config audience WORD Uniquely identifies a resource server. This is used to validate against the aud claim. [admin:controller]: virtualservice> jwt_config audience dfsrX789jsbfheDHUW2838nfewsjdf [admin:controller]: virtualservice:jwt_config> jwt_location jwt_location_query_params [admin:controller]: virtualservice:jwt_config> jwt_location jwt_location_query_param jwt_name "jwt_token" [admin:controller]: virtualservice:jwt_config> save
Adding Authentication Policies
Use the authentication policy option under the configure ssopolicy <sso policy name> mode to add authentication policies to enable JWT authentication only for paths /login and /default.
[admin:controller]: > configure ssopolicy ssopolicy-3 [admin:controller]: ssopolicy> [admin:controller]: ssopolicy> type sso_type_jwt [admin:controller]: ssopolicy> authentication_policy [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy> default_auth_profile_ref authprofile-1 [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy> authn_rules New object being created [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy:authn_rules> action type skip_authentication [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy:authn_rules:action> save [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy:authn_rules> index 1 [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy:authn_rules> name rule1 [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy:authn_rules> match [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy:authn_rules:match> path [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy:authn_rules:match:path> match_str "login" [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy:authn_rules:match:path> match_str "default" [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy:authn_rules:match:path> match_criteria does_not_equal [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy:authn_rules:match:path> save [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy:authn_rules:match> save [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy:authn_rules> save [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authentication_policy> save [admin:controller]: ssopolicy> save +----------------------------+-----------------------------------------+ | Field | Value +----------------------------+------------------------------------------+ | uuid | ssopolicy-6d831f8d-4ccf-43f9-af73-aa9aae8beae4 | | name | ssopolicy-3 | authentication_policy | | default_auth_profile_ref | authprofile-1 | authn_rules[1] | | name | rule1 | index | 1 | enable | True | match | | path | | match_criteria | DOES_NOT_EQUAL | match_case | INSENSITIVE | match_str[1] | login | match_str[2] | default | action | | type | SKIP_AUTHENTICATION | type | SSO_TYPE_JWT | tenant_ref | admin +----------------------------+-----------------------------------------+
Adding Authorization Policies
Use the authorization policy option under the configure ssopolicy <sso policy name> mode to enable authorization with access token match.
[admin:controller]: > configure ssopolicy ssopolicy-3 [admin:controller]: ssopolicy> authorization_policy [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authorization_policy> authz_rules index 1 name rule1 [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authorization_policy:authz_rules> action status_code http_response_status_code_403 type http_local_response [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authorization_policy:authz_rules:action> save [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authorization_policy:authz_rules> match [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authorization_policy:authz_rules:match> access_token [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authorization_policy:authz_rules:match:access_token> matches [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authorization_policy:authz_rules:match:access_token:matches> type jwt_claim_type_string [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authorization_policy:authz_rules:match:access_token:matches> string_match match_str "AT-dsjfndjfndsj1234-jnfdjk" [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authorization_policy:authz_rules:match:access_token:matches:string_match> match_criteria equals [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authorization_policy:authz_rules:match:access_token:matches:string_match> save [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authorization_policy:authz_rules:match:access_token:matches> save [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authorization_policy:authz_rules:match:access_token> save [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authorization_policy:authz_rules:match> save [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authorization_policy:authz_rules> save [admin:controller]: ssopolicy:authorization_policy> save [admin:controller]: ssopolicy> save +----------------------------+-----------------------------------------+ | Field | Value +----------------------------+------------------------------------------+ | uuid | ssopolicy-6d831f8d-4ccf-43f9-af73-aa9aae8beae4 | | name | ssopolicy-3 | authentication_policy | | default_auth_profile_ref | authprofile-1 | authn_rules[1] | | name | rule1 | index | 1 | enable | True | match | | path | | match_criteria | DOES_NOT_EQUAL | match_case | INSENSITIVE | match_str[1] | login | match_str[2] | default | action | | type | SKIP_AUTHENTICATION | authorization_policy | | authz_rules[1] | | match | | access_token | | matches[1] | | is_mandatory | True | validate | True | type | JWT_CLAIM_TYPE_STRING | string_match | | match_criteria | EQUALS | match_str[1] | AT-dsjfndjfndsj1234-jnfdjk | action | | type | HTTP_LOCAL_RESPONSE | status_code | HTTP_RESPONSE_STATUS_CODE_403 | type | SSO_TYPE_JWT | tenant_ref | admin +----------------------------+------------------------------------------+
Revocation of JWT
JWTs are designed to be portable, decoupled identities. Once authentication is performed against an authorization server and a JWT is recieved, the JWT token’s re-validation is not required. They can not be revoked at the level of the authorization server.
