Conditional Backhaul (CBH) is a feature designed for Hybrid SD-WAN branch deployments that have at least one Public and one Private link. Whenever there is a Public Internet link failure on a VMware SD-WAN Edge, tunnels to VMware SD-WAN Gateway, Cloud Security Service (CSS), and Direct breakout to Internet are not established. In this scenario, the Conditional Backhaul feature, if enabled, will make use of the connectivity through Private links to designated Backhaul Hubs, giving the SD-WAN Edge the ability to failover Internet-bound traffic over Private overlays to the Hub and provide reachability to Internet destinations.
Whenever Public Internet link fails and Conditional Backhaul is enabled, the Edge can failover the following Internet-bound traffic types:
- Direct to Internet
- Internet via SD-WAN Gateway
- Cloud Security Service traffic
Behavioral Characteristics of Conditional Backhaul
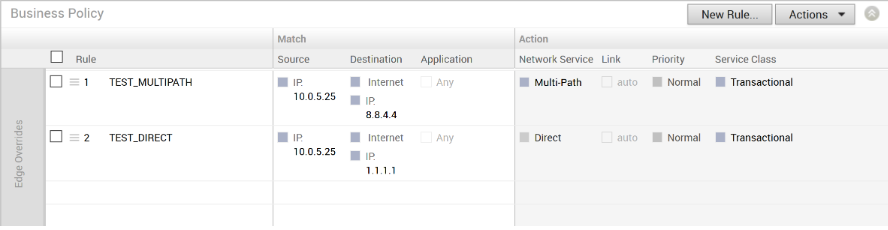
- When Conditional Backhaul is enabled, by default all Business Policy rules at the branch level are subject to failover traffic through CBH. You can exclude traffic from Conditional Backhaul based on certain requirements for selected policies by disabling this feature at the selected business policy level.
- Conditional Backhaul will not affect existing flows that are being backhauled to a Hub already if the Public link(s) goes down. The existing flows will still forward data using the same Hub.
- If a branch location has backup Public links, the backup Public link will take precedence over CBH. Only if the primary and backup links are all inoperable then the CBH gets triggered and uses the Private link.
- If a Private link is acting as backup, traffic will fail over to Private link using CBH feature when active Public link fails and Private backup link becomes Active.
- In order for the feature to work, both Branches and Conditional Backhaul Hubs need to have the same Private Network name assigned to their Private links. (The Private tunnel will not come up otherwise.)
Operational Flow
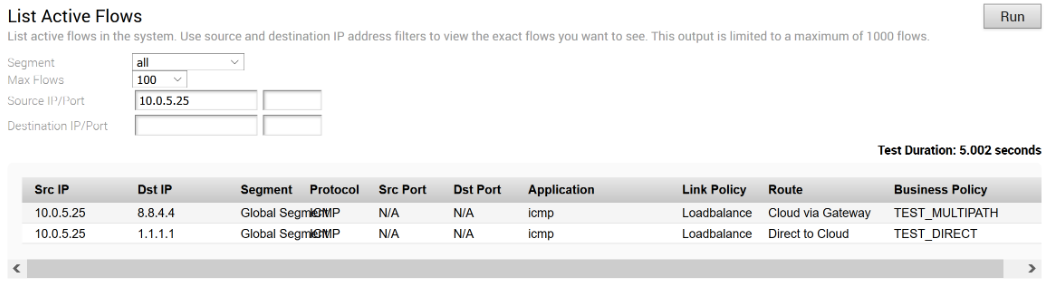
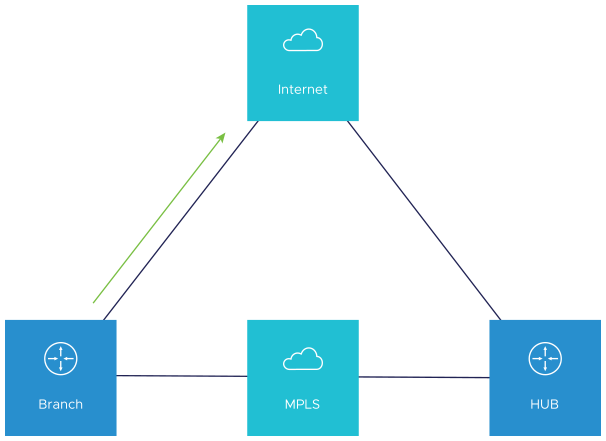
Under normal operations, the Public link is UP and Internet-bound traffic will flow normally either Direct or via SD-WAN Gateway as per the Business Policies configured.
