You must first set up your infrastructure and then configure your environment for Gateway Security.
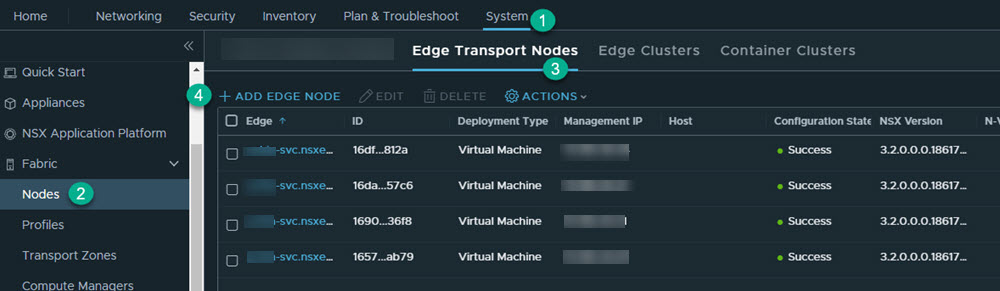
1. Deploy NSX Edge Transport Node
You must first deploy the NSX edge transport node.
Prerequisites
You have deployed the NSX Manager and configured the valid licenses.
Procedure
1.1: Provision NSX Edge Cluster
You should have two edge nodes in an edge cluster for high availability.
Procedure
- Add the edge cluster. Go to and click Add Edge Cluster.
- In the Name text box, enter name for the edge cluster. For example, Edge-cluster-1.
- Move the created edge node (Edge-1) from the Available to the Selected window, and click Add.
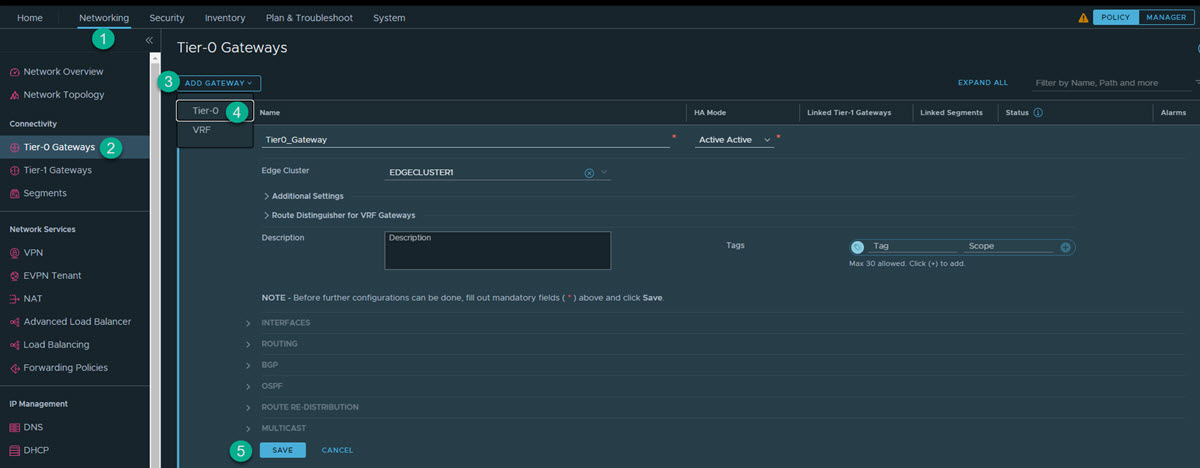
2. Create a Tier-0 or Tier-1 Gateway
Depending on your use case, create a tier-1 or tier-0 gateway.
Procedure
3. Create Interfaces on Tier-0 or Tier-1 Gateway
NSX gateway has different interface types. Based on the network topology, you can select the required interfaces to connect to the network and provide firewalling for traffic passing through the gateway.
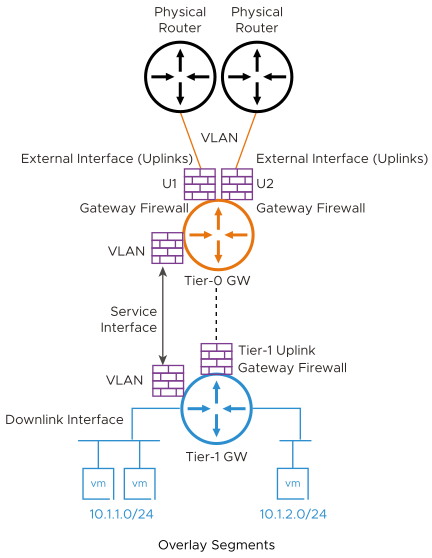
Tier-0 External Interfaces:
- Connects to physical router for external connectivity
- You create this interface on the VLAN segments on the tier-0 gateway
Tier-1 Uplink Interfaces:
- Connects to gier-0
- System creates this interface as tier-1 connects to tier-0
Service Interface:
- Used for providing NSX Services (GFW and other) to non-NSX managed VLAN workloads
- Connects to VLAN segment
- Supported on both tier-0 and tier-1
Downlink Interface:
- Overlay segment Interface on gateway
- Supported on both tier-0 and tier-1
- No GFW support
- VLAN connected workloads
- NSX network overlay segments connected workloads
Each of these scenarios follows slightly different steps to create the network interfaces as described later in this section.
