NSX Advanced Load Balancer includes many options for rate shaping and throttling of traffic. This can be applied at the virtual service, pool/server, or client level. These options exist in several places throughout the UI, depending on the specific object they are applied against. Additionally, DataScripts can be used to create customized limits.
Virtual Service Limits
Within the , the following options allow specifying limits to connections and requests for the specific virtual service:
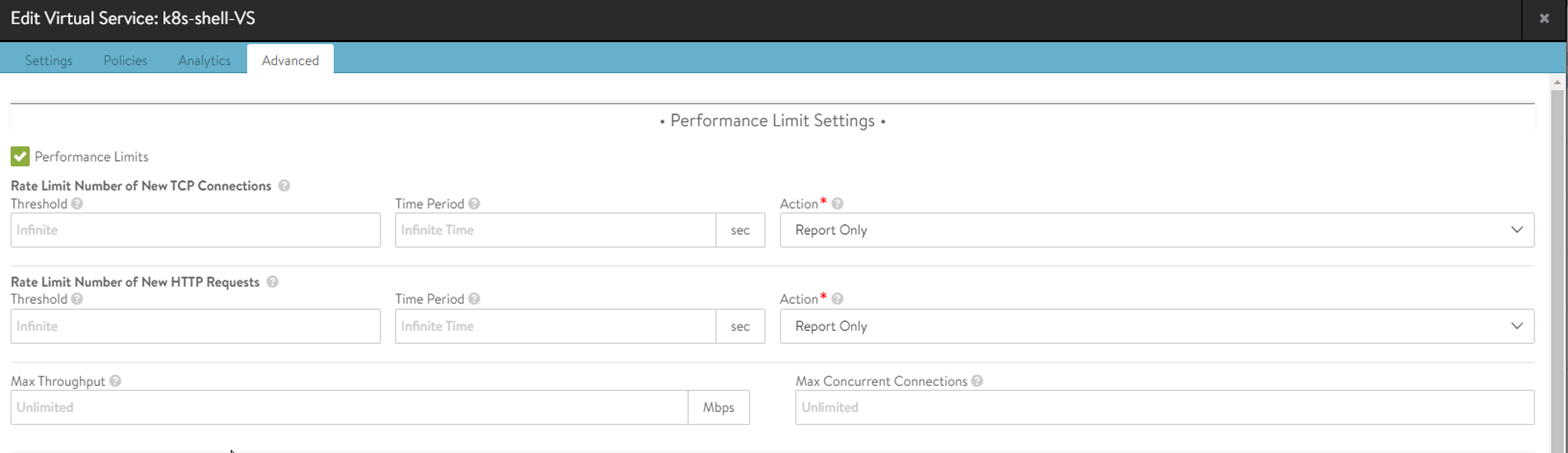
Rate Limit Number of New TCP Connections: Set the maximum threshold of new connections from all clients that can be created for this virtual service over the configured Time Period. The Report action will generate logs for excessive connections but otherwise, allow them to proceed as normal. Drop SYN will silently discard the client SYN, and RST will send a connection reset back to the client.
Rate Limit Number of New HTTP Requests: Set the maximum Threshold of HTTP requests from all clients for this virtual service over the configured Time Period. The Report action will generate logs for excessive requests but otherwise, allow them to proceed as normal. Close TCP Connection will send a connection RST to the client. Send Local Response allows NSX Advanced Load Balancer to respond with a simple web page and appropriate status code. Send HTTP Redirect will forward excessive requests to another URI or destination.
Max Throughput: Specify the maximum bandwidth for the virtual service in bits per second for each SE. For instance, if the virtual service is scaled-out to 3 SE, each SE will throttle after 1 Gbps, so effectively, there will be 3 Gbps in total. So, throughput will also scale horizontally when the virtual service is placed on more SE. Traffic that exceeds this limit will be discarded and may require retransmission by either the client or server. When this limit is set, the Analytics tab of the Virtual Service Details page will show a dashed horizontal line on the Throughput metric chart that shows the current throughput versus the maximum allowed throughput.
