Follow this workflow to configure EVPN with Inline mode.
Prerequisites
A typical BGP EVPN Inline mode deployment topology has the following characteristics:
- There are point-to-point uplinks between edge nodes and external routers over individual VLAN segments.
- There are BGP peering sessions between edge nodes and external routers using loopback interfaces.
- Loopback reachability can be achieved using either static routing or OSPF protocol.
The following diagram depicts a typical BGP EVPN Inline mode deployment topology:
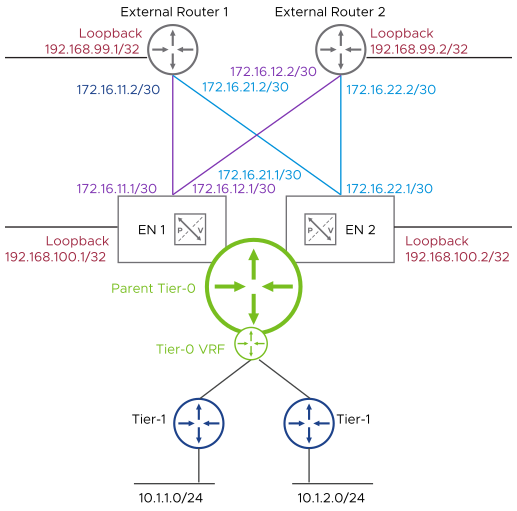
Procedure
- Create a VNI pool. See Add an NSX EVPN/VXLAN VNI Pool.
- Configure a tier-0 gateway and enable EVPN. See Configure a Tier-0 Gateway for EVPN Inline Mode.
- Configure BGP neighbors. See Configure an NSX BGP Neighbors for a Tier-0 Gateway.
- Configure a tier-0 VRF gateway. See Configure a Tier-0 VRF Gateway for EVPN Inline Mode.
- Verify the BGP neighbor session status.
- Select .
- Click the menu icon (three dots) of the tier-0 gateway and select Generate BGP Summary.
- Verify that Connection Status for the neighbor is Established and that Address Families displays L2VPN EVPN.
- Verify the tier-0 VRF gateway forwarding table.
- Select .
- Click the menu icon (three dots) of the tier-0 VRF gateway and select Download Forwarding Table.
- Verify that the remote routes received from the external router are installed in the tier-0 VRF gateway forwarding table.