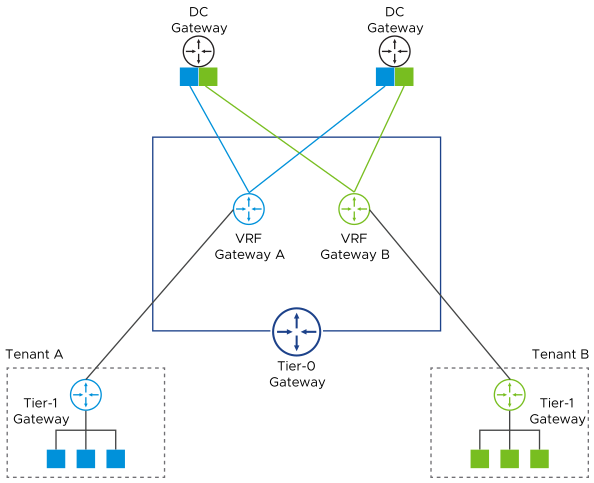
Virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) makes it possible to instantiate isolated routing and forwarding tables within a router. VRFs are supported by deploying tier-0 VRF gateways. A tier-0 VRF gateway must be linked to a parent tier-0 gateway and inherits some of the tier-0 gateway settings, such as HA mode, Edge cluster, internal transit subnet, T0-T1 transit subnets, and BGP routing configuration.
Multiple tier-0 VRF instances can be created under the same parent tier-0, which allows the separation of segments and tier-1 gateways into multiple isolated tenants. With tier-0 VRF gateways, tenants can use overlapping IP addresses without any interference or communication with each other.
NSX tier-0 VRF gateways can be used to connect tenant networks to external routers using static routes or BGP [RFC4364]. This is also known as VRF-Lite.
NSX tier-0 VRF gateways can also be deployed with EVPN. For more information, see Ethernet VPN (EVPN).
NSX Federation Support
Sarting with NSX 4.2.1:
- You can configure a tier-0 VRF gateway on a Global Manager in an NSX Federation. The Global VRF can have its own locale operation mode and fallback preference and uses the same HA mode as tier-0 gateway.
- You can also stretch a tier-0 VRF gateways to multiple sites and enable inter-SR routing for an active-active tier-0 gateway.
Prior to NSX 4.2.1, it was not possible to create a tier-0 VRF gateway on a Global Manager in a Federation setup and stretch the VRF gateway to multiple sites. Also, asymmetric traffic failures were supported only on tier-0 gateway, but not on VRF gateways. Starting with 4.2.1, Inter-SR routing is also supported on VRF gateways within a single site. You can also stretch a VRF gateway to multiple sites in a Federation setup and enable Inter-SR routing on them. To enable this feature, you must first turn on the Multi-VRF Inter SR toggle under the Additional Settings section while configuring a tier-0 gateway. Turning on this toggle runs MP-BGP between edges that is required for inter-node route sync to handle asymmetric VRF connectivity and inter-site connectivity for stretched VRFs. If the Multi-VRF Inter SR toggle is off, inter-SR routing cannot be enabled for a VRF gateway on this tier-0 and the VRF gateway cannot be stretched to multiple sites. Note that in a Federation setup, the Multi-VRF Inter SR toggle can be turned on the Global Manager only when all sites where the tier-0 spans are on the same version.
When you turn on the Multi-VRF Inter SR toggle:
- There will be a traffic disruption.
- You cannot turn the toggle off.
| Multi-VRF Inter SR | Inter SR iBGP | |
|---|---|---|
| Single Site | ||
| Off | You can create a tier-0 VRF gateway. | Inter SR routing will be available only for an active-active tier-0 gateway, but not on the VRF gateway connected to it. |
| On | You can create a tier-0 VRF gateway. | Inter SR routing will be available for an active-active tier-0 gateway and the VRF gateway connected to it. |
| Federation | ||
| Off | You can create a single-site tier-0 VRF gateway on the Global Manager for one of the locations of the parent tier-0 gateway. | Inter SR routing will be available across the sites for an active-active tier-0 VRF gateway, but not within the same site. |
| On | You can create a tier-0 VRF gateway from the Global Manager and stretch it to multiple locations that are subsets of the parent tier-0 gateway. Note: It can be enabled on Global Manager only when all Local Managers are on the same version. |
Inter SR routing will be available across the sites for an active-active tier-0 VRF gateway and also within the same site. |
Note that even though a tier-0 VRF gateway has an HA mode, it does not have a mechanism to respond to a communication failure that is independent of the parent tier-0 gateway's mechanism. If a tier-0 VRF gateway loses connectivity to a neighbor but the criteria for the tier-0 gateway to fail over is not met, the VRF gateway will not fail over. The only time a VRF gateway will fail over is when the parent tier-0 gateway does a failover.