Max Concurrent Connections: Specify the maximum number of concurrent open connections. Connection attempts that exceed this number will be reset (TCP) or dropped (UDP) until the total number of concurrent connections falls below the threshold. When this limit is set, the Analytics tab of the virtual service Details page will show a dashed horizontal line on the Open Connections metric that shows the currently open connections versus the maximum number of allowed connections.
Server Pool Limits
Within the , the following option can be used to set server concurrent connection limits.
Connections per Server: Specify the maximum number of concurrent connections allowed for a server. If all servers in the Pool reach this maximum, then the virtual service will send a reset for TCP connections or silently discard new UDP streams unless otherwise specified in the Server Down Settings, described above. As soon as an existing connection to the server is closed, that server is eligible to receive the next client connection. Valid value is zero, which disables the connection limit, or any number from 50 to 10,000.
Client Limits
Within the , create a new policy with the action set to rate limit.
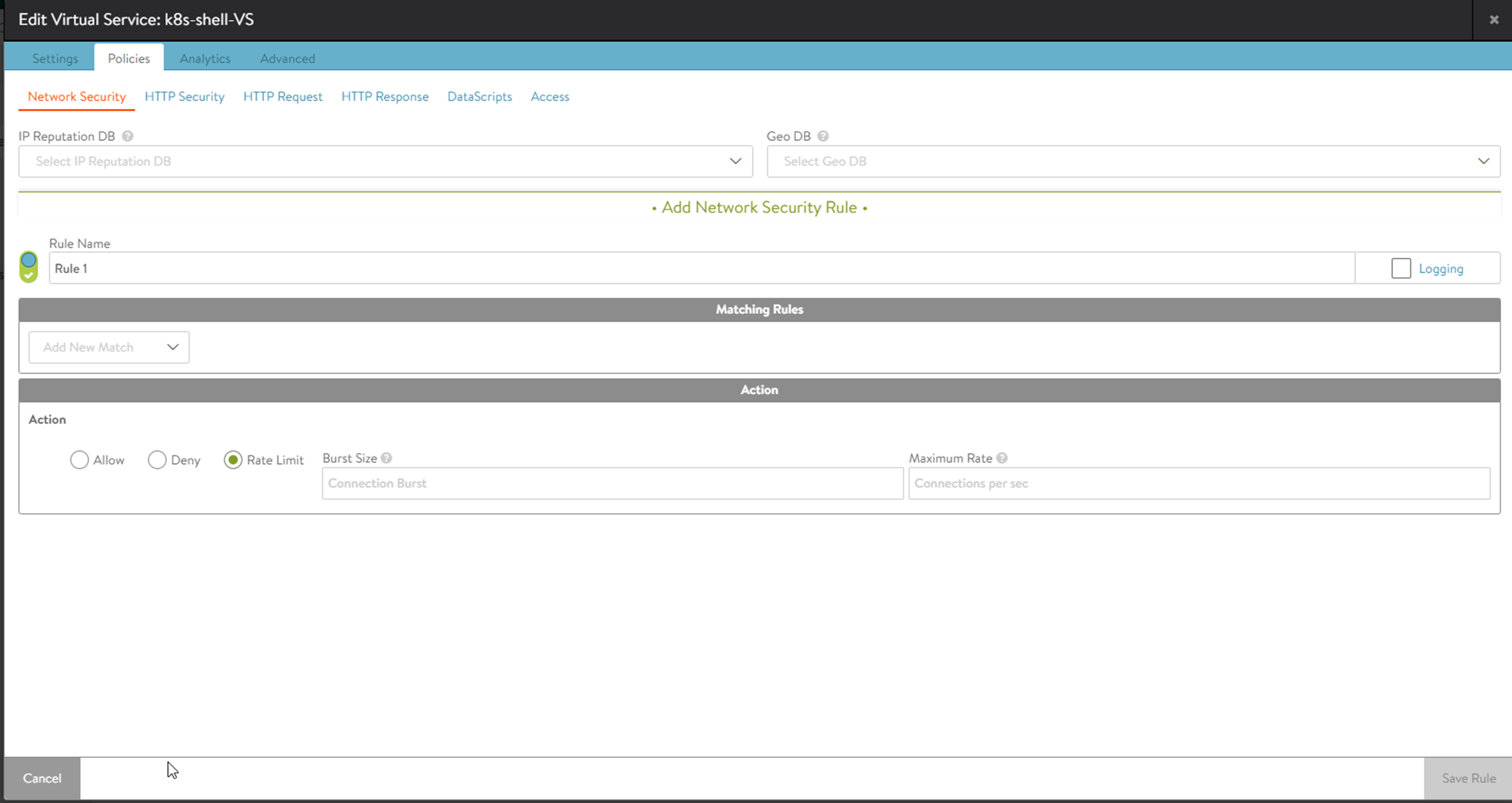
Rate Limit: Restrict clients from opening greater than the specified number of connections per second in the Maximum Rate field. Clients that exceed this number will have their excessive connection attempts silently discarded. If Burst Size is selected, clients may be able to burst above the Max Rate, provided they have not recently been opening connections. This feature may be applied to TCP or UDP. All clients that match the Match criteria will be treated as one bucket. For instance, if no Match is defined, all IP addresses will increment the Max Rate counter. Throttling would occur for all new connecting clients. Individual limits can be applied to separate networks, geographies, or IP and port criteria.
Within the , several options are available using the drop-down menu from the Rate Limit HTTP and TCP Settings.
Rate Limit Connections from a Client: Rate limit all connections made from any single client IP address to the virtual service.
Rate Limit Requests from a Client to all URLs: Rate limit all HTTP requests from any single client IP address to all URLs of the virtual service.
Rate Limit Requests from all Clients to a URL: Rate limit all HTTP requests from all client IP addresses to any single URL.
Rate Limit Requests from a Client to a URL: Rate limit all HTTP requests from any single client IP address to any single URL.
