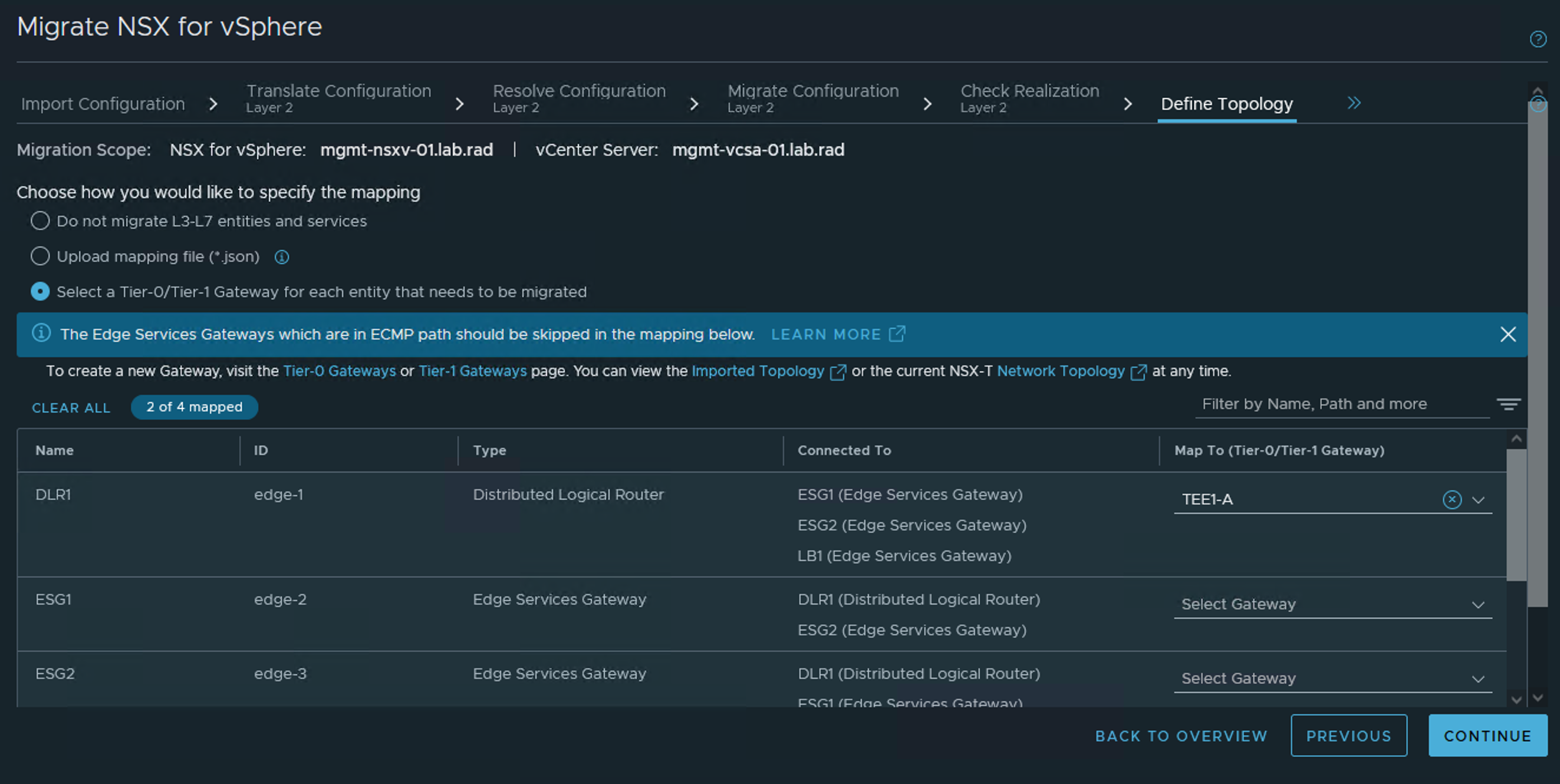
In this step, you specify the topology that will be migrated. This can be done through the NSX Manager UI or by using a mapping file in JSON format.
