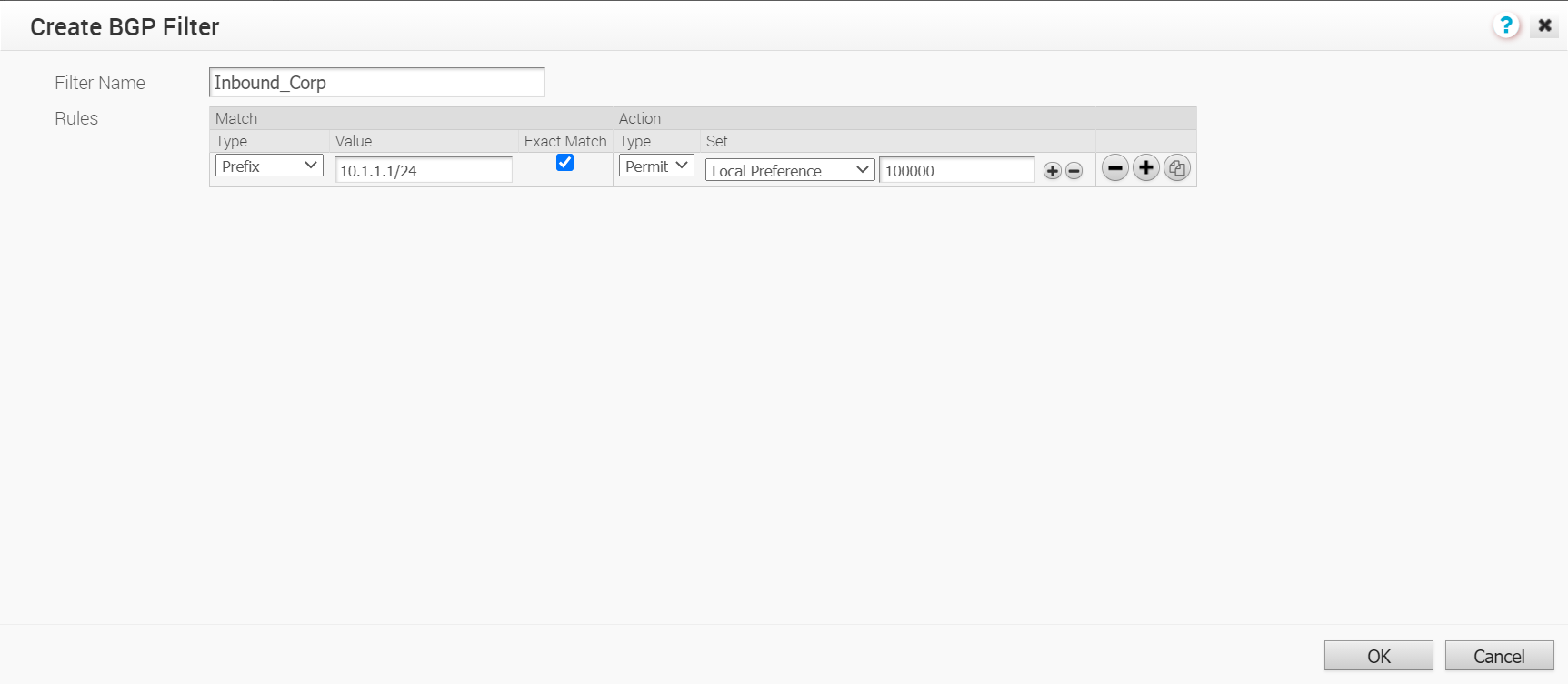
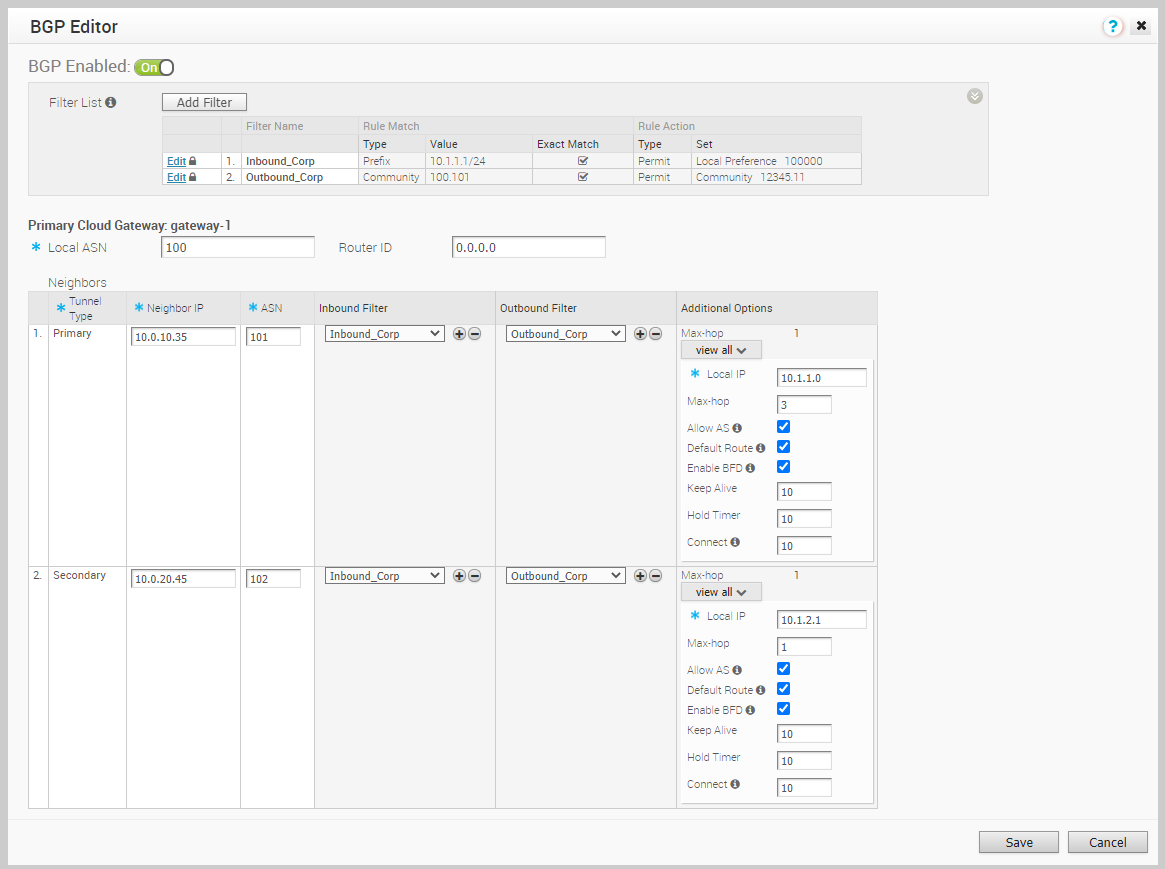
You can configure BGP Settings for SD-WAN Gateways over IPSec tunnels.
Only eBGP is supported with BGP over IPsec.
To configure the BGP settings for a Gateway:
Prerequisites
Ensure that you have configured the following:
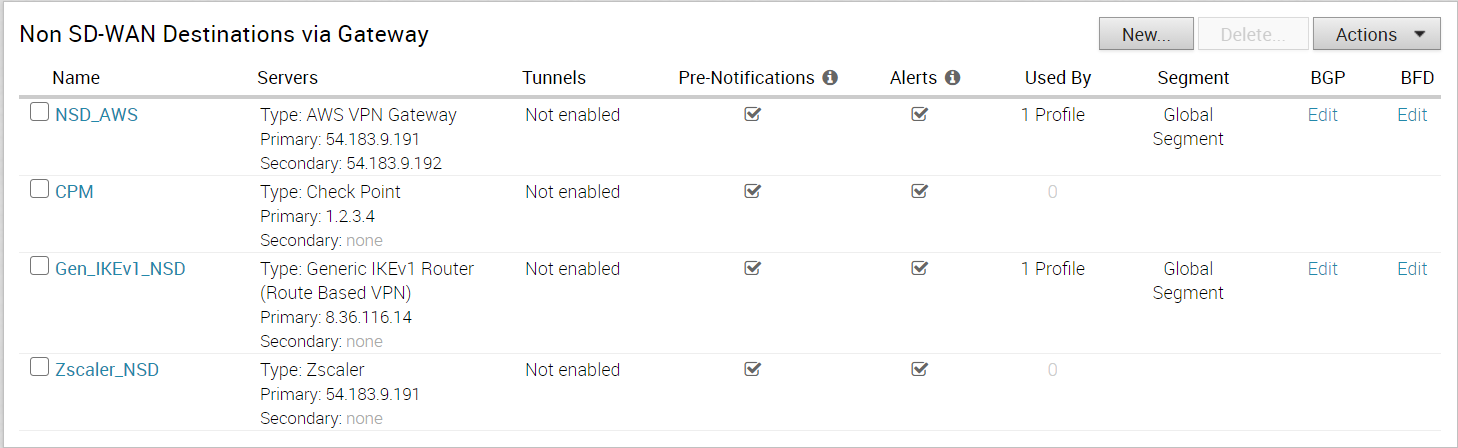
- Create a Non SD-WAN Destination via Gateway for one of the following sites:
- Associate the Non SD-WAN Destination to a Profile See Configure a Tunnel Between a Branch and a Non SD-WAN Destinations via Gateway.
Note: It is recommended to turn on
Distributed Cost Calculation for best performance and scaling when using BGP over IPsec via Gateway. The
Distributed Cost Calculation is supported starting from Release 3.4.0.
For more information on Distributed Cost Calculation, refer to the Configure Distributed Cost Calculation section in the VMware SD-WAN Operator Guide available at: https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-SD-WAN/index.html.