If your NSX-V environment has a topology that is the same as one of those described below, you can migrate it end to end by choosing the Fixed Topology option.
Support for firewall is independent of the topology. Every topology listed below supports the following:
- NSX Manager
- Distributed Firewall
- Service Composer
- Grouping Objects
Unsupported Features
In all topologies, the following features are not supported:
- IP Multicast.
- IPv6.
- SSL VPN
For detailed information about which features and configurations are supported, see Detailed Feature Support for Migration.
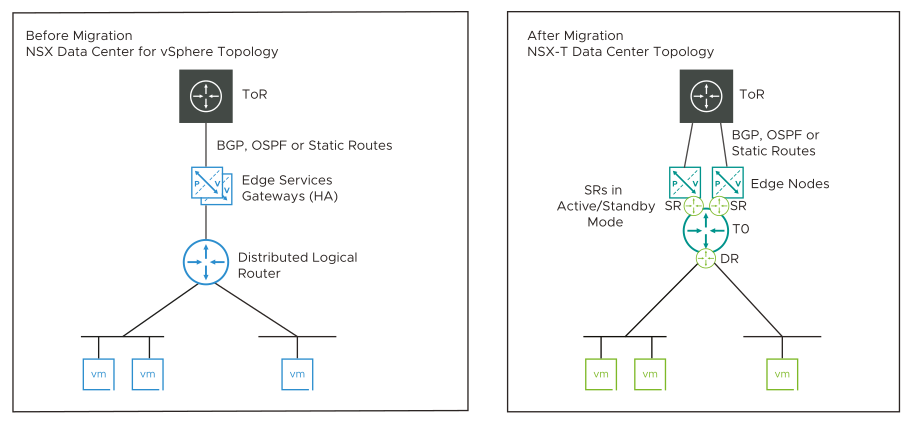
ESG with High Availability and L4-L7 Services (Topology 1)
This topology contains the following configurations:
- A Distributed Logical Router (DLR) peering with Edge Services Gateway (ESG).
- ECMP is not configured.
- The ESGs are in a high availability configuration.
- BGP, OSPF or static routing is configured between the ESG and top-of-rack (ToR) northbound routers. If BGP is configured, all ESGs must be configured with the same global BGP settings.
- The ESGs can be running L4-L7 services:
- VPN, NAT, DHCP server, DHCP relay, DNS forwarding, Edge Firewall are supported services.
- Load balancer is not supported in this topology.
About migrating DHCP relay:
- Although DHCP relay can be configured on either ESG or DLR, only DHCP relay on DLR will be migrated.
- In this topology, if DHCP relay is running on the DLR, and DHCP server is running on the ESG, both DHCP relay and DHCP server will be migrated to the same NSX gateway. They will not be migrated separately.
After migration, this configuration is replaced with a tier-0 gateway.
- The tier-0 gateway service router is in active/standby mode.
- The IP addresses of the DLR interfaces are configured as downlinks on the tier-0 gateway.
- The BGP, OSPF or static routing configuration of the ESG is translated to a BGP, OSPF or static routing configuration on the tier-0 gateway.
Note: When static routing is used, the NSX HA Virtual IP (VIP) address is not configured automatically. You must add the NSX HA VIP address manually after the migration.
- Supported services are migrated to the tier-0 gateway.
Note: Depending on your configuration, you might need to provide new IP addresses for the tier-0 gateway uplinks. For example, on an ESG, you can use the same IP address for the router uplink and for the VPN service. On a tier-0 gateway, you must use the different IP address for VPN and uplinks. See
Example Configuration Issues for more information.
