The NSX Intelligence Recommendations feature can provide you with recommendations to help you microsegment your applications.
Generating an NSX Intelligence recommendation involves recommendations of security policies, policy security groups, and services for the application. NSX Intelligence makes the policy recommendations based on the traffic pattern of communication between virtual machines (VMs) and physical servers in your NSX environment.
You can generate an NSX Intelligence recommendation by selecting the input entities of groups or 100 VMs and physical servers, or a combination of groups, VMs, and physical servers, or existing security policies. The total number of VMs and physical servers that you can select as input cannot exceed 100 of those entities. The total number of effective VMs and physical servers that you can use in an input that includes groups, VMs, or physical servers cannot exceed 250 input entities.
For example, if you select 50 VMs and 50 physical servers as part of your recommendation input entities, you can only select groups with no more than 150 compute members combined.
You can only generate a new recommendation for security groups that were created in Policy mode. The security groups must have at least one of the supported member types in order for the NSX Intelligence feature to begin a recommendation analysis for those security groups. The supported member types include virtual machines, physical servers, virtual network interfaces (VIFs), logical ports, and logical switches. If at least one supported member type is present in the security group, the recommendation analysis can proceed, but unsupported member types are not considered during the recommendation analysis.
There are multiple ways to generate a recommendation using the NSX Intelligence user interface. The following procedure describes the available methods to use.
Prerequisites
Activate NSX Intelligence 3.2 or later on the NSX Application Platform 3.2 or later. See the Activating and Upgrading VMware NSX Intelligence 3.2 or later document.
Ensure that you have the required privileges to generate recommendations. See Role-Based Access Control in NSX Intelligence for more information.
Procedure
- From your web browser, log in with the required privileges to an NSX Manager at https://<nsx-manager-ip-address>.
- Initiate the generation of a new recommendation using one of the following methods.
Where to Start
Next Step
Select Plan & Troubleshoot > Recommendations.
Click Start New Recommendation.
Select Plan & Troubleshoot > Discover & Take Action
- Click the recommendation icon
 located on the left side of the Flows bar.
located on the left side of the Flows bar. Select Start Recommendations.
For a recommendation for a group or multiple groups, select Plan & Troubleshoot > Discover & Take Action.
Verify that the Groups view is selected in the Security view selection area.
Right-click the node for the group on which you want to generate a recommendation. Alternatively, select one or more group nodes using the select icon
 .
.Right-click one of the nodes in your selection and select Start Recommendation from the drop-down menu.
Alternatively, if you used the select icon
 to make your selection, click the recommendation icon
to make your selection, click the recommendation icon  in the Selected panel.
in the Selected panel.
For recommendations for VMs or physical servers, select Plan & Troubleshoot > Discover & Take Action.
Select at least one VM or physical server, or a combination of both.
In the Security view selection area, click the down arrow next to Groups and select Computes.
Click All and select specific VMs or physical servers or a combination of both from the Available items list. Alternatively, click All > Show All Types and select VMs or Physical Servers from the drop-down menu.
Click Apply.
Click the recommendation icon
 located on the left side of the Flows bar.
located on the left side of the Flows bar.Select Start Recommendations for the Filtered Computes.
Alternatively, if you selected the compute entity nodes using the select icon
 , click the recommendation icon
, click the recommendation icon  in the Selected panel.
in the Selected panel.
The following image shows the default values used when you initiate a new recommendation.
