You can use the NSX Command Line Interface (CLI) to troubleshoot the L2 VPN service over both SSL and IPSec tunnels.
Problem
L2 VPN service is not working as expected.
Solution
- Use the following central CLI command to view configuration issues:
show edge <edgeID> configuration l2vpn.
For example, show edge edge-1 configuration l2vpn.
- Use the following commands on both the client and server Edge:
- For L2 VPN over an SSL tunnel, run the show configuration l2vpn command, and check the four following key values on the server.
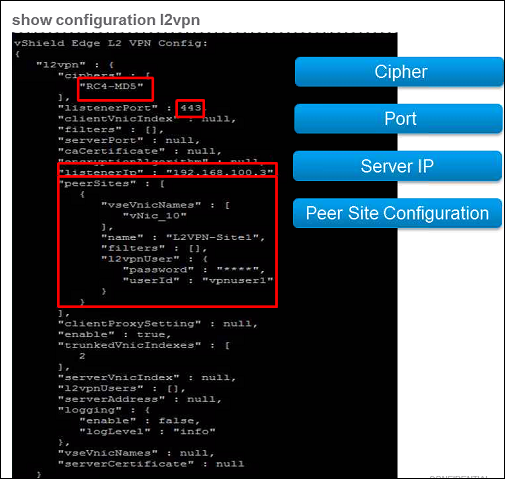
- For L2 VPN over an IPSec tunnel, run the show configuration l2vpn command, and observe the site ID of each tunnel. Check whether the site ID of each tunnel in the L2 VPN configuration matches the site ID that was auto-generated when you created the route-based IPSec tunnels.
- For L2 VPN over both SSL and IPSec tunnels, run the show service l2vpn bridge command to know the MAC addresses learned from the local and remote sites. If the ON BRIDGE flag is false, the MAC addresses learned on the trunk interface belong to the VMs on the local site. Similarly, if the ON BRIDGE flag is false, the MAC addresses learned on the tap devices (
tap0/na<index>/l2t-<index>) belong to the VMs on the remote site.For L2 VPN over both IPSec client and server, the CLI output of the show service l2vpn bridge command is as follows:nsx-edge> show service l2vpn bridge bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces br-sub 8000.005056902e5f no l2t-1 vNic_1 List of learned MAC addresses for L2 VPN bridge br-sub ------------------------------------------------------------------- INTERFACES MAC ADDR VLAN ID ON BRIDGE AGING TIMER vNic_1 00:50:56:90:2e:5f 0 yes 0.00 vNic_1 00:50:56:90:c2:e4 0 no 220.05 l2t-1 9a:80:b8:56:c7:0e 0 yes 0.00For L2 VPN over an SSL server, the CLI output of the show service l2vpn bridge command is as follows:nsx-edge> show service l2vpn bridge bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces br-sub 8000.00505690a99b no na1 vNic_1 List of learned MAC addresses for L2 VPN bridge br-sub ------------------------------------------------------------------- INTERFACES MAC ADDR VLAN ID ON BRIDGE AGING TIMER vNic_1 00:50:56:90:0d:52 30 no 16.88 na1 00:50:56:90:0d:52 10 no 11.87 vNic_1 00:50:56:90:a9:9b 30 yes 0.00 na1 d6:60:19:cb:e7:ca 0 yes 0.00For L2 VPN over an SSL client, the CLI output of the show service l2vpn bridge command is as follows:nsx-edge> show service l2vpn bridge bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces br-sub 8000.005056900d52 no tap0 vNic_1 List of learned MAC addresses for L2 VPN bridge br-sub ------------------------------------------------------------------- INTERFACES MAC ADDR VLAN ID ON BRIDGE AGING TIMER vNic_1 00:50:56:90:0d:52 10 yes 0.00 vNic_1 00:50:56:90:a9:9b 30 no 3.84 tap0 00:50:56:90:a9:9b 20 no 0.84 tap0 00:50:56:90:a9:9b 10 no 2.84 - For L2 VPN over an IPSec tunnel, run the show service l2vpn command on both the server and the client. For example, the following CLI output on the server shows the status of two IPSec tunnels:
NSX-edge-23-0> show service l2vpn L2 VPN is running ---------------------------------------- L2 VPN type: Server/Hub SITENAME IPSECSTATUS VTI GRE Site 1 UP vti-1 l2t-36 Site 2 UP vti-1 l2t-34
Make sure that the tunnel status is UP. If the tunnel status is UP, check whether the site ID of the tunnel matches the site ID that was auto-generated when you created the route-based IPSec tunnels. - For L2 VPN over an IPSec tunnel, run the show interface [interface-name] command to view details of all VTI interfaces.
- For L2 VPN over SSL and IPSec tunnels, run the show service l2vpn trunk table command.
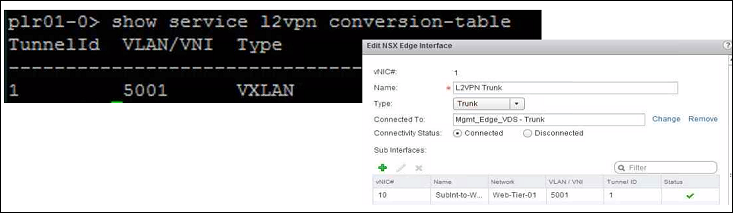
- For L2 VPN over SSL and IPSec tunnels, run the show service l2vpn conversion table command. In the following example, an Ethernet frame that arrives on tunnel #1 has its VLAN ID 1 converted to VXLAN with a VLAN of 5001 before the packet is passed to the VDS.
- For L2 VPN over an SSL tunnel, run the show configuration l2vpn command, and check the four following key values on the server.