The NSX Public Cloud Gateway (PCG) provides north-south connectivity between the public cloud and the on-prem management components of NSX-T Data Center.
| Public Cloud | PCG instance type |
|---|---|
| AWS | c5.xlarge. Some regions might not support this instance type. Refer to AWS documentation for details. |
| Microsoft Azure | Standard DS3 v.2 |
Architecture
The PCG can either be a standalone gateway appliance or shared between your public cloud VPCs or VNets to achieve a hub and spoke topology.
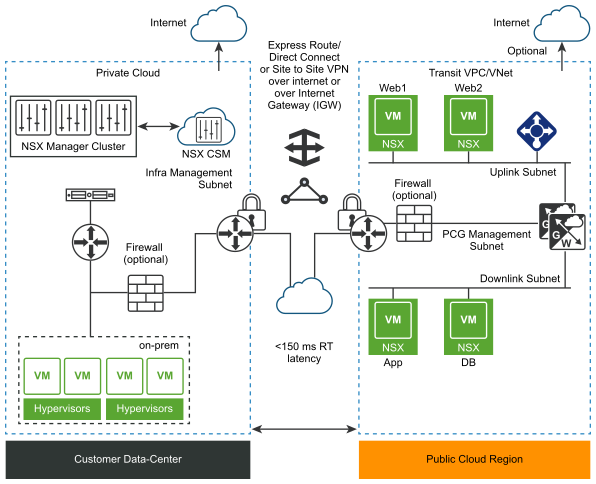
Modes of Deployment
Self-managed VPC/VNet: When you deploy the PCG in a VPC or VNet, it qualifies the VPC or VNet as self-managed, that is, you can bring VMs hosted in this VPC or VNet under NSX management.
Transit VPC/VNet: A self-managed VPC/VNet becomes a Transit VPC/VNet when you link Compute VPCs/VNets to it.
Compute VPC/VNet: VPCs/VNets that do not have the PCG deployed on them but link to a Transit VPC/VNet are called Compute VPCs/VNets.
Subnets Required in Your VPC/VNet to deploy PCG
- Management subnet: This subnet is used for management traffic between on-prem NSX-T Data Center and PCG. Example range: /28.
- Uplink subnet: This subnet is used for north-south internet traffic. Example range: /24.
- Downlink subnet: This subnet encompasses the workload VM's IP address range. Size this subnet bearing in mind that you might need additional interfaces on the workload VMs for debugging.
PCG deployment aligns with your network addressing plan with FQDNs for the NSX-T Data Center components and a DNS server that can resolve these FQDNs.
Modes of VM-Management
NSX Enforced Mode: In this mode, workload VMs are brought under NSX management by installing NSX Tools on each workload VM to which you apply the tag nsx.network=default in your public cloud.
Native Cloud Enforced Mode: In this mode, your workload VMs can be brought under NSX management without the use of NSX Tools.
Quarantine Policy
- In the NSX Enforced Mode, you can enable or disable Quarantine Policy. As a best practice, disable Quarantine Policy and whitelist all your VMs when onboarding workload VMs.
- In the Native Cloud Enforced Mode Quarantine Policy is always enabled and cannot be disabled.
Possible Design Options
Regardless of the mode you deploy the PCG in, you can link a Compute VPC/VNet to it in either mode.
| PCG Deployment Mode in Transit VPC/VNet | Possible Modes when linking a Compute VPCs/VNets to this Transit VPC/VNet |
|---|---|
| NSX Enforced Mode |
|
| Native Cloud Enforced Mode |
|
Once a mode is selected for a Transit or Compute VPC/VNet, you cannot change the mode. If you want to switch modes, you must undeploy the PCG and redeploy it in the desired mode.