NSX Advanced Load Balancer uses the following methods to revoke a JWT:
Configure the access tokens (JWTs) to be short-lived. As the JWT gets expired, the client will be forced to re-authenticate or to use a refresh token to request for the new JWT.
Maintain a list of the revoked token in a string group with jti as the key, one for each authorization server.
Use the SSO policy to configure authorization rules based on certain claims like jti, or sub, or iss, etc. JWT has a claim named jit which is used to uniquely identify a JSON Web Token. For example: If it is known that a particular token with a specific jit is compromised, authorization rules can be added to revoke the token with a particular jit.
Logs and Troubleshooting
Virtual server logs available on NSX Advanced Load Balancer can be used to troubleshoot the JWT validation issues.
To view the reason for various response codes generated by NSX Advanced Load Balancer,
Navigate to Templates > Virtual Services
Click on the required virtual service and go to Logs.
Select the option Significant.
Some of the errors that NSX Advanced Load Balancer generates are as discussed below:
Error |
Response Code |
Explanation |
Authorization Header Missing |
403 |
Authorization header is missing 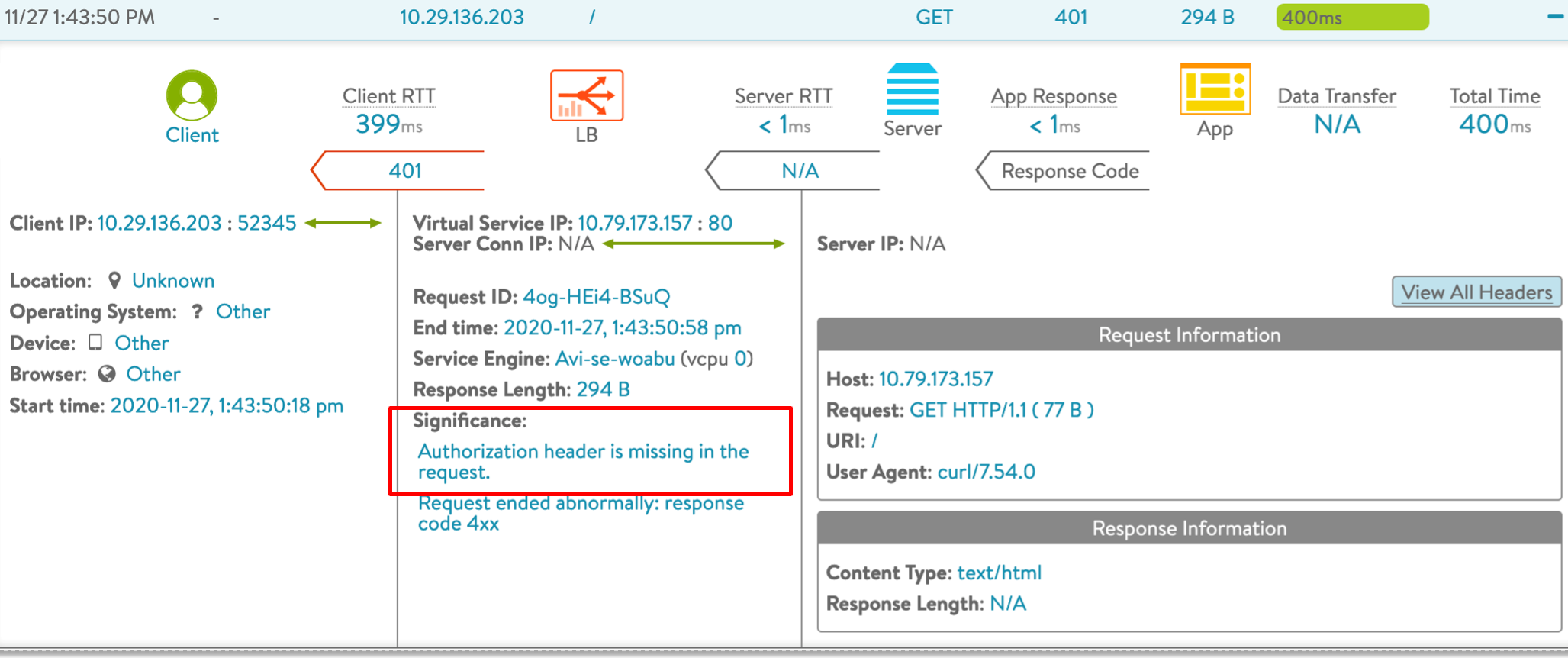 |
Wrong or Unknown User |
4xx |