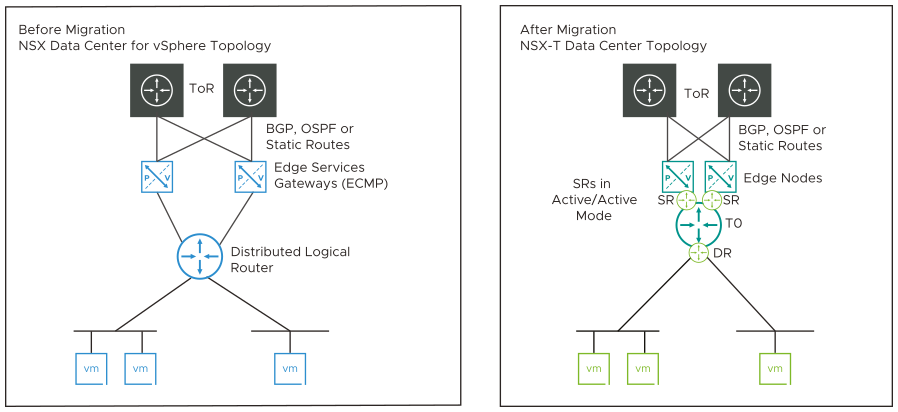
ESG with No L4-L7 Services (Topology 2)
This topology contains the following configurations:
- The DLR has ECMP enabled and peers with multiple ESGs.
- BGP, OSPF or static routing is configured between the ESG and top-of-rack (ToR) northbound routers. If BGP is configured, all ESGs must be configured with the same global BGP settings.
- If BGP is configured between the DLR and ESG, all BGP neighbors on the DLR must have the same weight.
- The ESGs must not be running L4-L7 services.
After migration, this configuration is replaced with a tier-0 gateway.
- The tier-0 gateway service router is in active/active mode.
- The IPs of the DLR interfaces are configured as downlinks on the tier-0 Gateway.
- The BGP or OSPF configuration of the ESGs is translated to a BGP or OSPF configuration, respectively, on the tier-0 gateway. Route redistribution configuration is translated.
- Static routes from ESGs and DLRs are translated to static routes on the tier-0 gateway.
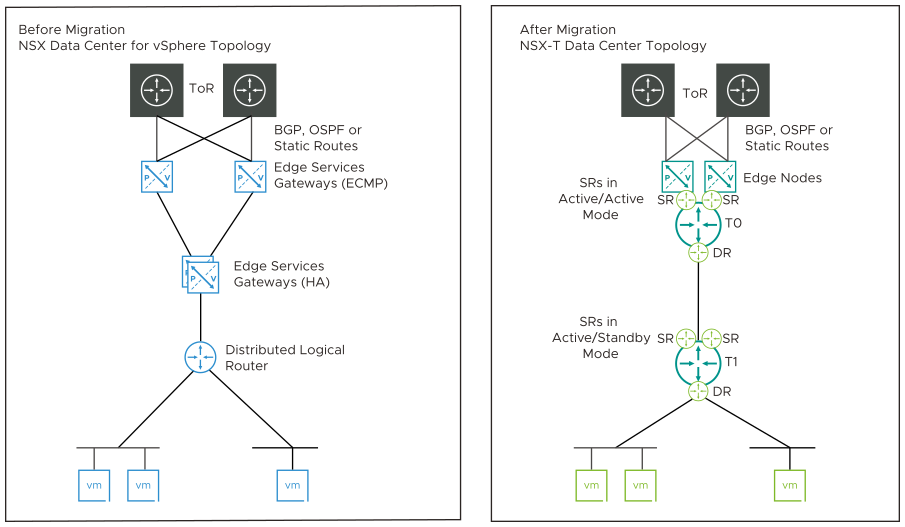
Two Levels of ESG with L4-L7 Services on Second-Level ESG (Topology 3)
The topology contains the following configurations:
- Two levels of ESGs with DLR.
- The first-level (ToR-facing) ESGs must not be running L4-L7 services.
- BGP, OSPF or static routing is configured between the first-level ESGs and top-of-rack (ToR) northbound routers. If BGP is configured, all ESGs must be configured with the same global BGP settings.
- The first-level ESGs have ECMP enabled and peer with the second-level ESGs.
- The second-level ESGs can run L4-L7 services:
- NAT, DHCP server, DHCP relay, DNS forwarding, inline load balancer, and Edge firewall are supported.
- VPN is not supported.
About migrating DHCP relay:
- Although DHCP relay can be configured on either ESG or DLR, only DHCP relay on DLR will be migrated.
- In this topology, if DHCP relay is running on the DLR, and DHCP server is running on the ESG, both DHCP relay and DHCP server will be migrated to the same NSX gateway. They will not be migrated separately.
After migration, this configuration is replaced with a tier-0 gateway and a tier-1 gateway.