Rate Limit Failed Requests from a Client to all URLs: Rate limit all requests from a client for a specified period of time once the count of failed requests from that client crosses a threshold for that period. Clients are tracked based on their IP address. Requests are deemed failed based on client or server-side error status codes, consistent with how NSX Advanced Load Balancer logs and metrics subsystems mark failed requests.
Rate Limit Requests from all Clients to a URL: Rate limit all requests to a URI for a specified period of time once the count of failed requests to that URI crosses a threshold for that period. Requests are deemed failed based on client or server-side error status codes, consistent with how NSX Advanced Load Balancer logs and metrics subsystems mark failed requests.
Rate Limit Failed Requests from a Client to a URL: Rate limit all requests from a client to a URI for a specified time once the count of failed requests from that client to the URI crosses a threshold for that period. Requests are deemed failed based on client or server-side error status codes, consistent with how NSX Advanced Load Balancer logs and metrics subsystems mark failed requests.
Rate Limit Scans from a Client to all URLs: Automatically track clients and classify them into Good, Bad, and Unknown groups. Clients are tracked based on their IP address. Clients are added to the Good group when the NSX Advanced Load Balancer scan detection system builds a history of requests from the clients that complete successfully. Clients are added to the Unknown group when there is insufficient history about them. Clients with a history of failed requests are added to the Bad group, and their requests are rate limited with stricter thresholds than the Unknown clients group. The NSX Advanced Load Balancer scan detection system automatically tunes itself so that the Good, Bad, and Unknown client IPs group members change dynamically with changes in traffic patterns through the ADC. In other words, if a change to the website causes mass failures (such as 404 errors) for most customers, NSX Advanced Load Balancer adapts and does not mark all clients as attempting to scan the site.
Rate Limit Scans from all Clients to all URLs: Similar to the previous limit, but restricts the scanning from all clients as a single entity rather than individually. Once all clients collectively reach a limit, any client that sends the subsequent failed request will be reset.
Rate-Limiting Clients Based on Header or Cookie: NSX Advanced Load Balancer can rate-limit clients based on a header or cookie. It tracks how many requests have been seen for the header or cookie value. If the specified threshold value is exceeded, the client is rate-limited.