The clusters in the NSX for vSphere environment are displayed on the Migrate Hosts page. The clusters are arranged into migration groups, each migration group contains one vSphere host cluster. There are several settings which control how the host migration is performed.
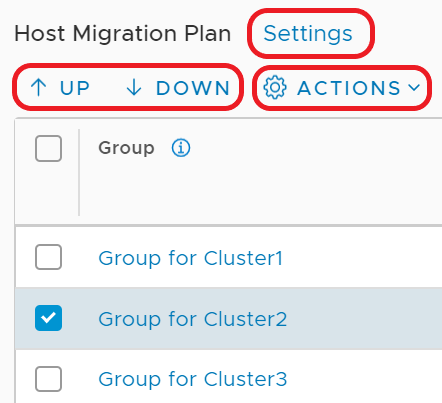
- Click Settings to change the global settings: Pause Between Groups and Migration Order Across Groups.
- Select a single host group (cluster) and use the arrows to move it up or down in the migration sequence.
- Select one or more host groups (clusters) and click Actions to change these host groups settings: Migration Order Within Groups, Migration State, and Migration Mode.
Pause Between Groups
Pause Between Groups is a global setting that applies to all host groups. If pausing is enabled, the migration coordinator migrates one host group, and then waits for input. You must click Continue to continue to the next host group.
By default, Pause Between Groups is disabled. If you want to verify the status of the applications running on each cluster before proceeding to the next one, enable Pause Between Groups.
Serial or Parallel Migration Order
-
Migration Order Across Groups is a global setting that applies to all host groups.
- Serial: One host group (cluster) at a time is migrated.
- Parallel: Up to five host groups at a time are migrated. After those five host groups are migrated, the next batch of up to five host groups are migrated.
Important: For migrations involving vSphere Distributed Switch 7.0, do not select parallel migration order across groups.
-
Migration Order Within Groups is a host group (cluster) specific setting, so can be configured separately on each host group.
- Serial: One host within the host group (cluster) at a time is migrated.
- Parallel: Up to five hosts within the host group are migrated at a time. After those hosts are migrated, the next batch of up to five hosts are migrated.
Important: Do not select parallel migration order within groups for a cluster if you plan to use Maintenance migration mode for that cluster.
By default, both settings are set to Serial. Together, the settings determine how many hosts are migrated at a time.
| Migration Order Across Groups (Clusters) | Migration Order Within Groups (Clusters) | Maximum Number of Hosts Attempting Migration Simultaneously |
|---|---|---|
| Serial | Serial | 1 One host from one host group |
| Serial | Parallel | 5 Five hosts from one host group |
| Parallel | Serial | 5 One host from five host groups |
| Parallel | Parallel | 25 Five hosts from five host groups |
If there is a failure to migrate a host, the migration process will pause after all in-progress host migrations have finished. If Parallel is selected for both migration across groups and migration within groups, there might be a long outage for the failed host before you can retry migration.
Sequence of Migration Groups
You can select a host group (cluster) and use the arrows to move it up or down in the list of groups.
If migration fails for a host, you can move its host group to the bottom of the list of groups. The migration of other host groups can proceed while you resolve the problem with the failed host.
Migration State
Host groups (clusters) can have one of two migration states:
- Enabled
Hosts groups with a migration state of Enabled are migrated to NSX-T when you click Start on the Migrate Hosts page.
- Disabled
You can temporarily exclude host groups from migration by setting the migration state for the groups to Disabled. Hosts in disabled groups are not migrated to NSX-T when you click Start on the Migrate Hosts page. However, you must enable and migrate all Disabled host groups before you can click Finish. Finish all host migration tasks and click Finish within the same maintenance window.
In the Resolve Configuration step, the migration coordinator identifies the hosts that are ineligible for migration. In the Migrate Hosts step, these hosts are assigned the migration state of Do not migrate. For example, hosts that do not have NSX for vSphere installed have the Do not migrate status.
Migration Mode
Migration Mode is a host group (cluster) specific setting, and can be configured separately on each host group. In the Migrate Hosts step, you select whether to use In-Place or Maintenance mode.
- Automated
- Manual
In-Place migration mode is not supported if your NSX for vSphere installation uses vSphere Distributed Switch 7.0.
If your environment uses Distributed Firewall, select Automated Maintenance migration mode. If you select a different migration mode, the following limitations apply to environments with Distributed Firewall:
- If you use Manual Maintenance migration mode, all VMs must be moved to NSX-T hosts, connected to NSX-T segments, and powered on before the last NSX for vSphere host starts migrating. When you migrate your last NSX for vSphere host, do not power off the VMs on the host. Move them to an NSX-T host using vMotion.
- If you use Manual Maintenance migration mode, VMs have a gap in firewall protection for up to 5 minutes after they move to an NSX-T host.
-
If you use In-Place migration mode, and you have Distributed Firewall rules that are applied to a VM, those rules are not pushed to the host until the host and all its VMs are migrated. Until the rules are pushed to the host, the following applies:
- If the NSX-T default rule is
deny, the VM is not accessible. - If the NSX-T default rule is
accept, the VM is not protected by the applied-to rules.
- If the NSX-T default rule is
-
In-Place migration mode
NSX-T is installed and NSX components are migrated while VMs are running on the hosts. Hosts are not put in maintenance mode during migration. Virtual machines experience a short network outage and network storage I/O outage during the migration.
-
Automated Maintenance migration mode
A task of entering maintenance mode is automatically queued. VMs are moved to other hosts using vMotion. Depending on availability and capacity, VMs are migrated to NSX for vSphere or NSX-T hosts. After the host is evacuated, the host enters maintenance mode, NSX-T is installed, and NSX components are migrated. VMs are migrated back to the newly configured NSX-T host.
-
Manual Maintenance migration mode
A task of entering maintenance mode is automatically queued. To allow the host to enter maintenance mode, do one of the following tasks:- Power off all VMs on the hosts.
- Move the VMs to another host using vMotion or cold migration.
Once the host is in maintenance mode, NSX-T is installed on the host and NSX components are migrated.