This mapping specifies how Edge Service Gateways (ESGs) and Distributed Logical Routers (DLRs) should map to gateways in
NSX. Before providing the mapping, evaluate your topology requirements and plan to do the following:
- Create tier-0 and tier-1 gateways and configure dynamic or static routing on the tier-0 gateways towards the northbound routers based on your requirements. For dynamic routing you can choose to configure either BGP or OSPF, based on your NSX-V configuration. You need to manually configure this northbound routing.
- When configuring northbound routing, you must create and configure uplink interfaces on the NSX-T tier-0 gateway. The uplink interface subnet can be the same subnet as the NSX-V ESG northbound uplinks. The uplink interface IP addresses must be different from the IP addresses of the ESG uplinks.
- After configuring the dynamic routing on tier-0 gateways, check that the dynamic routing has converged, that is, BGP sessions are established or OSPF neighborships are FULL as applicable.
- Determine how you will map the ESGs and DLRs. The northbound ESGs without any L4-L7 services should be skipped. These are usually the ESGs peering with northbound routers and are in ECMP path. If you are using VPN on a northbound ESG, migrating to active-standby tier-0 is recommended. In other cases, migrating the ESGs/DLRs to tier-1 is recommended. An ESG and a DLR can be merged in one mapping entry.
When defining a mapping, make sure that the following conditions are met. Note that a tier-1 distributed router (DR)-only gateway is a tier-1 gateway without any Edge cluster.
- A tier-0 gateway must have an uplink interface.
- A tier-1 DR-only gateway must be connected to a tier-0 gateway that has an uplink interface.
- When UDLR is mapped to a stretched tier-1 DR only, the stretched tier-0 to which it is connected must have an uplink on all sites.
- When UDLR is mapped to a stretched tier-0, the stretched tier-0 must have an uplink on all sites.
- When UDLR is mapped to an active-standby stretched tier-1, the primary site of this gateway must match the primary site of the connected stretched tier-0.
An example of a mapping file that maps ESGs to a tier-0 gateway:
[
{
"name":"nsxv-to-nsxt-mapping",
"v_edges_to_policy_gateways_mappings":[
{
"v_edges":[
"edge-1",
"edge-2"
],
"policy_gateway_name": "tier0-gateway"
"policy_gateway_path": "/infra/tier-0s/tier0-gateway"
}
]
}
]
Here is a sample mapping file for migrating a cross-vCenter environment to NSX Federation:
[
{
"name": "london",
"nsxv_id": "10.206.106.163",
"nsxt_site_id": "1722c659-b0a9-4e70-b7ba-f264e057e1ea",
"v_edges_to_policy_gateways_mappings": [
{
"v_edges": [
"edge-2"
]
"policy_gateway_name": "Tier1Gateway1",
"policy_gateway_path": "/infra/tier-1s/Tier1Gateway1"
}
]
},
{
"name": paris",
"nsxv_id": "10.206.96.206",
"nsxt_site_id": "00d3802e-5673-4791-b86d-71805a2c0aa6",
"v_edges_to_policy_gateways_mappings": [
{
"v_edges": [
"edge-2"
]
"policy_gateway_name": "Tier1Gateway1",
"policy_gateway_path": "/infra/tier-1s/Tier1Gateway1"
}
]
},
{
"name": "site-GM",
"nsxv_id": "10.206.106.163",
"nsxt_site_id": "",
"v_edges_to_policy_gateways_mappings": [
{
"v_edges": [
"edge-4e5065d6-d12d-49b1-a7da-5d9fcc7888f0"
]
"policy_gateway_name": "Tier1Gateway1",
"policy_gateway_path": "/infra/tier-1s/Tier1Gateway1"
}
]
},
]
If you are migrating a cross-vCenter environment to NSX Federation, note the following:
- Tier-0 gateways created on Local Manager must have an Edge cluster assigned.
- Tier-1 gateways created on Local Manager must either have an Edge cluster assigned or be connected to a tier-0 gateway that has an Edge cluster assigned.
- Tier-0 and tier-1 gateways created on Global Manager must span all the sites.