This section covers the mechanisms used to detect and prevent a split-brain state in an Edge deployment using a high availability topology.
There are two mechanism for detecting and preventing a split-brain condition in a high availability deployment (where both HA Edges become Active).
The first mechanism involves sending layer 2 broadcast heartbeats between the two HA Edges when the HA heartbeat link between the devices is lost. A layer 2 broadcast (EtherType 0x9999) heartbeat is sent from the Active Edge on all its WAN interfaces in an effort to find the Standby Edge in that broadcast network. When the Standby Edge receives this packet, it interprets the packet as an indication to maintain its current Standby state. This mechanism is used by a Legacy High Availability deployment where both HA Edges have their WAN ports connected to the same layer 2 Switch.
The second mechanism used to detect and prevent split-brain conditions leverages the Primary Gateway used by the HA Edges. This mechanism is the sole means of detecting and preventing split-brain in an Enhanced High Availability deployment as this topology does not connect both HA Edges to an upstream layer 2 switch.
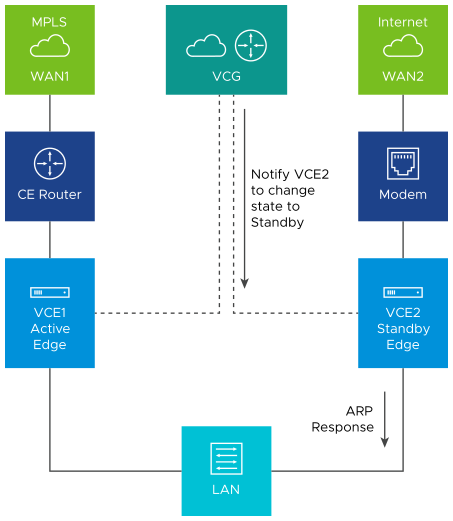
The Primary Gateway has a pre-existing connection to the Active Edge (VCE1). In a split-brain condition, the Standby Edge (VCE2) changes state to Active and tries to establish a tunnel with the Primary Gateway (VCG). The Gateway will send a response back to the Standby Edge (VCE2) instructing it to move to Standby state, and will not allow the tunnel to be established. The Primary Gateway will always have tunnels only from the Active Edge.
As soon as the HA link fails, VCE2 moves to the Active state and enables the LAN/WAN ports, and tries to establish tunnels with the Primary Gateway. If the VCE1 still has tunnels, the Primary Gateway instructs the VCE2 to revert to the Standby state and thus the VCE2 blocks its LAN ports. Only the LAN interfaces remain blocked (as long as the HA cable is down). As illustrated in the following figure, the Gateway signals VCE2 to go into the Standby state. This will logically prevent the split-brain scenario from occurring.