The JWT issuer is not known or not supported by NSX Advanced Load Balancer 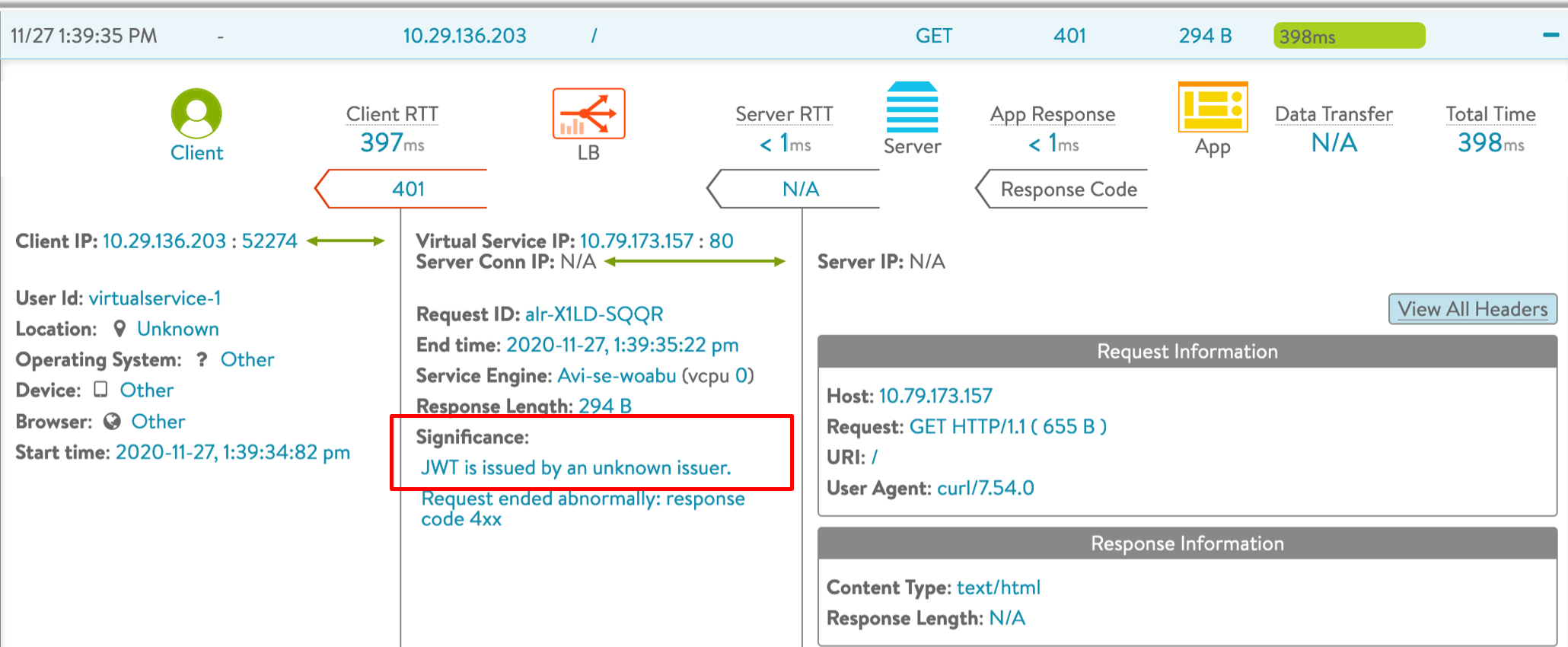 |
Wrong Audience |
4xx |
JWT is not issued for the selected application 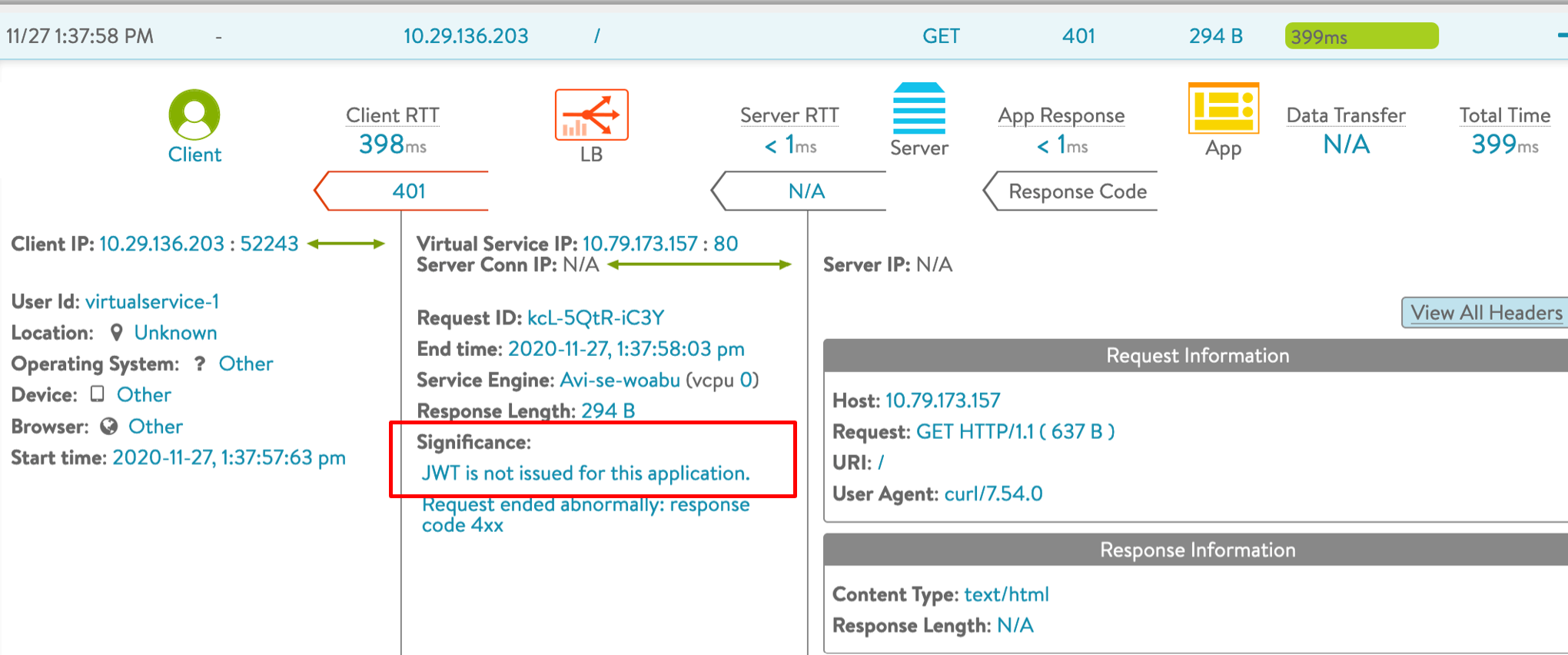 |
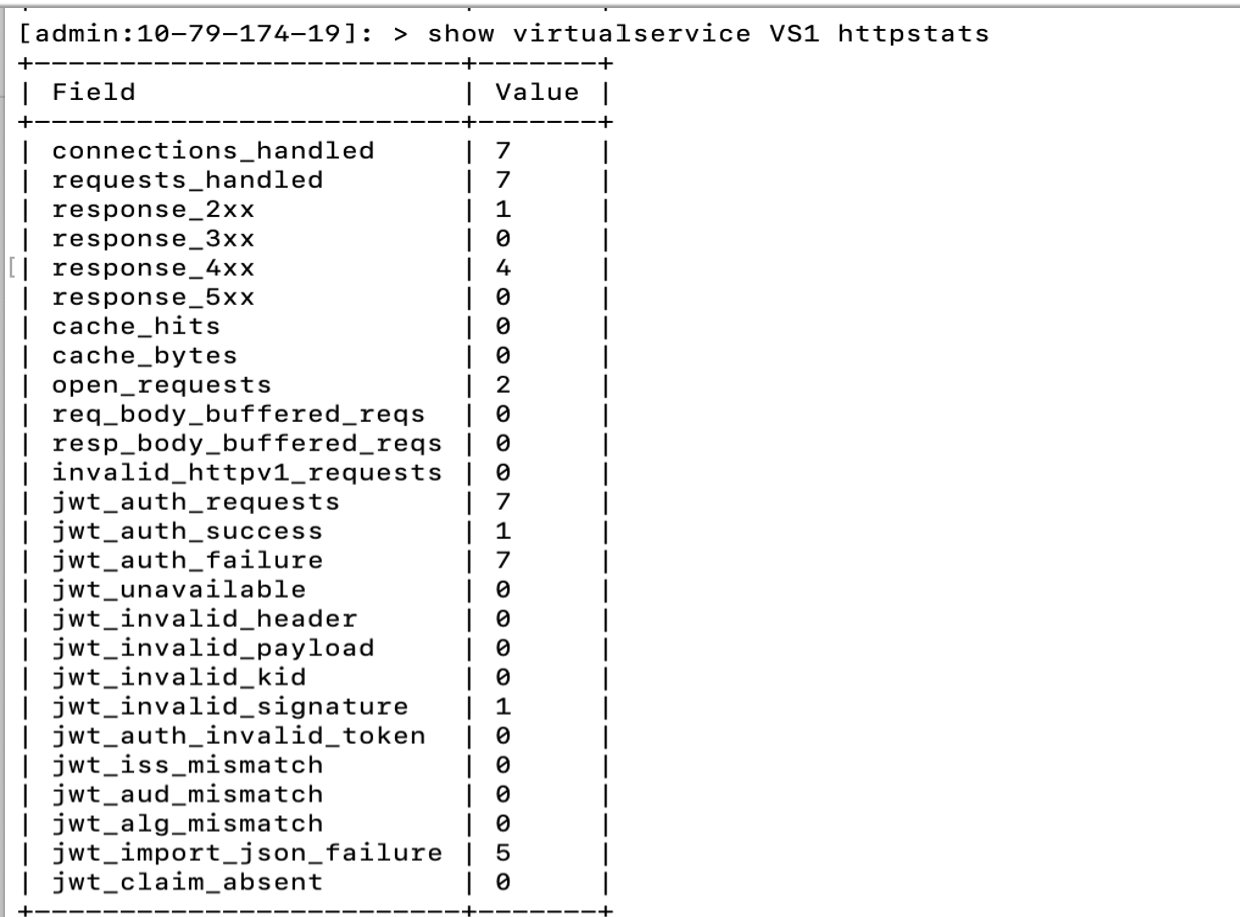
Login to the NSX Advanced Load Balancer CLI and use the show virtualservice <virtual service name> stats command to check the various statistics associated with JWT validation.