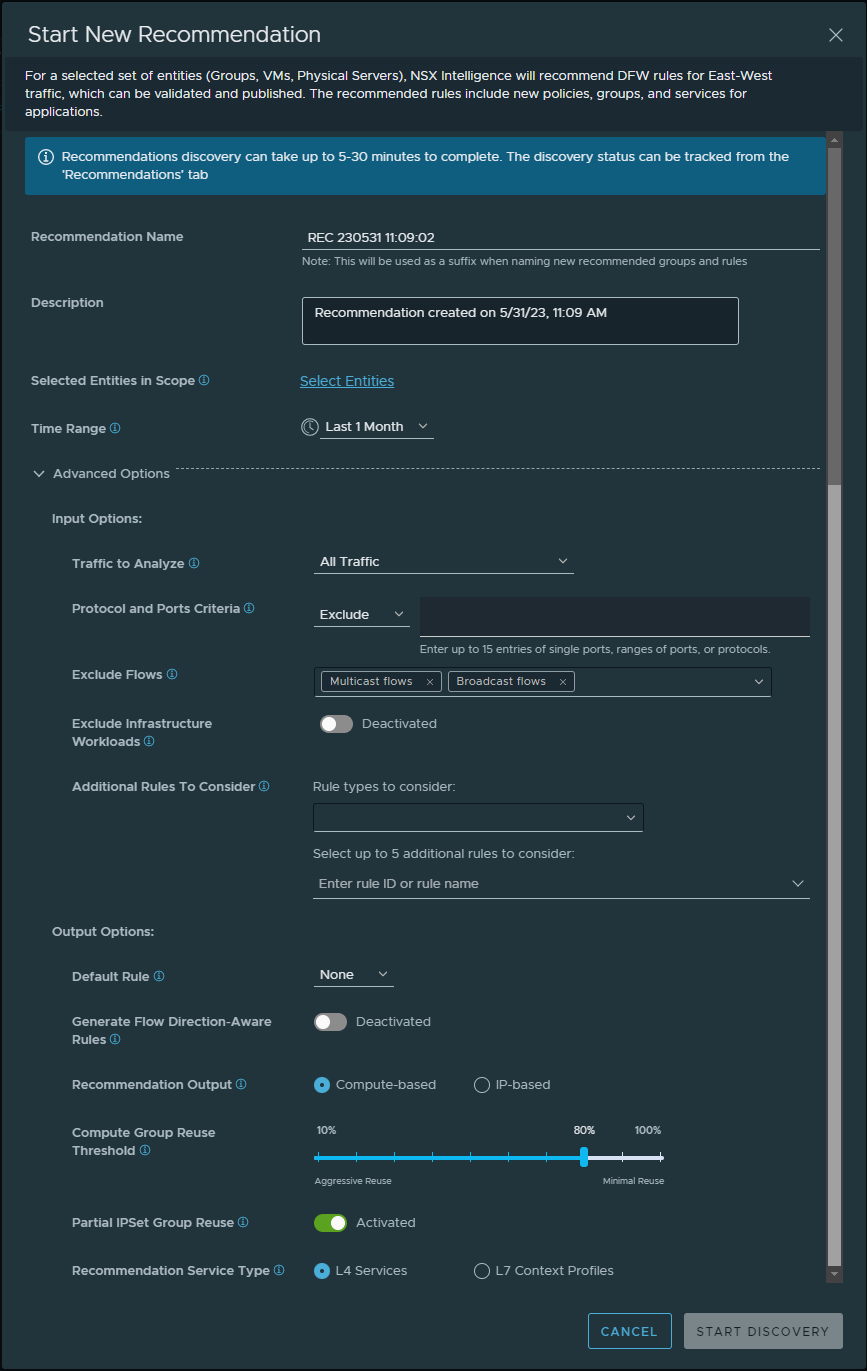
- Click the recommendation icon
- In the Start New Recommendation dialog box, change the default value for the Recommendation Name text box.
Give a name that reflects the application for which the microsegmentation is being done. This name is used when creating the names of the recommended groups and rules created during the recommendation analysis.
- Change the default value for the Description text box to make it easier to recall the information about the recommendation.
- Define or modify the VMs or physical servers that are to be used as the boundary for the security policy recommendation.
- In Selected Entities in Scope section, click Select Entities. If you already selected the groups, VMs, or physical servers before starting the new recommendation, you can click the link to the number of selected entities to modify your current selection.
- In the Select Entities dialog box, to select one or more groups that you want to include, click Groups. To select the VMs or physical servers that you want to use as the boundary for the analysis, click the VMs tab or the Physical Servers tab, and make your selection.
You can select groups and up to 100 VMs or physical servers, but no more than a total of 250 effective compute entities to use for the recommendation boundary. Deselect the entities you do not want to include. You can also click Filter and select the attributes you want to use to filter the groups, VMs, or physical servers that you want to be selected. To deselect any currently selected entities, click Clear.
- Click Save.
- (Optional) If the system found that there are existing distributed firewall (DFW) sections associated with the groups that you selected in the previous step, the Select Distributed FW Section dialog box is displayed. If you want to use an existing L4 or L7 distributed firewall (DFW) section, select one from the list. If you want the system to create a new section, select Create New Section.
- (Optional) Click Save.
The system updates the Selected Entities in Scope text box with links that indicate the number of entities that you selected. To modify your selections, click the number links.
If you selected to use an existing distributed DFW section during the recommendation analysis, the system indicates that under the Selected Entities in Scope text box.
- (Optional) In the Time Range text box, change the default value shown.
The default value is Last 1 Month. The traffic flows that occurred between the selected VMs or physical servers, or groups of VMs or physical servers during the selected time range are used during the recommendation analysis. Other time range values to select from are Last 1 hour, Last 12 hours, Last 24 hours, Last 1 week, or Last 2 weeks.