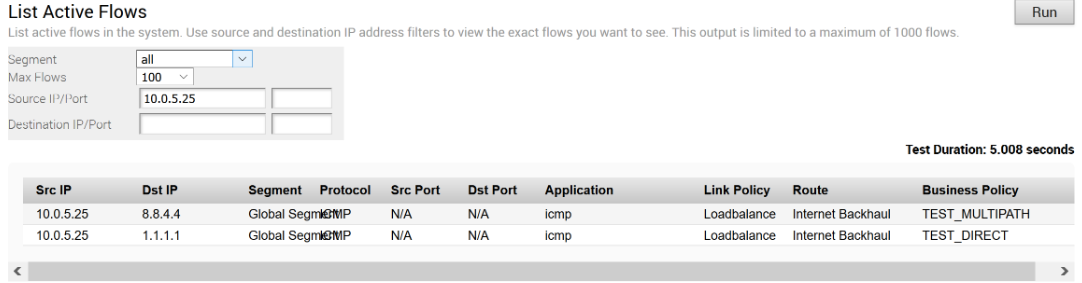
When the Public Internet link goes DOWN, or the SD-WAN Overlay path goes to QUIET state (no packets received from Gateway after 7 heartbeats), the Internet-bound traffic is dynamically backhauled to the Hub.
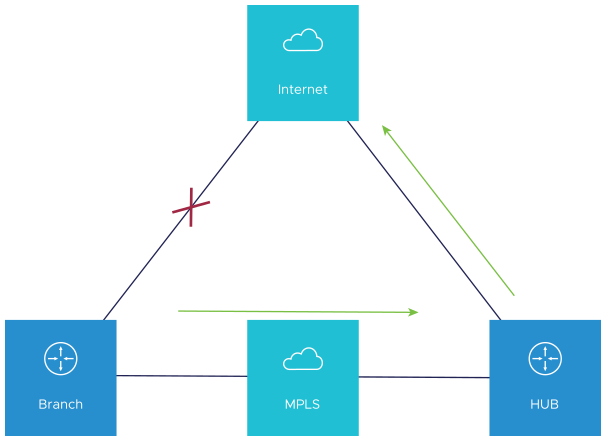
- Direct from Hub
- Hub to Gateway and then breakout from the Gateway
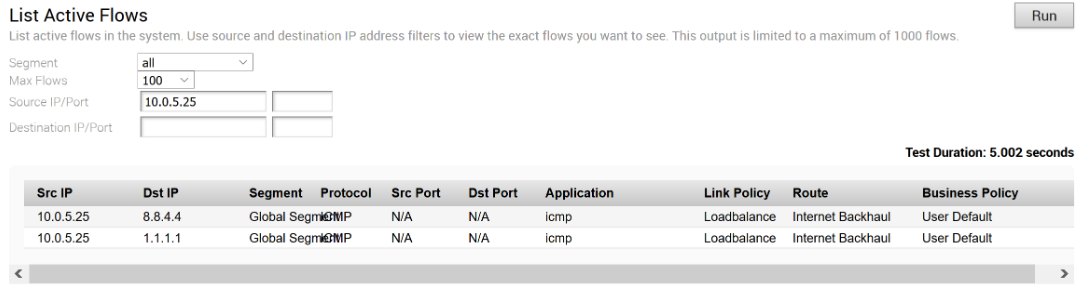
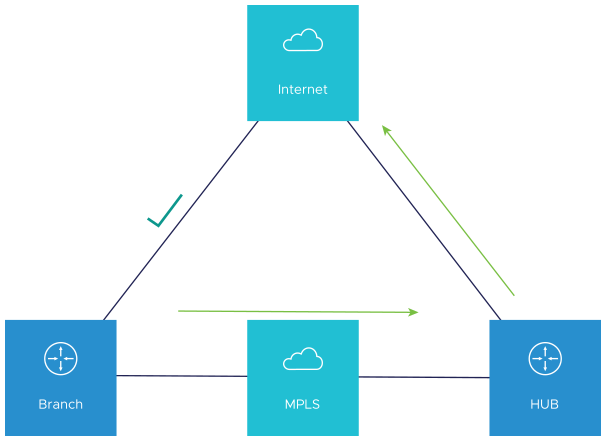
When the Public Internet link comes back, CBH will attempt to move the flows back to the Public link. To avoid an unstable link causing traffic to flap between the Public and Private links, CBH has a default 30 seconds holdoff timer. After the holdoff timer is reached, flows will be failed back to the Public Internet link.
.
Configuring Conditional Backhaul
- From the SD-WAN Orchestrator, go to Configure > Profiles. The Configuration Profiles page appears.
- Select a profile you want to configure Cloud VPN and click the icon under the Device column. The Device Settings page for the selected profile appears.
- From the Configure Segment drop-down menu, select a profile segment to configure Conditional Backhaul. By default, Global Segment [Regular] is selected.
Note: The Conditional Backhaul feature is Segment aware and therefore must be enabled at each Segment where it is intended to work.
- Go to Cloud VPN area and enable Cloud VPN by turning the toggle button to On.
- To configure Branch to SD-WAN Hubs, under Branch to Hubs, select the Enable checkbox.
- Click the Select Hubs link. The Manage Cloud VPN Hubs page for the selected profile appears.