3.1: Create NSX Gateway Firewall Interface for VLAN Connected Workloads
You must perform the following steps to set up your environment.
- Create a VLAN segment in NSX.
- In the NSX Manager, click .
- Provide the following information.
Segment Name Enter the name for the segment. For example, VLAN-100. Transport Zone Select the default transport zone for the VLAN traffic. For example, nsx-vlan-transportzone. VLAN Enter 100. - Click Save.
- Create a Service Interface(s) on the tier-0 or tier-1 gateway.
- In the NSX Manager, click .
- Edit the created gateway. For example, T1-gateway-1.
- Under Service Interfaces, click Set.
- Click Add Interface.
- Provide the following information.
Name Enter the name of the interface. For example, SI-VLAN-100. IP Address/Mask Enter an IP address. For example, 192.168.50.12/24. Connected To (Segment) Select the configured segment. For example,VLAN-100. - Click Save.
Create more service interfaces based on the network requirements.
On tier-0, you have an option to create an external interface, or a service interface based on the connectivity requirement. If an external interface is created, you need to create one external interface per edge, part of the edge cluster.
As part of the workflow, select the edge node to create that interface, in addition to the mentioned parameters.
For more information, see NSX Administration Guide.
3.2: Create NSX Gateway Firewall Interface for Network Overlay Workloads
- Create a Tier-1 Gateway.
- Click .
- Enter the name for the tier-1 gateway. For example, PROD-Tier1.
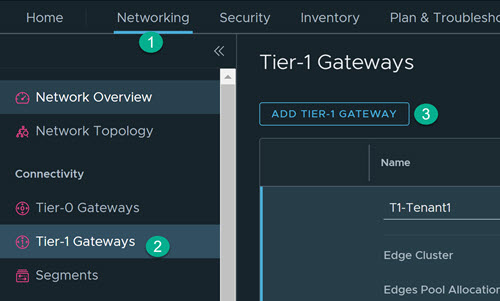
- Select the tier-0 gateway to create an uplink on the tier-1.
- Select the edge cluster for implementing the gateway services.
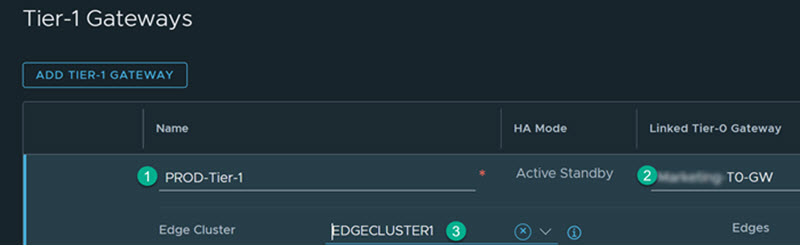
- Click Save.
- Additionally, you should create an overlay segment(s) for connecting workloads. This creates a downlink interface on the gateway and also makes the NSX segments available on the ESXi for network connectivity with the virtual machine.
- Click .
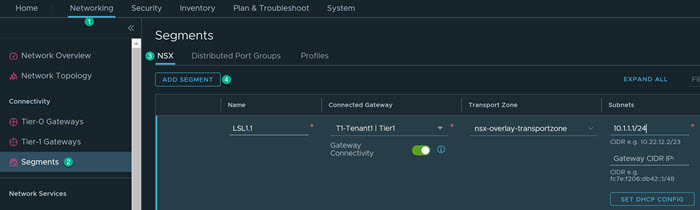
- Provide the following information.
Name Enter the name for the segment. For example, LS1.1. Connectivity Select the configured tier-1 gateway. For example, T1-Tenant1. Transport Zone Select the default transport zone for Overlay traffic. For example, nsx-overlay-transportzone. Subnets Enter the required subnet. For example, 10.x.x.1/24. - Click Save.
- Click .
- Validate the configured overlay segment is available in the VMware vCenter. In VMware vCenter, go to Host and Clusters, and validate VMs that are created and connected to the configured overlay segment.
For more information, see NSX Installation Guide.