- Expand the Advanced Options section.
- In the Input Options subsection, modify the assigned default values, as necessary.
If you are not using an existing DFW section, you can modify the default assigned values. If you chose to use an existing DFW section, the values shown in this section are obtained from that existing DFW section.
- In the Traffic to Analyze drop-down menu, select the type of traffic flows to consider in the recommendation analysis. The default is All Traffic.
Incoming and Outgoing Traffic - All traffic flow types that originate from inside the application boundary to outside the boundary, and from outside the application boundary to inside of the boundary are considered.
Incoming Traffic - Only traffic flows that originate outside of your application boundary are considered.
All Traffic - All outbound, inbound, and intra-application traffic flow types are considered.
Incoming and Intra-application Traffic - All traffic flow types that originate from outside of your application boundary and intra-application traffic are considered.
- In the Protocol and Ports Criteria section, select Exclude or Match Any to specify whether you want to exclude or match any of the ports, ranges of ports, or protocols that you enter in the text box.
By default, traffic flows that occurred from all known ports and protocols in your environment during the specified time range are used during the recommendation analysis. To filter the traffic flows that are to be used during the recommendation analysis, enter any mix of up to 15 entries of single ports, range of ports, or protocols whose traffic flows you want to either exclude or use to match any of the entries. For example, 88, 90-98, TCP:100-111, UDP.
- In the Exclude Flows section, specify the types of traffic flows you want to be excluded during the recommendation analysis.
By default, multicast flows and broadcast flows are excluded. You can deselect one or both flow types by clicking X next to the flow type name.
- To exclude the infrastructure compute entities from being included in the new recommendation analysis, activate the Exclude Infrastructure Workloads toggle.
When you activate this toggle, the Recommendation engine excludes all infrastructure compute entities and traffic flows that occurred with them from the recommendation analysis. The Recommendation engine does not reuse groups that contain infrastructure entities. The context input does not change even if it contains any infrastructure compute entities. However, the Recommendation engine does not recommend any firewall rules that have any infrastructure compute entities in the rule source or destination.
See Managing Compute Entity Classifications in NSX Intelligence for more information.
- In the Additional Rules to Consider section, optionally specify rules that should also be used to determine which traffic flows are considered unsegmented.
By default, the Recommendation engine uses the rule where Source and Destination have the
Anyvalue.If you want more rules to be considered during the recommendation analysis, you can select up to three rule types from the Rule types to consider drop-down menu or from the Additional rules to consider drop-down menu, select up to five specific rules.
Rule types or specific rules Description Rules with ANYin SourceWhen selected, non-default rules whose Source value is
ANYare considered default rules. Traffic flows that encounter these rules are considered unmicrosegmented. For the reuse of existing sections, these additional default rules are not considered for modification.Rules with ANYin DestinationIf selected, non-default rules whose Destination value is
ANYare considered as default rules. Traffic flows that encounter these rules are considered unmicrosegmented. For the reuse of existing sections, these additional default rules are not considered for modification.Rules with ANYin ServiceIf selected, non-default rules whose Service value is
ANYare considered as default rules. Traffic flows that encounter these rules are considered unmicrosegmented. For the reuse of existing sections, these additional default rules are not considered for modification.List of specific rule IDs or rule names This list can include up to five rule IDs or rule names that are considered as additional default rules. Traffic flows that encounter the default rules and these rules are considered unmicrosegmented. For the reuse of existing sections, these additional default rules are not considered for modification.
- In the Traffic to Analyze drop-down menu, select the type of traffic flows to consider in the recommendation analysis. The default is All Traffic.
- In the Output Options subsection of the Start New Recommendation section dialog box, optionally make modifications to the default settings.
- From the Default Rule drop-down menu, select a connectivity strategy to use to create the default rule for the security policy. Appropriate action is set on the rule based on the connectivity strategy value you selected. The default is None.
Denylist - Creates a default allow rule.
Allowlist - Creates a default drop rule.
None - No default rule is created.
- Activate the Generate Flow Direction-Aware Rules toggle if you want the Recommendation engine to create and recommend more granular rules that are based on the direction of the unmicrosegmented traffic flows.
During the recommendation analysis, unsegmented traffic flows with different directions are not aggregated together to recommend a new rule. The source groups and destination groups of a recommended rule consist of either members of context profiles or non-members of context profiles. The recommendation boundary is defined by the selection you made in the Selected Entities in Scope section of the Start New Recommendation dialog box. The DFW recommendation that results from the analysis helps ensure that no external entity has an allow rule to go within the recommendation boundary unless there was an explicit flow from an outside entity to an entity with the specified recommendation boundary.