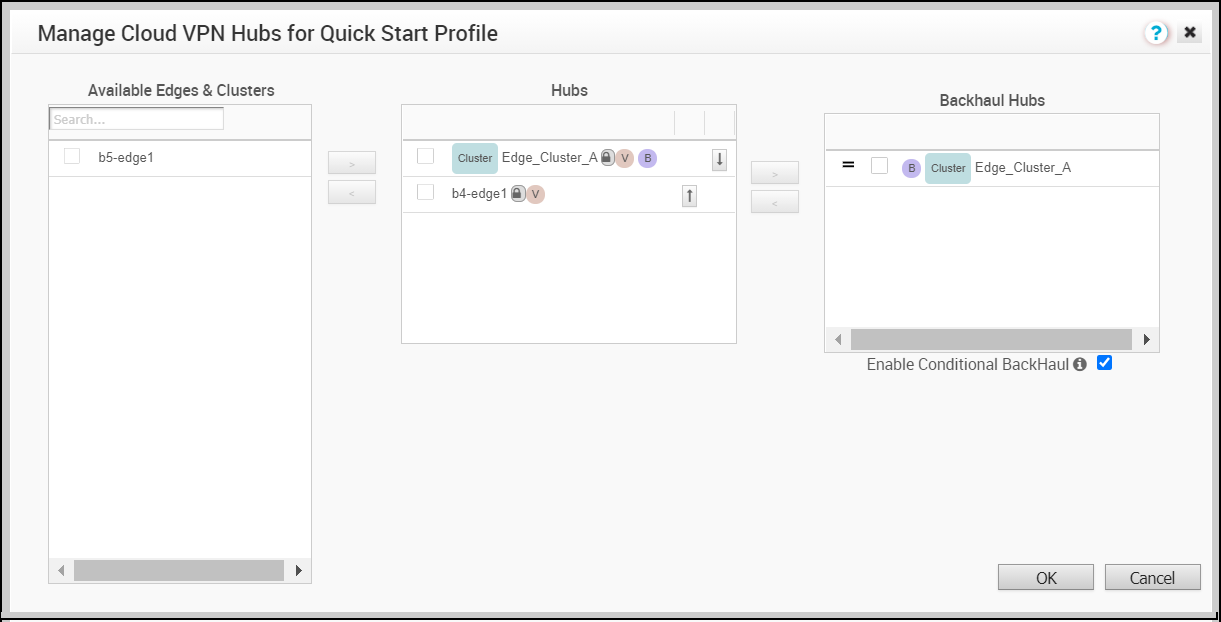
From Hubs area, select the Hubs to act as Backhaul Hubs and move them to Backhaul Hubs area by using the > arrow.
- To enable Conditional Backhaul, select the Enable Conditional BackHaul checkbox.
With Conditional Backhaul enabled, the Edge will be able to failover Internet-bound traffic (Direct Internet traffic, Internet via SD-WAN Gateway and Cloud Security Traffic via IPsec) to MPLS links whenever there is no Public Internet links available. Conditional Backhaul when enabled will apply for all Business Policies by default. If you want to exclude traffic from Conditional Backhaul based on certain requirements, you can disable Conditional Backhaul for selected policies to exclude selected traffic from this behavior by selecting the Disable Conditional Backhaul checkbox in the Action area of the Configure Rule screen for the selected business policy.
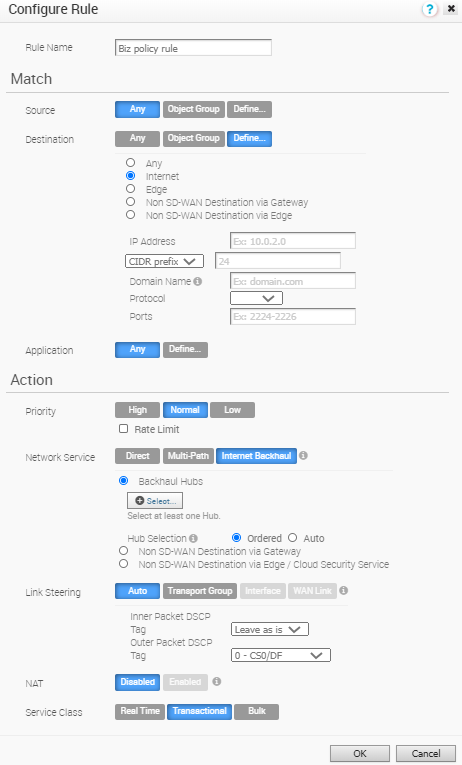 Note:
Note:- Conditional Backhaul and SD-WAN Reachability can work together in the same Edge. Both Conditional Backhaul and SD-WAN reachability support failover of Cloud-bound Gateway traffic to MPLS when Public Internet is down on the Edge. If Conditional Backhaul is enabled and there is no path to Gateway and there is a path to hub via MPLS then both direct and Gateway bound traffic apply Conditional Backhaul. For more information about SD-WAN reachability, see SD-WAN Service Reachability via MPLS.
- When there are multiple candidate hubs, Conditional Backhaul will use the first hub in the list unless the hub has lost connectivity to Gateway.
- Click Save Changes.
Troubleshooting Conditional Backhaul