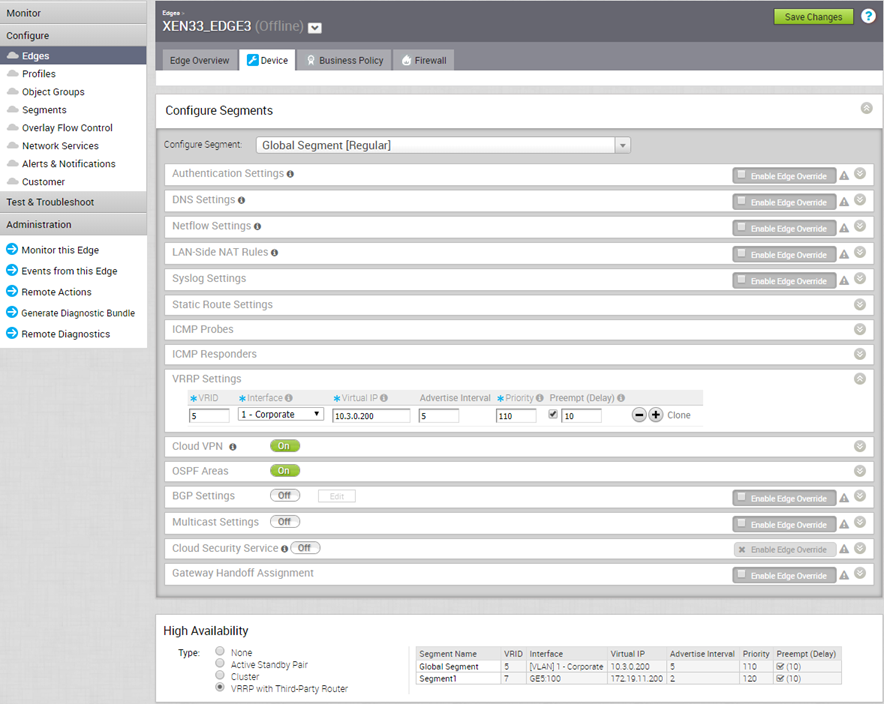
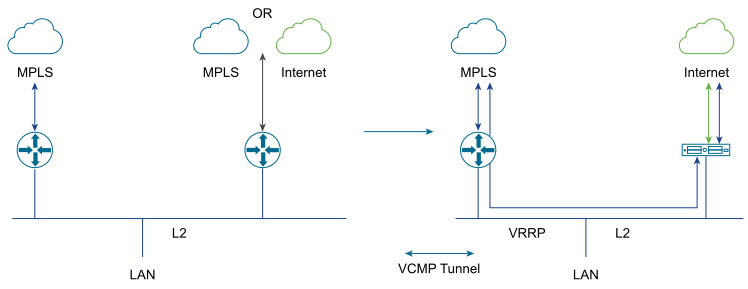
You can configure Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) on an Edge to enable next-hop redundancy in the SD-WAN Orchestrator network by peering with third-party CE router. You can configure an Edge to be a primary VRRP device and pair the device with a third-party router.
Prerequisites
Consider the following guidelines before configuring VRRP:
- You can enable VRRP only between the SD-WAN Edge and third party router connected to the same subnet through an L2 switch.
- You can add only one SD-WAN Edge to the VRRP HA group in a branch.
- You cannot enable both Active-Standby HA and VRRP HA at the same time.
- VRRP is supported on primary routed port, sub-interface, and VLAN interfaces.
- SD-WAN Edge must be configured as the primary VRRP device, by setting higher priority, in order to steer the traffic through SD-WAN.
- If the SD-WAN Edge is configured as the DHCP server, then virtual IP addresses are set as the default Gateway address for the clients. When you use a separate DHCP server relay for the LAN, then the admin must configure the VRRP virtual IP address as the default Gateway address.
- When DHCP server is enabled in both the SD-WAN Edge and third-party router, then split the DHCP pool between the Edge and third party router, to avoid the overlapping of IP addresses.
- VRRP is not supported on an interface enabled with WAN Overlay, that is on the WAN link. If you want to use the same link for LAN, then create a sub-interface and configure VRRP on the sub-interface.
- You can configure only one VRRP group in a broadcast domain in a VLAN. You cannot add additional VRRP group for the secondary IP addresses.
- Do not add WI-FI link to the VRRP enabled VLAN. As the link failure would never happen, the SD-WAN Edge always remains as the primary device.
Procedure
Results
In a branch network VLAN, if the Edge goes down, then the clients behind the VLAN are redirected through the backup router.
The SD-WAN Edge that acts as a primary VRRP device becomes the default Gateway for the subnet.
If the SD-WAN Edge loses connectivity with all the SD-WAN Edge/Controllers, then the VRRP priority gets reduced to 10 and the SD-WAN Edge withdraws the routes learned from the SD-WAN Edge and routes in the remote Edges as well. This results in the third-party router to become the primary device and take over the traffic.
SD-WAN Edge automatically tracks overlay failure to the SD-WAN Edge. When all the overlay paths to the SD-WAN Edge are lost, the VRRP priority of the SD-WAN Edge is reduced to 10.
When the Edge gets into the VRRP backup mode, the Edge drops any packets that go through the virtual MAC. When the path is UP, the Edge becomes the primary VRRP device again, provided the preemption mode is enabled.
When VRRP is configured on a routed interface, the interface is used for local LAN access and can failover to the backup router.
VRRP is not supported on a routed interface enabled with WAN Overlay. In such cases, a subinterface, sharing the same physical interface, must be configured for local LAN access to support VRRP.
When LAN interface is down, VRRP instance would go to INIT state, and then the SD-WAN Edge sends the route withdrawal request to the SD-WAN Edge/Controller and all the remote SD-WAN Edge remove those routes. This behavior is applicable for the static routes added to the VRRP enabled interface as well.
If the private overlay is present with the SD-WAN Edge peer Hub, then the route is not removed from the Hub, and can cause asymmetric routing. For example, when SD-WAN spoke Edge loses connectivity with public gateway, the third-party router forwards the packets from the LAN to the SD-WAN Hub Edge. The Hub sends the return packets to the SD-WAN spoke Edge instead of the third-party router. As a workaround, enable the SD-WAN Reachable functionality, so that the SD-WAN Edge is reachable on private overlay and remains as the primary VRRP device. As the Internet traffic is also steered through the private link over the overlay through the SD-WAN Edge, there might be some limitation on the performance or throughput.
The conditional backhaul option is used to steer the Internet traffic through the Hub. However, in VRRP-enabled SD-WAN Edge, when public overlay goes down the Edge becomes Backup. So the conditional backhaul feature cannot be utilized on a VRRP-enabled Edge.