- Change the default value for the Recommendation Output, if necessary.
Compute-Based is the default output mode used. This mode means the DFW policy recommendation that the recommendation engine generated contains groups whose members are VMs, physical servers, or both.
If the IP-Based recommendation output mode is selected, the generated DFW policy recommendation contains groups whose members are IP set objects with a static list of IP addresses. An IP-based recommendation is not tightly bound to a VM. If a VM gets deleted and its IP address gets assigned to a new VM, the new VM gets assigned to the same group. NSX Intelligence also applies the existing DFW policies for the group to the new VM.
- Change the default value for the Compute Group Reuse Threshold as you see fit to use when generating the rule recommendation.
You can set the threshold percentage value from 10 through 100. The value specifies how strictly the system reuses existing compute-based groups (non-IP Set groups) to cover the detected flows that are not micro-segmented. Use this value to control whether existing groups are to be reused or new groups created. The Group Reuse feature is applicable for any recommendation job with an existing security policy or new security policy.
If you set this value to 100, the groups picked for the recommendation must not have any extraneous compute entities. A group's compute members do not have to be the same as the leaked compute entities. For example, if the leaked compute entities are [VM1, VM2] and group G1 has [VM1] as a member and group G2 has [VM2] as a member, then compute members of G1 and G2 are not the same as the leaked compute entities but they can be picked together to cover the leaked [VM1, VM2] compute entities.
Using a very high value can result in creating more new groups, however, as existing groups are less likely to be reused in rules being modified.
Setting this value to lower values, like 10 or 20, means that even compute-based groups with extraneous members, other than the compute entities the system is seeking to group, can be picked as additional rule sources or destinations. Using a lower value can result in an aggressive group reuse and hence fewer new groups will be recommended.
- Deactivate the Partial IP Set Group Reuse toggle if, during the recommendation analysis, you want the Recommendation engine to only reuse existing IP groups whose IP set is the same as the IP set of the leaked IPs.
By default, this toggle is activated.
- If necessary, change the value for Recommendation Service Type.
The default type is L4 Services, which is composed of the respective transport layer port and protocol. Alternatively, you can select L7 Context Profiles to indicate that you want an application layer protocol rule recommendation.
Beginning with NSX Intelligence 4.1.1 release, if you selected an existing L7 DFW section in the Selected Entities in Scope area of the dialog box, L7 rule recommendations are included for existing sections. For more information, see Recommendation for existing DFW sections.
- From the Default Rule drop-down menu, select a connectivity strategy to use to create the default rule for the security policy. Appropriate action is set on the rule based on the connectivity strategy value you selected. The default is None.
- To begin the recommendation analysis, click Start Discovery.
NSX Intelligence processes the submitted recommendations jobs serially. On average, it can take anywhere between three to four minutes to finish each recommendation analysis, depending on whether there are recommendation jobs that are still waiting to be processed. If NSX Intelligence must analyze many traffic flows, the generation of a recommendation can take anywhere from 10 to 15 minutes.
The Recommendations table displays the status of the recommendation job. The following screenshot shows a sample Recommendations page that displays a recommendation job that is waiting to be processed and another recommendation that is ready to be published. The expanded row for the recommendation that is ready to be published displays the details used to generate that DFW recommendation.
