Configuring OSPF on a logical router enables VM connectivity across logical routers and from logical routers to edge services gateways (ESGs).
OSPF routing policies provide a dynamic process of traffic load balancing between routes of equal cost.
An OSPF network is divided into routing areas to optimize traffic flow and limit the size of routing tables. An area is a logical collection of OSPF networks, routers, and links that have the same area identification.Areas are identified by an Area ID.
Prerequisites
A Router ID must be configured, as shown in OSPF Configured on the Logical (Distributed) Router.
When you enable a router ID, the text box is populated by default with the uplink interface of the logical router.
Procedure
Example: OSPF Configured on the Logical (Distributed) Router
One simple NSX scenario that uses OSPF is when a logical router (DLR) and an edge services gateway (ESG) are OSPF neighbors, as shown here.
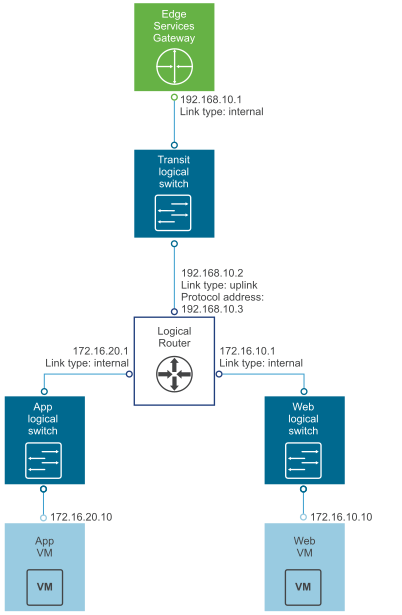
On the
Global Configuration page, the configuration settings are as follows:
- Gateway IP: 192.168.10.1. The logical router's default gateway is the ESG's internal interface IP address (192.168.10.1).
- Router ID: 192.168.10.2. The router ID is the uplink interface of the logical router. In other words, the IP address that faces the ESG.
On the
OSPF Configuration page, the configuration settings are as follows:
- Forwarding Address: 192.168.10.2
- Protocol Address: 192.168.10.3. The protocol address can be any IP address that is in the same subnet and is not used anywhere else. In this case, 192.168.10.3 is configured.
- Area Definition:
- Area ID: 0
- Type: Normal
- Authentication: None
The uplink interface (the interface facing the ESG) is mapped to the area, as follows:
- Interface: To-ESG
- Area ID: 0
- Hello Interval (seconds): 10
- Dear Interval (seconds): 40
- Priority: 128
- Cost: 1
What to do next
Make sure the route redistribution and firewall configuration allow the correct routes to be advertised.
In this example, the logical router's connected routes (172.16.10.0/24 and 172.16.20.0/24) are advertised into OSPF. To verify the redistributed routes, on the left navigation panel, click
Route Redistribution, and check the following settings:
- Route Redistribution Status shows that OSPF is enabled.
- Route Redistribution Table shows the following:
- Learner: OSPF
- From: Connected
- Prefix: Any
- Action: Permit
If you enabled SSH when you created the logical router, you must also configure a firewall filter that allows SSH to the logical router's protocol address. For example, you can create a firewall filter rule with the following settings:
- Name: ssh
- Type: User
- Source: Any
- Destination: Protocol address with value: 192.168.10.3
- Service: SSH