- The first-level ESGs are replaced with a tier-0 gateway. The service router is in active/active mode.
- The IPs of the first-level ESG uplinks are used for the tier-0 gateway uplinks.
- The tier-0 gateway peers with northbound routers (ToR) using BGP or OSPF.
- The second-level ESGs are translated to a tier-1 gateway, which is linked to the tier-0 gateway.
- The IPs of the DLR interfaces are configured as downlinks on the tier-1 Gateway.
- Any services running on the second-level ESG are migrated to the tier-1 gateway. The active/passive Service Routers on the tier-1 gateway use the same Edge nodes that are used for the tier-0 gateway.
- The BGP or OSPFconfiguration on the first-level ESGs is translated to a BGP or OSPF configuration, respectively, on the tier-0 gateway. Route redistribution configuration is translated.
- Static routes from ESGs and DLRs are translated to static routes on the tier-0 gateway. Static routes between the DLR and second-level ESGs are not needed, and so are not translated.
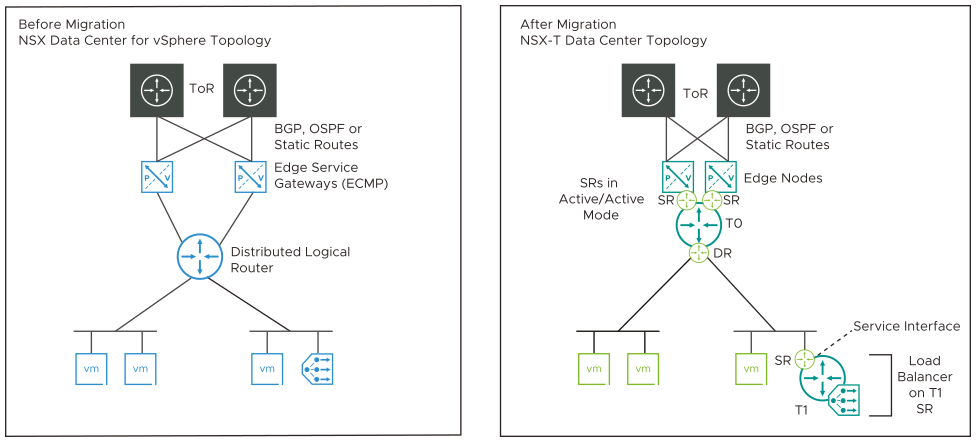
One-Armed Load Balancer (Topology 4)
This topology contains the following configurations:
- The DLR has ECMP enabled and peers with multiple ESGs.
- BGP, OSPF or static routing is configured between the ESG and top-of-rack (ToR) northbound routers. If BGP is configured, all ESGs must be configured with the same global BGP settings.
- If BGP is configured between the DLR and ESG, all BGP neighbors on the DLR must have the same weight.
- The ToR-facing ESGs must not be running L4-L7 services.
- An ESG is a single-arm load balancer attached to a Logical Switch, which is connected to a DLR. This ESG can also run Edge firewall and DHCP.
After migration, the top-level (ToR-facing) Edge Services Gateways and the DLR are replaced with a tier-0 gateway. The ESG performing load balancing service is replaced with a tier-1 gateway.
- The tier-0 gateway service router is in active/active mode.
- The IPs of the DLR interfaces are configured as downlinks on the tier-0 Gateway.
- The BGP or OSPF configuration of the top-level ESGs is translated to a BGP or OSPF configuration, respectively, on the tier-0 gateway. Route redistribution configuration is translated.
- Static routes from the top-level ESGs and DLRs are translated to static routes on the tier-0 gateway.
- The load balancing configuration on the ESG is translated to a one-arm load balancer using Service Interface (SI) configuration on the tier-1 Service Router.
VLAN-Backed Micro-Segmentation (Topology 5)
This topology uses Distributed Firewall to provide firewall protection to workloads connected to VLAN-backed distributed port groups.
This topology uses the following
NSX-V features:
- NSX Manager
- Host Preparation (Distributed Firewall only)
- Distributed Firewall
- Service Composer
- Grouping Objects
This topology must not contain the following features:
- Transport Zone
- VXLAN
- Logical Switch
- Edge Services Gateway
- Distributed Logical Router