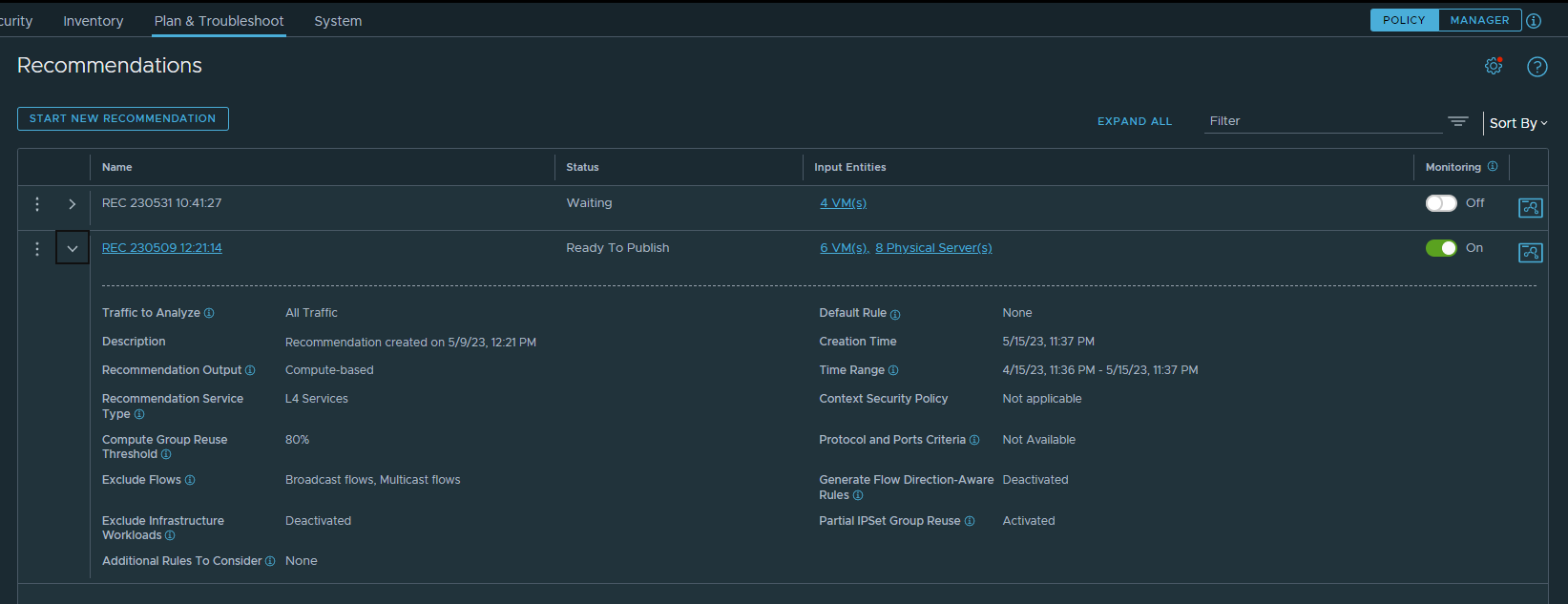
You can track the status of the recommendation analysis job in the Status column of the Recommendations table. The status progresses from Waiting, to Discovery in Progress, to Ready to Publish, and Published.
If the system does not generate a recommendation, the
Statusvalue gets set to No Recommendations Available. If the recommendation analysis failed for some reason, the displayed status is Failed.Recommendation jobs that have the Waiting status or the Discovery in Progress status can be canceled. Click the Actions menu icon
 and select Cancel Discovery.
and select Cancel Discovery.Canceling a recommendation job removes the job from the recommendation queue and its status is changed to Discovery Canceled. After a recommendation discovery is canceled, you can select Review and Rerun in the Actions menu, make any modifications to your previous input selections, and resubmit the recommendation analysis job.
You can also select Delete from the Actions menu if a recommendation job is in the Waiting or Discovery in Progress or Discovery Canceled state. Deleting a recommendation job removes all information about the selections you made before initiating the recommendation analysis.
The Input Entities column lists the entities that were used to generate the recommendation. Clicking the linked text in this column displays the Selected Entities dialog box in a read-only mode. You review the groups and their members, and any VMs that were included in the recommendation analysis.
The Monitoring column indicates whether changes are being monitored for the original input entities used to generate the recommendation. This feature is available for recommendations with a status of Ready to Publish, No Recommendations Available, or Failed. You can set the Monitoring toggle to On or Off. When the toggle is on, changes in the scope of the input entities or connectivity strategy are checked every hour.
If any changes occurred with any of the input entities used, the change-detected icon
 appears next to the Ready to Publish, No Recommendations Available, or Failed status. You can review the changes and rerun the recommendation. See Rerun NSX Intelligence Recommendations for more information.
appears next to the Ready to Publish, No Recommendations Available, or Failed status. You can review the changes and rerun the recommendation. See Rerun NSX Intelligence Recommendations for more information.When you click the canvas icon
 on the rightmost side of the recommendation row, the visualization of the selected entities is displayed in the graphical canvas under the Plan & Troubleshoot > Discover and Take Action user interface. If the recommendation status displayed is Published, when you click the canvas icon, recommended groups are displayed in the Discover and Take Action graphical canvas.
on the rightmost side of the recommendation row, the visualization of the selected entities is displayed in the graphical canvas under the Plan & Troubleshoot > Discover and Take Action user interface. If the recommendation status displayed is Published, when you click the canvas icon, recommended groups are displayed in the Discover and Take Action graphical canvas.
- When the Status value is
Ready to Publish, review the generated recommendation and decide whether to publish it. For more information, see Review and Publish Generated NSX Intelligence Recommendations.