Edge uplinks go out through VLAN logical switches.
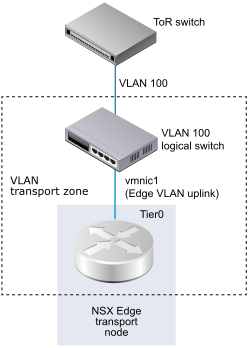
When you are creating a VLAN logical switch, it is important to have in mind a particular topology that you are building. For example, the following simple topology shows a single VLAN logical switch inside of a VLAN transport zone. The VLAN logical switch has VLAN ID 100. This matches the VLAN ID on the TOR port connected to the hypervisor host port used for the Edge's VLAN uplink.
Prerequisites
-
To create a VLAN logical switch, you must first create a VLAN transport zone.
- An NSX vSwitch must be added to the NSX Edge. To confirm on an Edge, run the get host-switches command. For example:
nsx-edge1> get host-switches Host Switch : c0a78378-1c20-432a-9e23-ddb34f1c80c9 Switch Name : hs1 Transport Zone : c46dcd72-808a-423d-b4cc-8752c33f6b2c Transport Zone : 73def985-d122-4b7b-ab6a-a58176dfc32d Physical Port : fp-eth0 Uplink Name : uplink-1 Transport VLAN : 4096 Default Gateway : 192.168.150.1 Subnet Mask : 255.255.255.0 Local VTEP Device : fp-eth0 Local VTEP IP : 192.168.150.102 - Verify that fabric nodes are successfully connected to the NSX management plane agent (MPA) and the NSX local control plane (LCP).
In the GET https://<nsx-mgr>/api/v1/transport-nodes/<transport-node-id>/state API call, the state must be success. See the NSX Installation Guide.
-
Verify that Manager mode is selected in the NSX Manager user interface. See NSX Manager. If you do not see the Policy and Manager mode buttons, see Configure the User Interface Settings.
Procedure
Results
What to do next
Add a logical router.